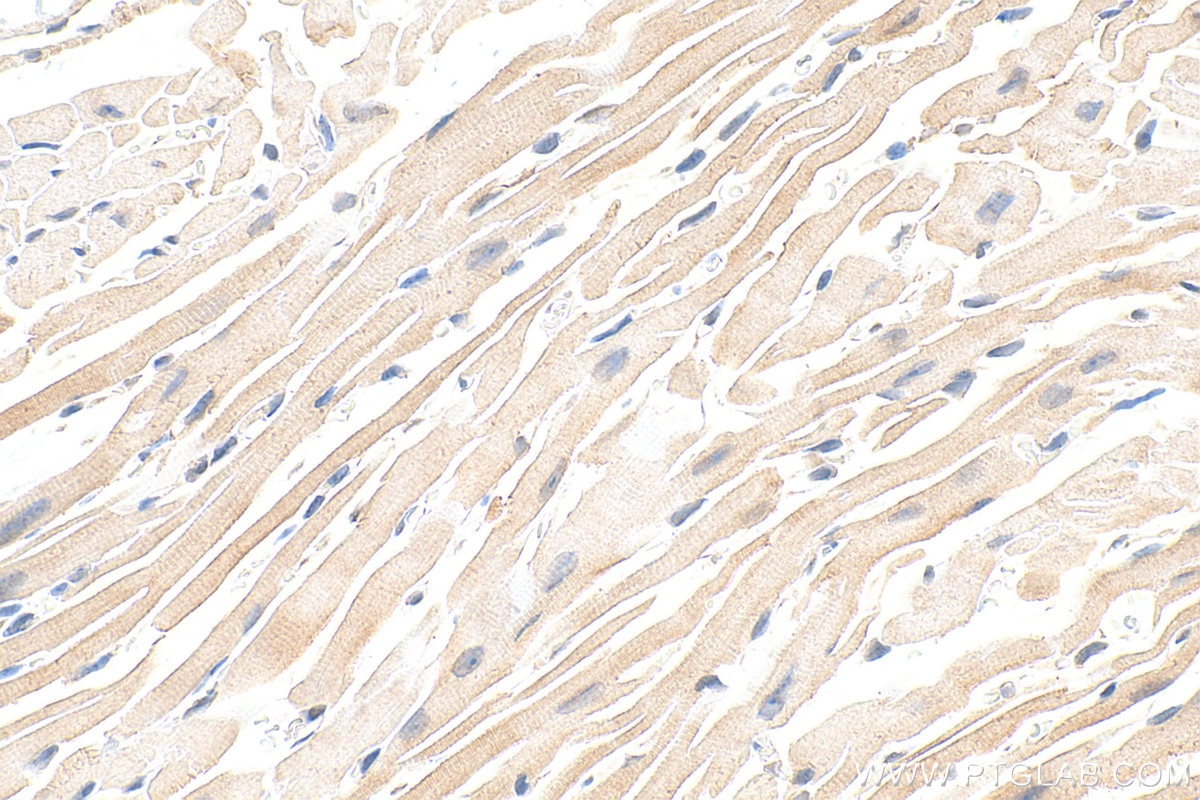
Tested Applications
| Positive IHC detected in | mouse heart tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
Biotin-55179 targets ATP1A2-Specific in IHC applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
Peptide Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | ATPase, Na+/K+ transporting, alpha 2 (+) polypeptide |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 112 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 100 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | NM_000702 |
| Gene Symbol | ATP1A2 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 477 |
| Conjugate | Biotin |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen Affinity Purified |
| UNIPROT ID | P50993 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
ATP1A2, also named as KIAA0778, belongs to the cation transport ATPase (P-type) family and Type IIC subfamily. It is the catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. Defects in ATP1A2 are the cause of familial hemiplegic migraine type 2 (FHM2). Defects in ATP1A2 are a cause of alternating hemiplegia of childhood (AHC). This antibody is specific to ATP1A2.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for Biotin ATP1A2-Specific antibody Biotin-55179 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |