Tested Applications
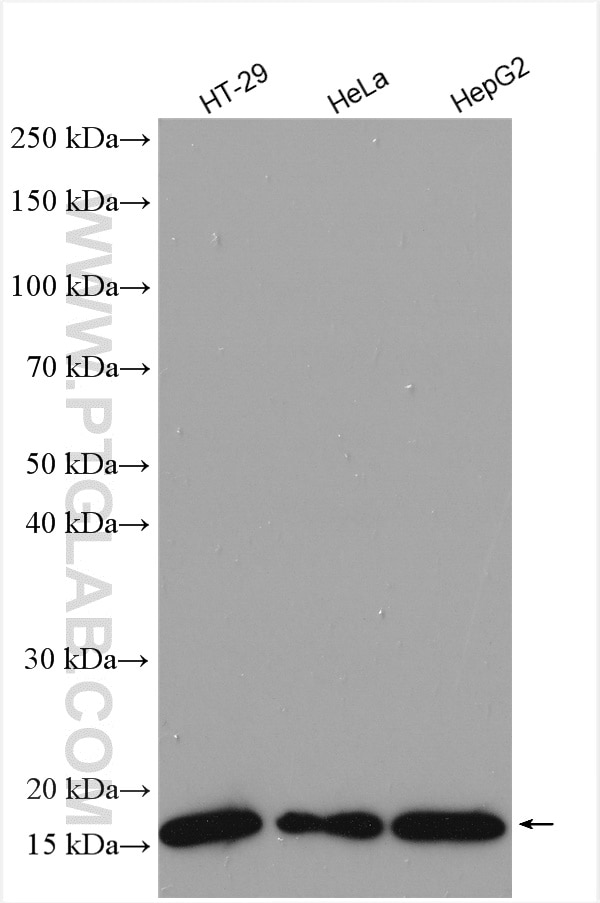
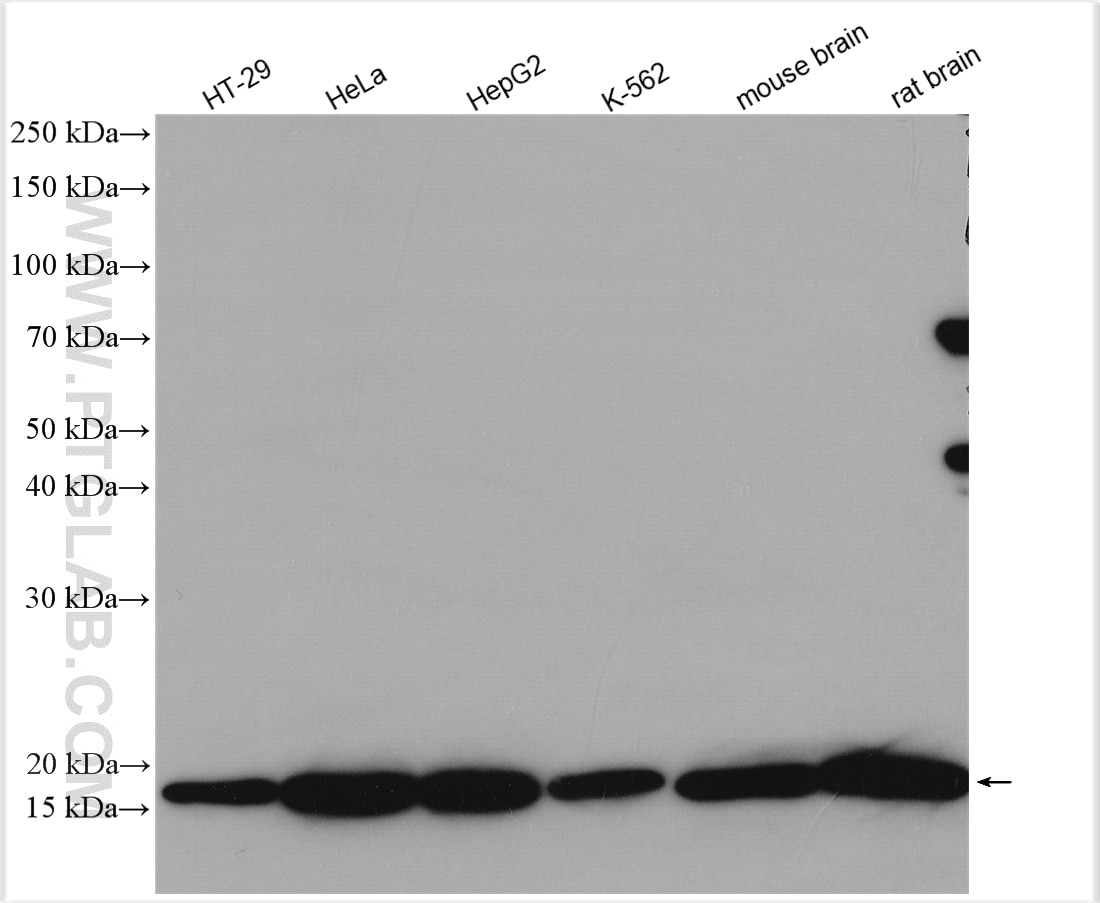
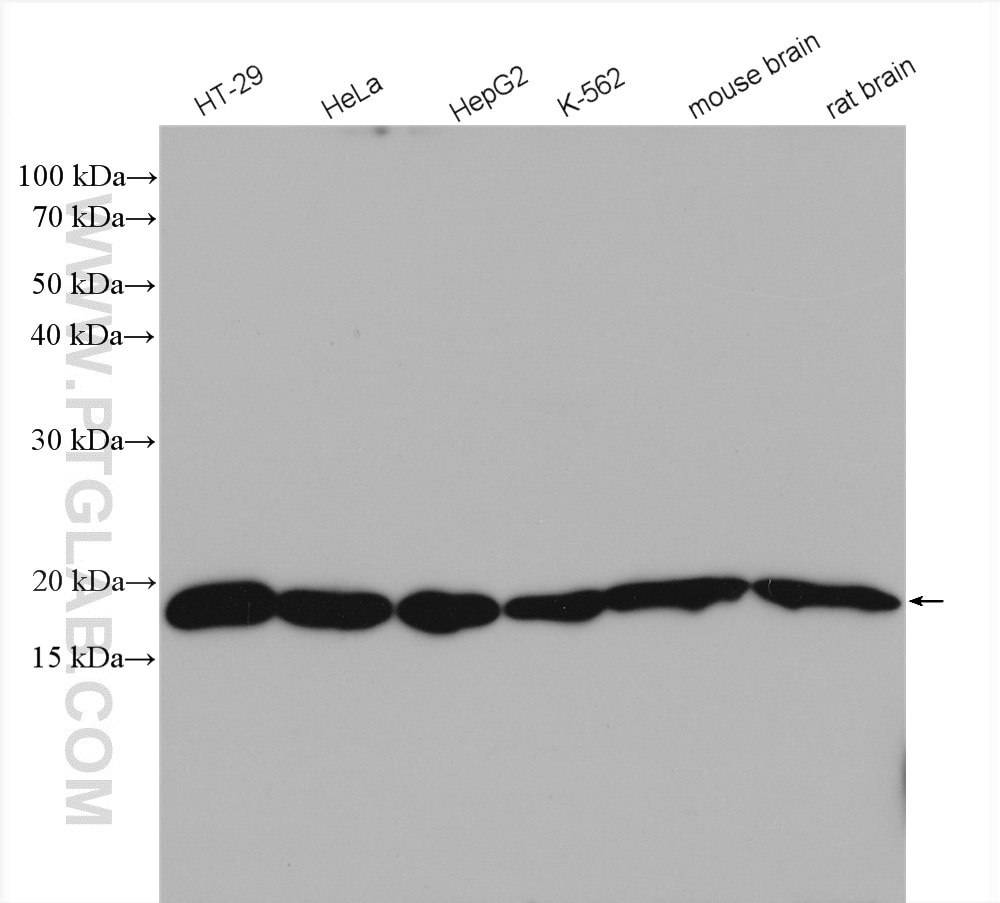
| Positive WB detected in | HT-29 cells, HeLa cells, HepG2 cells, K-562 cells, mouse brain tissue, rat brain tissue |
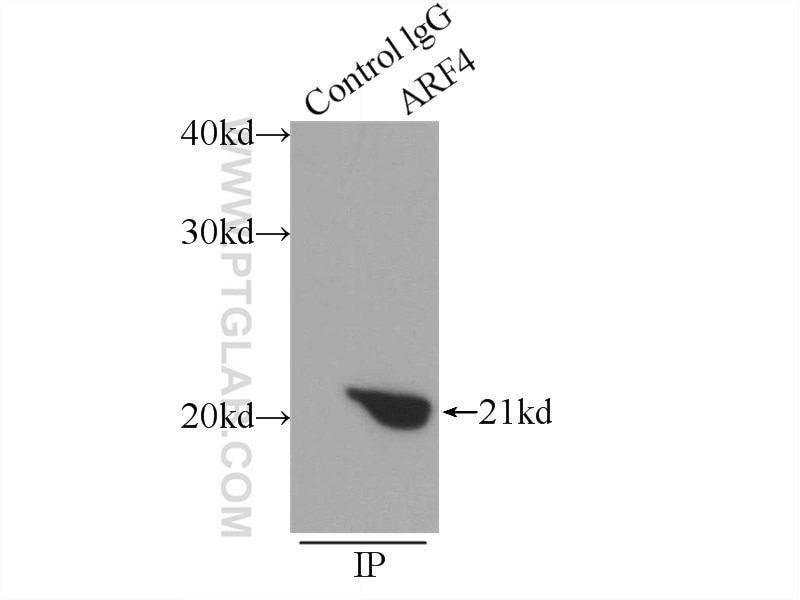
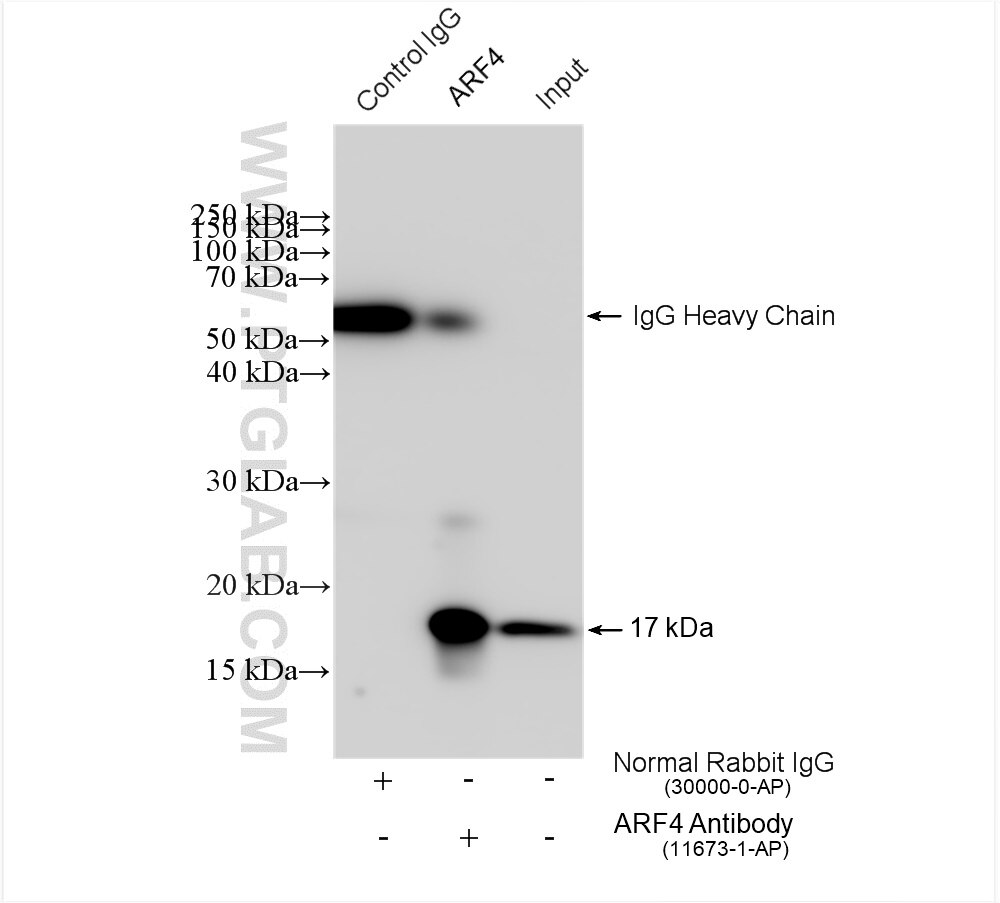
| Positive IP detected in | HepG2 cells, mouse brain tissue |
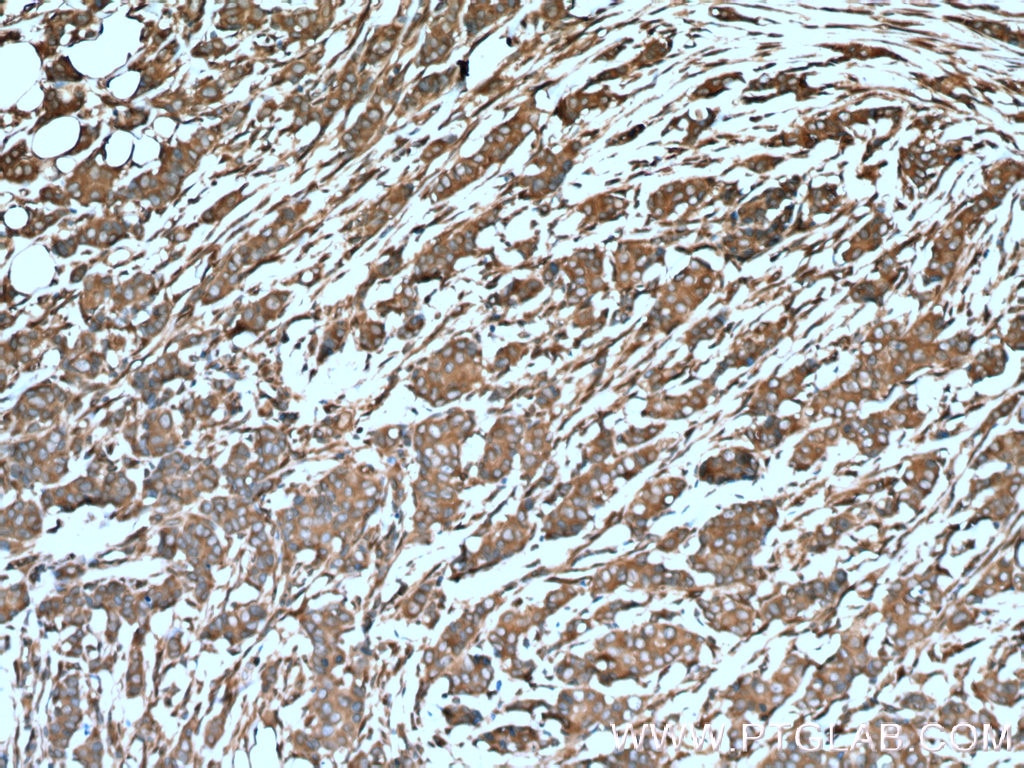
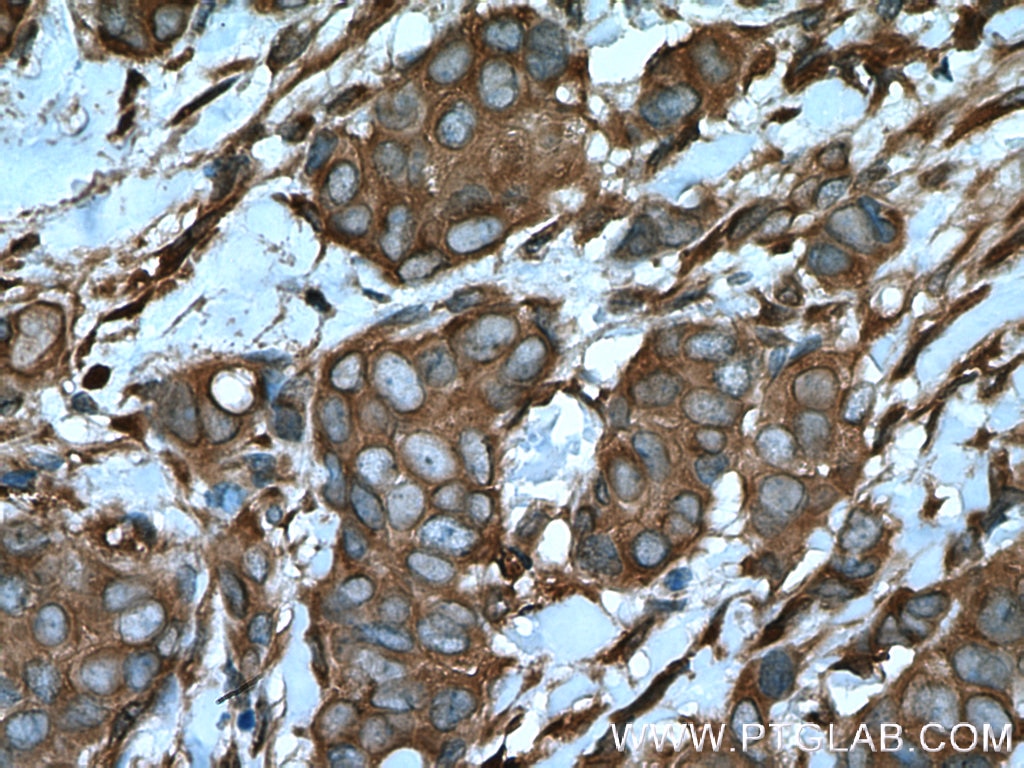
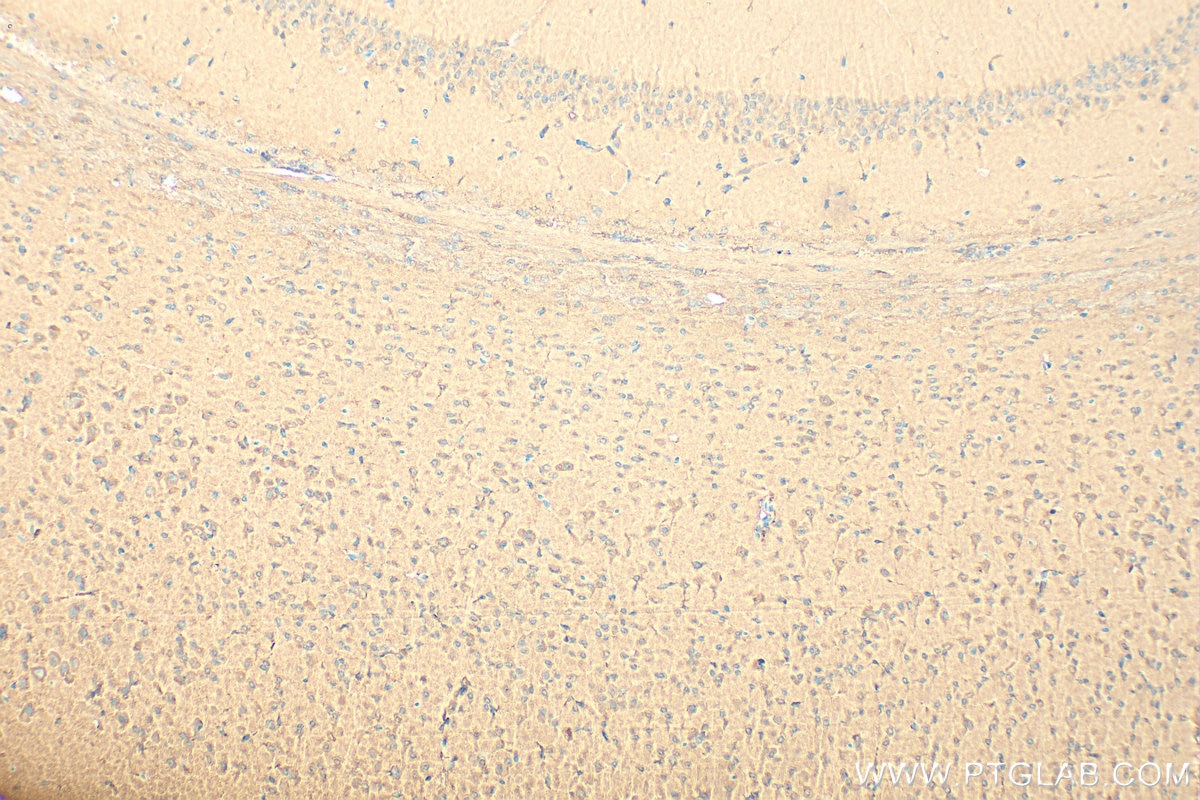
| Positive IHC detected in | human breast cancer tissue, mouse brain tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
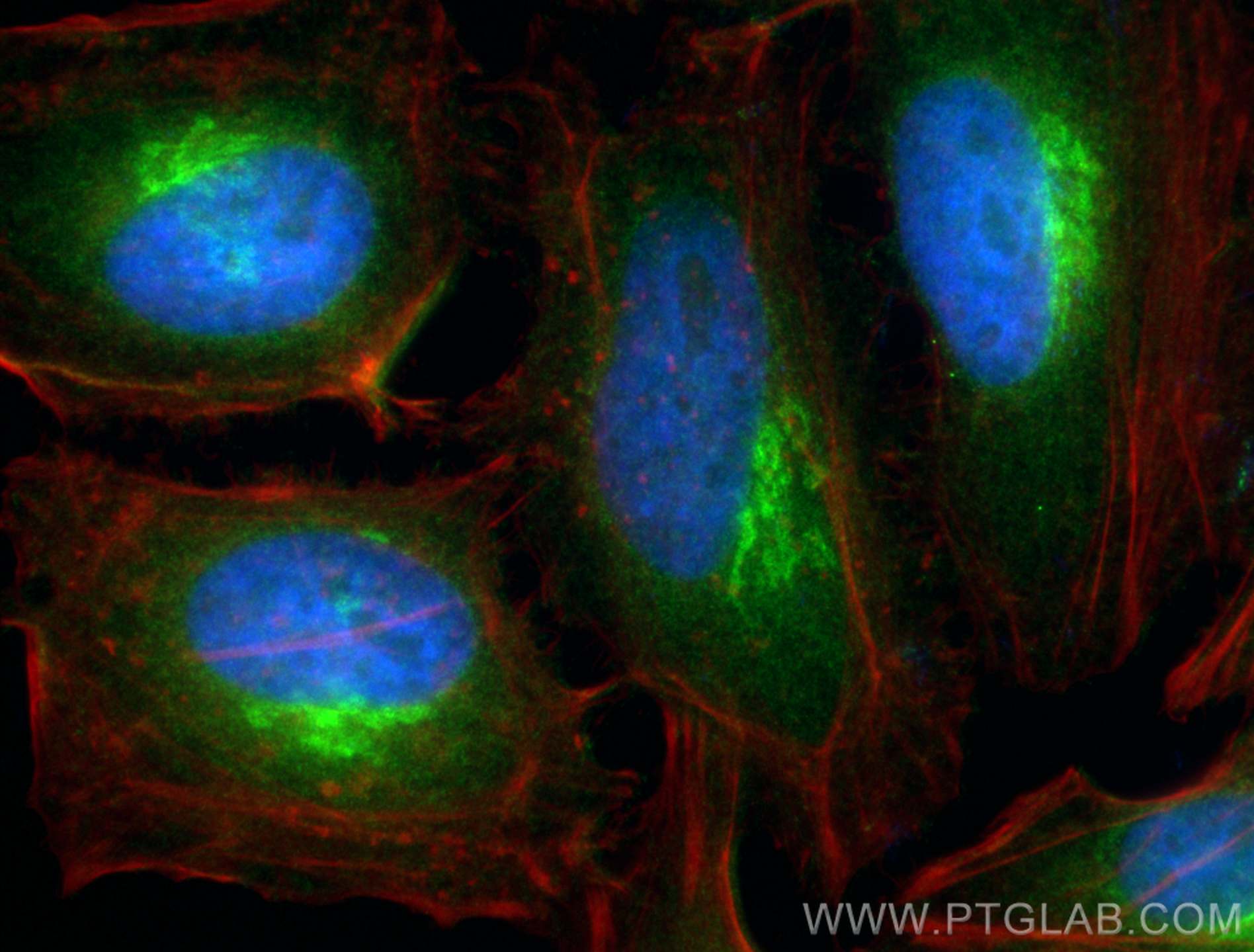
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HeLa cells |
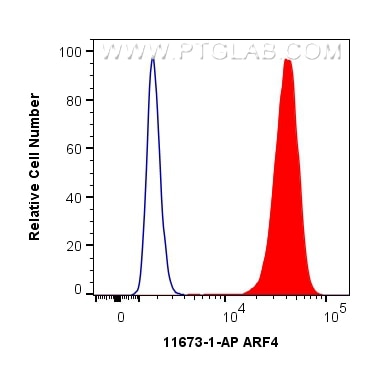
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | K-562 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:6000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.40 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
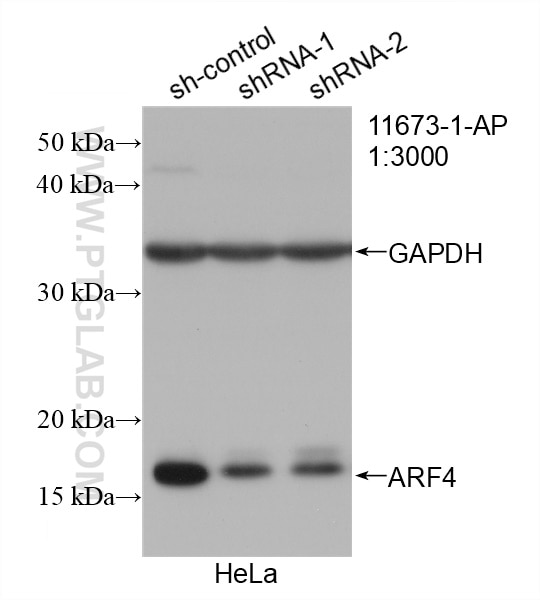
| KD/KO | See 10 publications below |
| WB | See 36 publications below |
| IHC | See 2 publications below |
| IF | See 7 publications below |
Product Information
11673-1-AP targets ARF4 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag2272 Product name: Recombinant human ARF4 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-180 aa of BC003364 Sequence: MGLTISSLFSRLFGKKQMRILMVGLDAAGKTTILYKLKLGEIVTTIPTIGFNVETVEYKNICFTVWDVGGQDRIRPLWKHYFQNTQGLIFVVDSNDRERIQEVADELQKMLLVDELRDAVLLLFANKQDLPNAMAISEMTDKLGLQSLRNRTWYVQATCATQGTGLYEGLDWLSNELSKR Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | ADP-ribosylation factor 4 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 180 aa, 21 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 16 kDa, 21 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC003364 |
| Gene Symbol | ARF4 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 378 |
| RRID | AB_2058463 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P18085 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
ARF4, also named as ARF2, belongs to the small GTPase superfamily and Arf family. ADP-ribosylation factors (ARFs) are members of the ARF family of GTP-binding proteins of the Ras superfamily, with 20 kDa protein size. ARFs bind and regulate GTP/GDP cycle by alternating between the active GTP-bound and inactive GDP-bound conformations. ARF family proteins are essential and ubiquitous in eukaryotes. Six highly conserved members of the family have been identified in mammalian cells. They function in vesicular traffic and actin remodelling and other bioprocesses in cells. ARF4 and ARF5 are class II ARFs. Their function are not fully described. (PMID: 7759471, PMID: 16042562). This antibody can bind ARFs for the close sequences.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for ARF4 antibody 11673-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for ARF4 antibody 11673-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for ARF4 antibody 11673-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for ARF4 antibody 11673-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for ARF4 antibody 11673-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Cell Biol A CREB3-ARF4 signalling pathway mediates the response to Golgi stress and susceptibility to pathogens. | ||
Cell Metab Hypomorphism for RPGRIP1L, a Ciliary Gene Vicinal to the FTO Locus, Causes Increased Adiposity in Mice. | ||
Nat Commun Ciliary membrane proteins traffic through the Golgi via a Rabep1/GGA1/Arl3-dependent mechanism. | ||
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A Whole-genome RNAi screen highlights components of the endoplasmic reticulum/Golgi as a source of resistance to immunotoxin-mediated cytotoxicity.
| ||