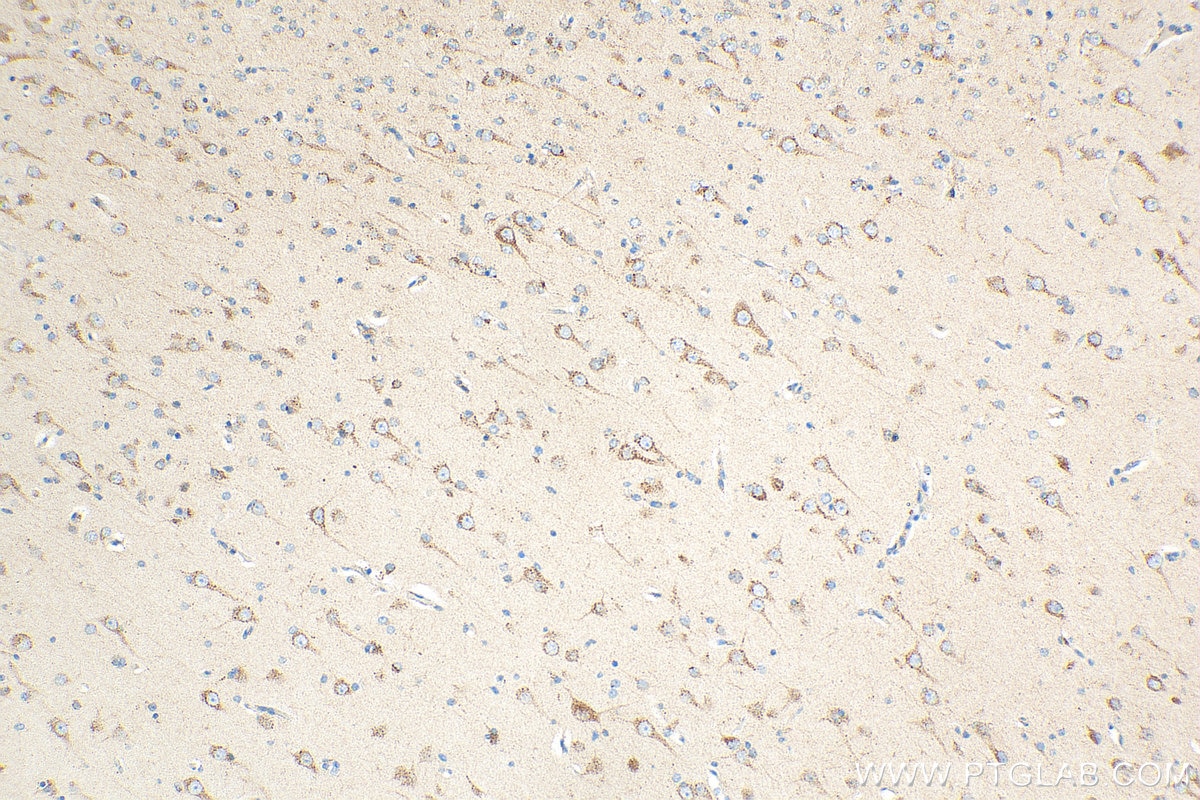
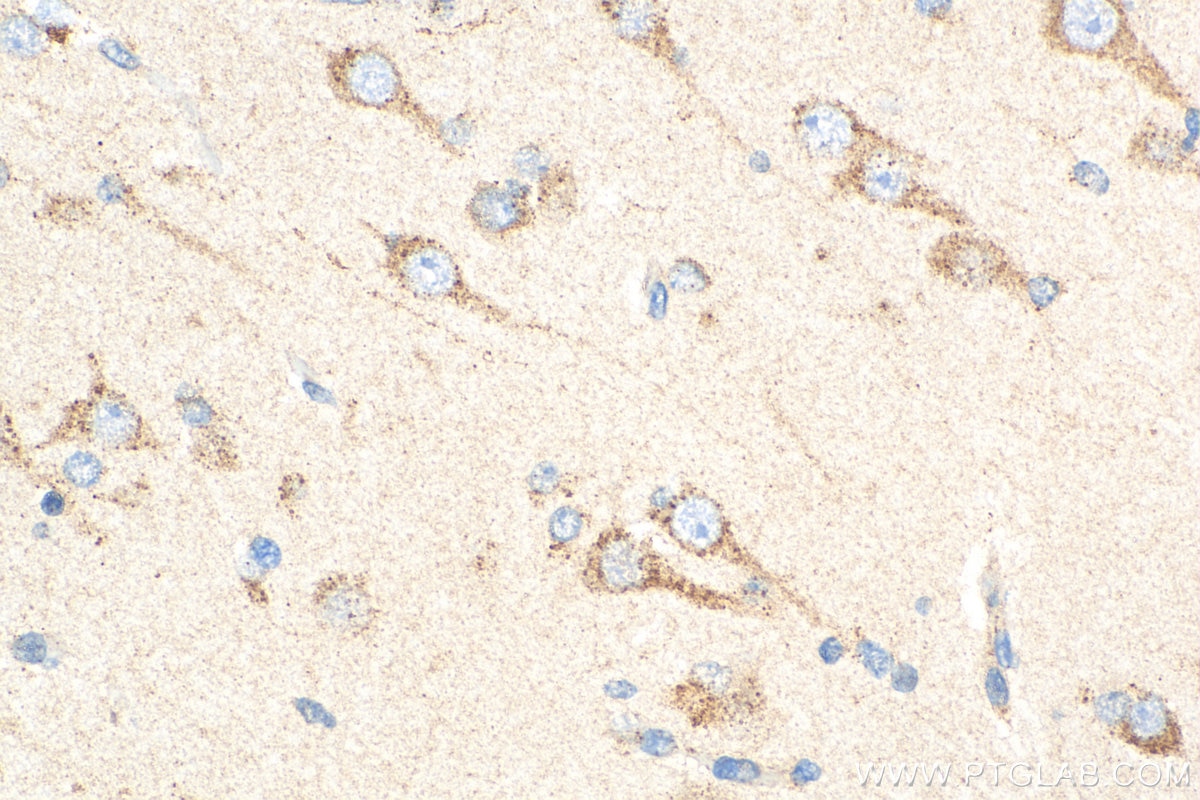
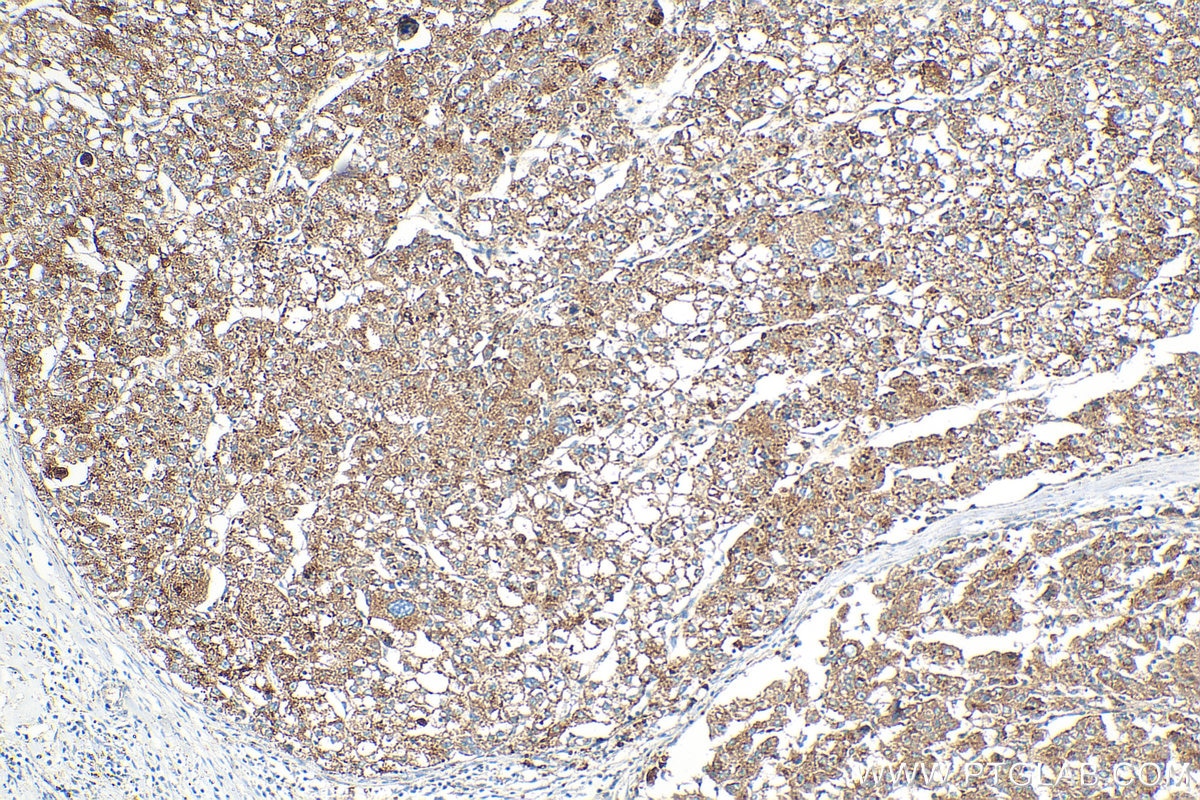
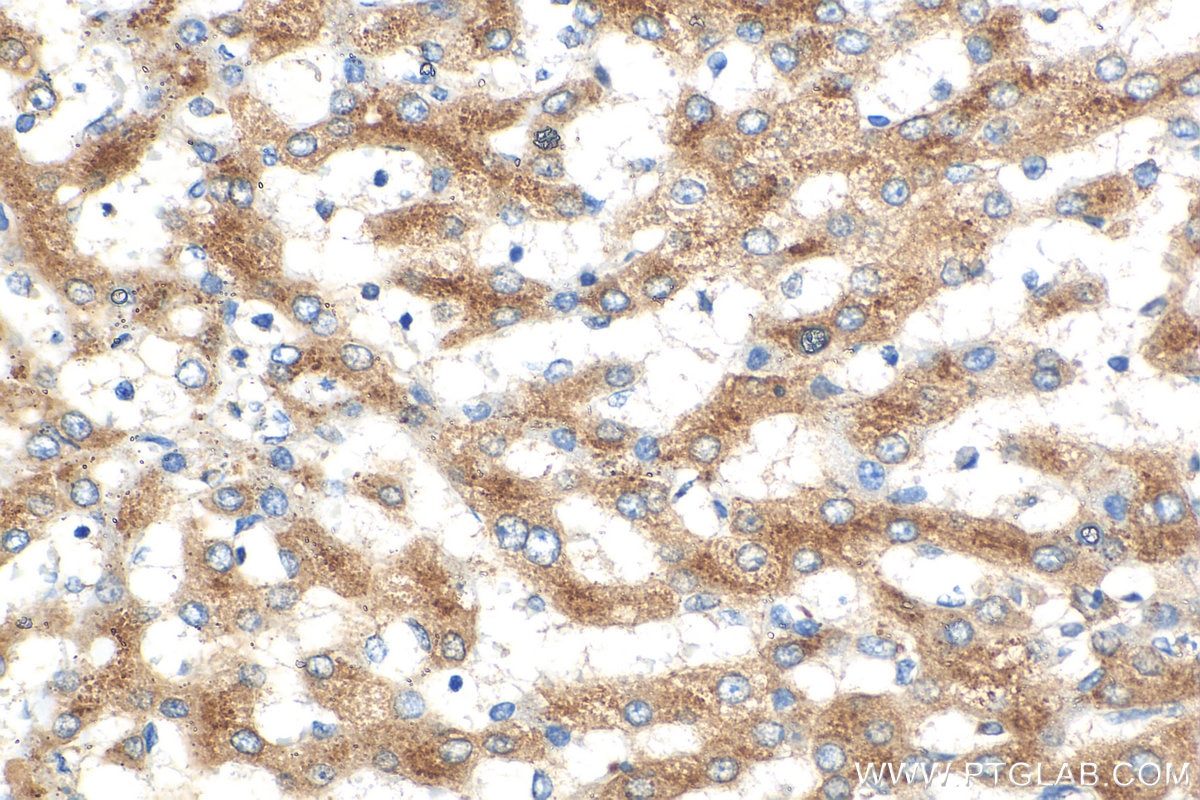
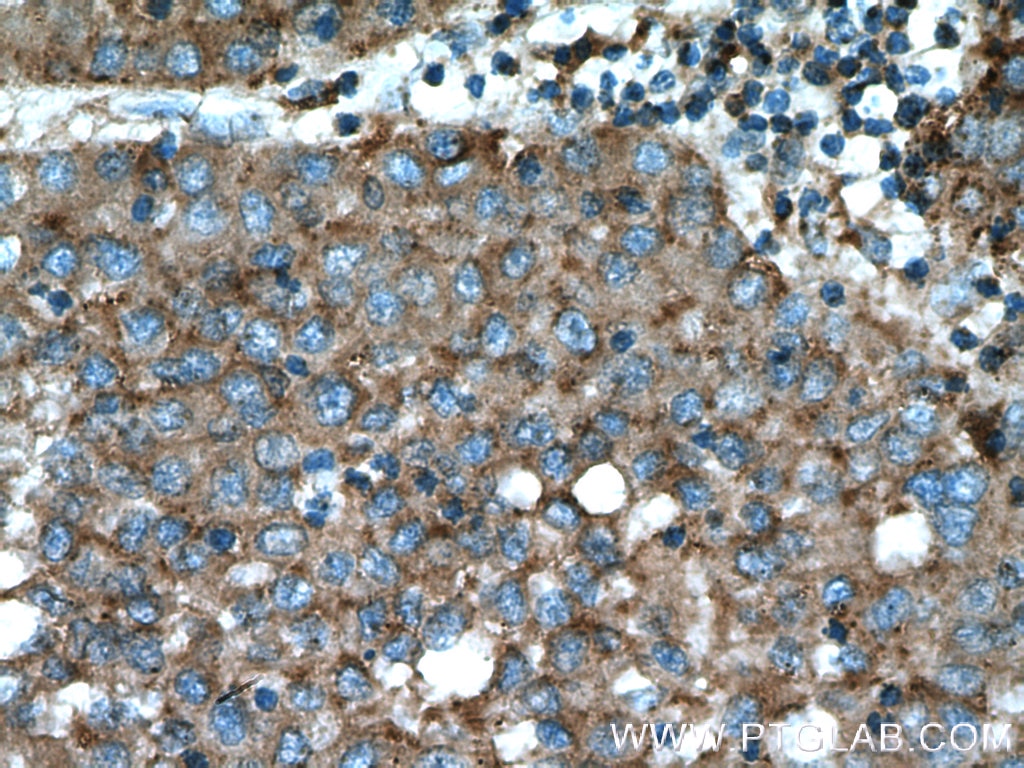
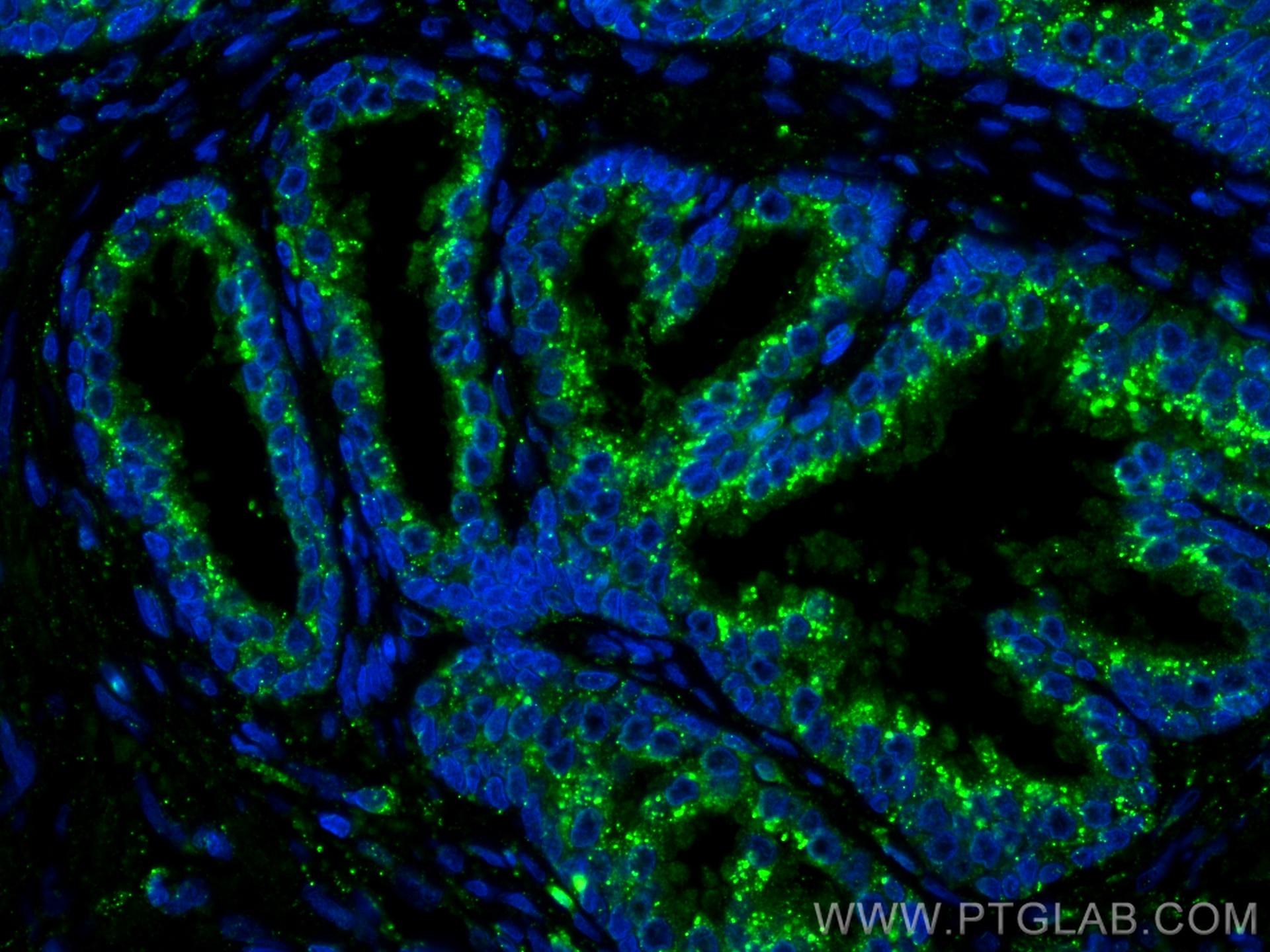
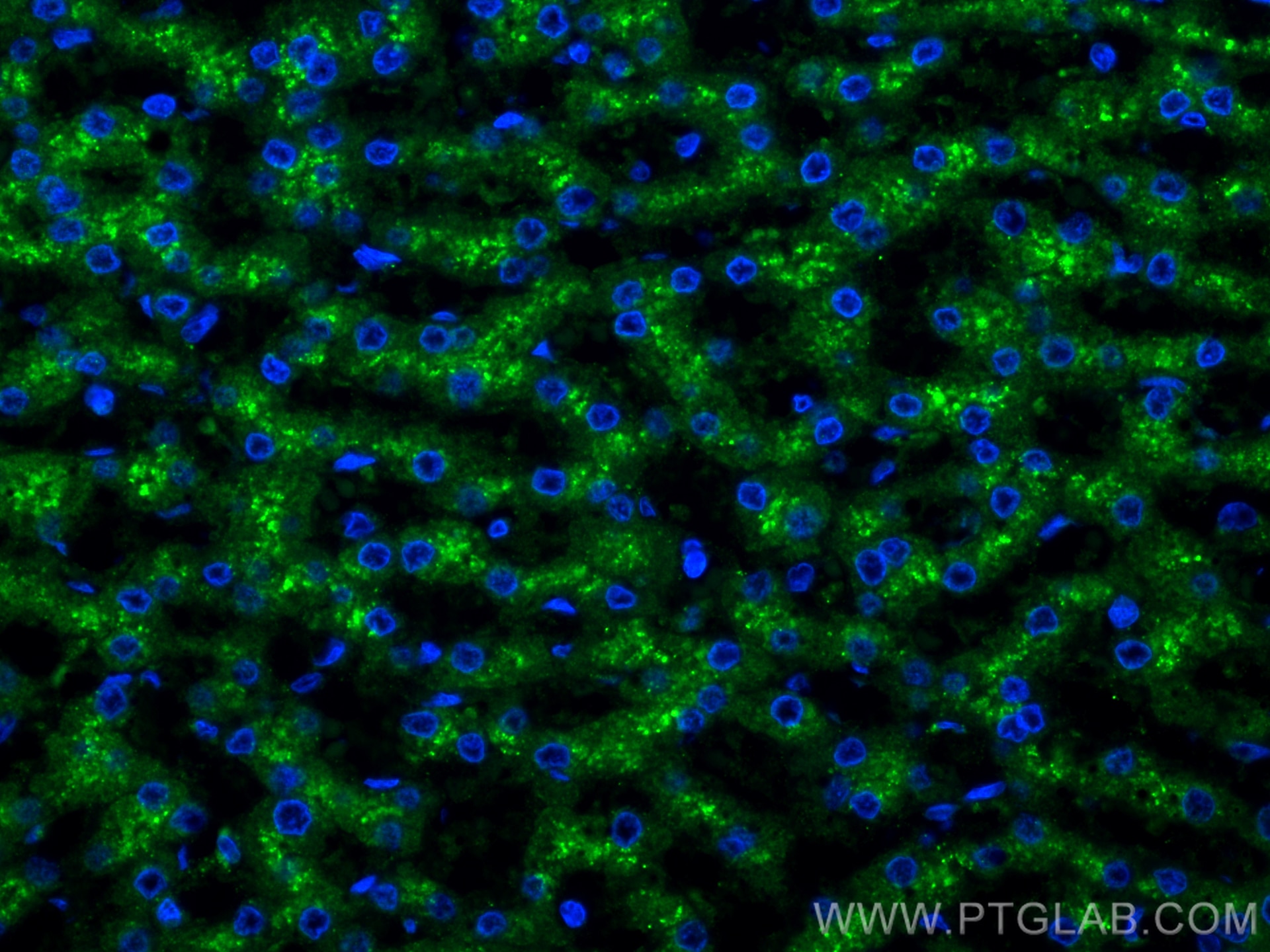
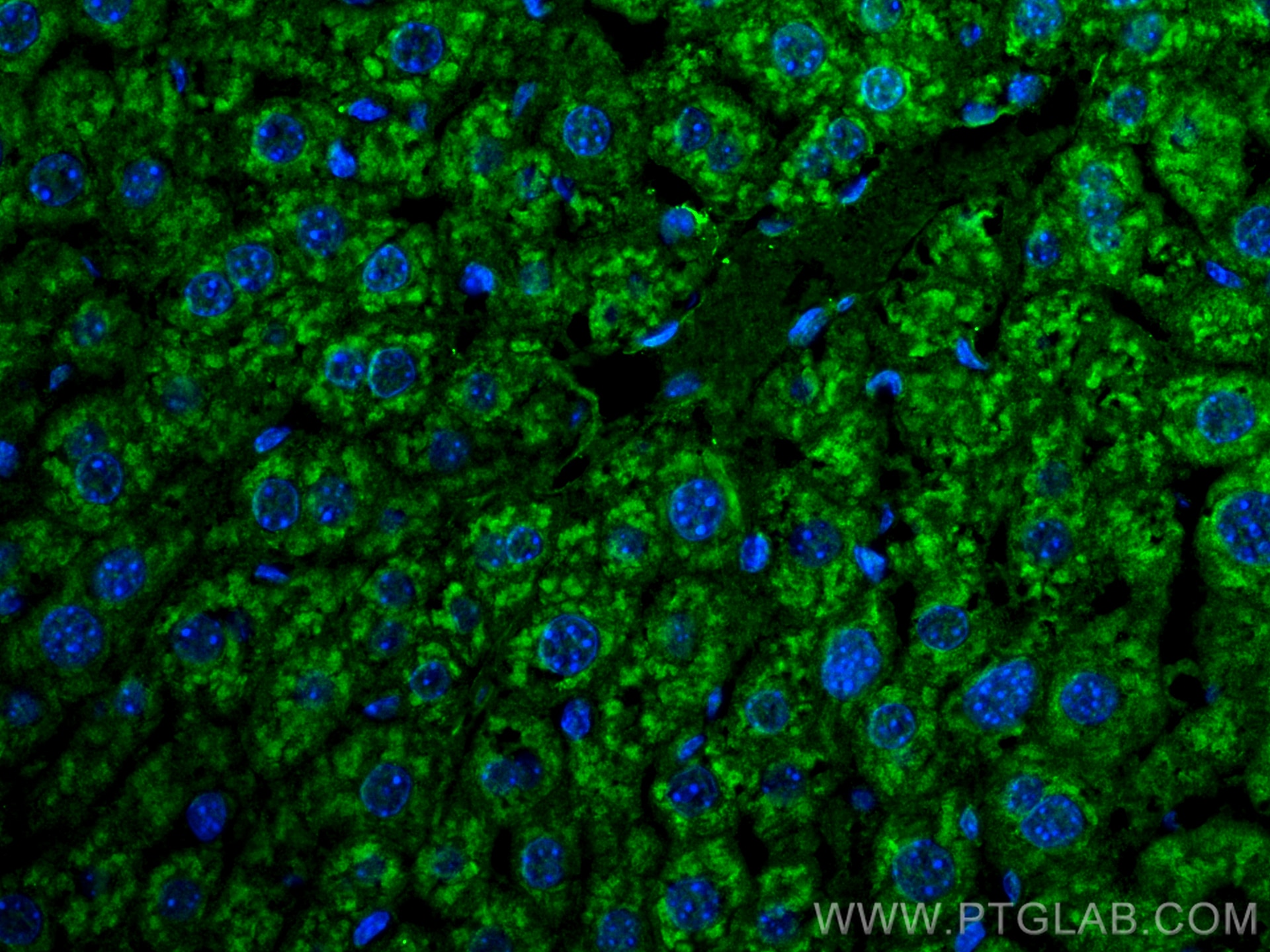
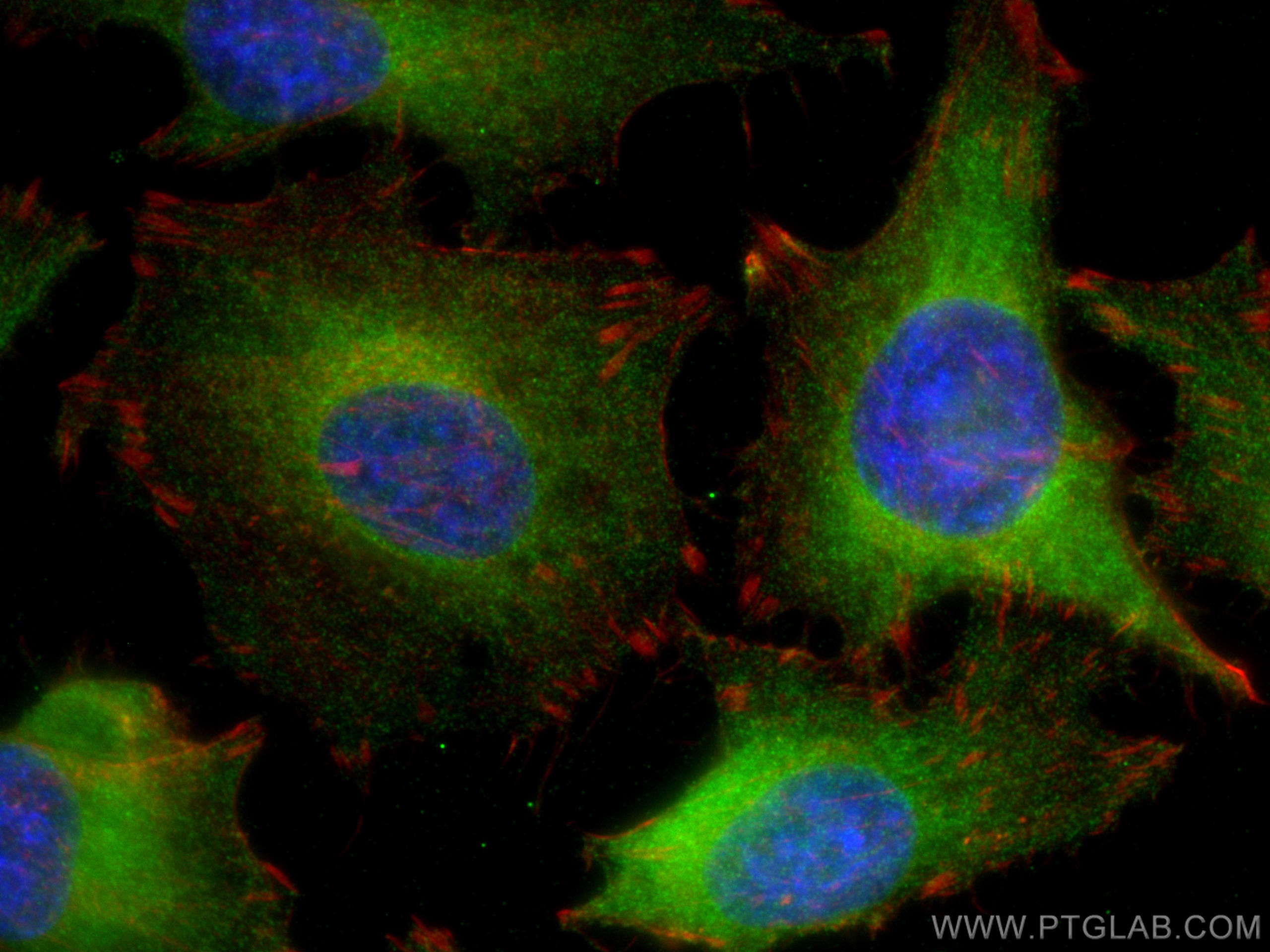
Product Information
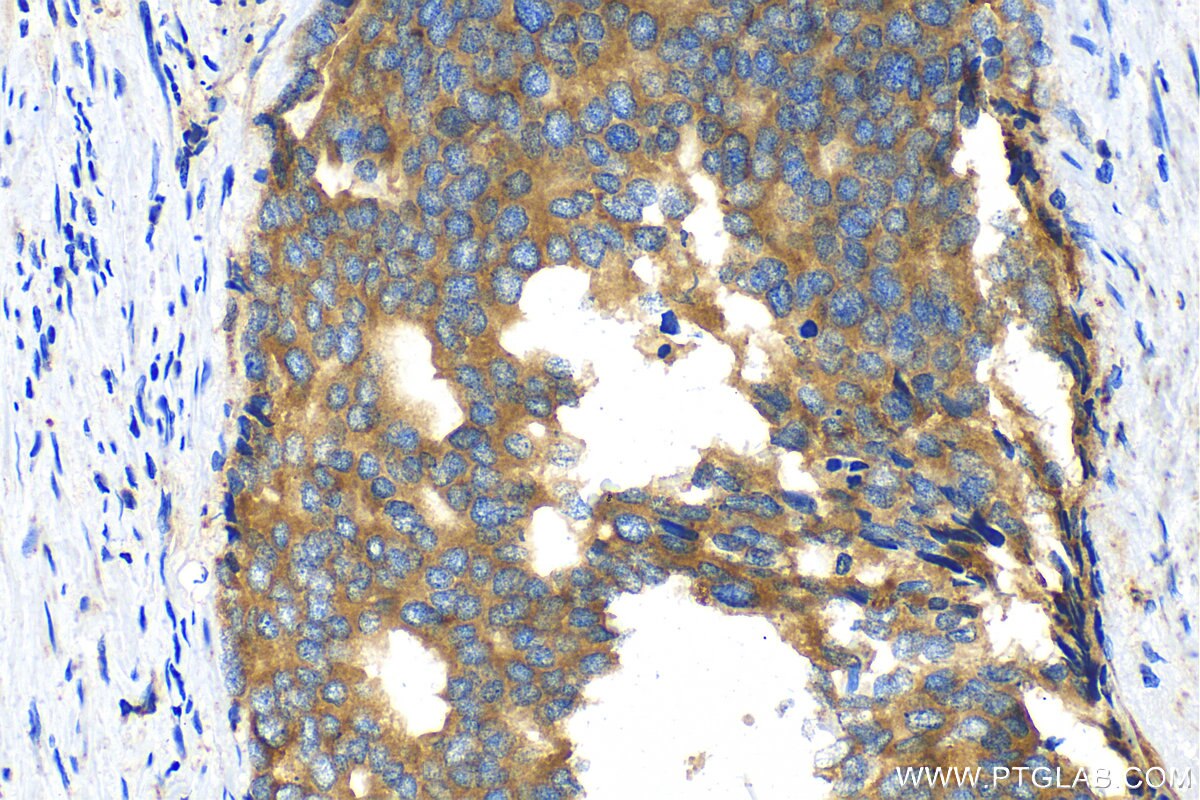
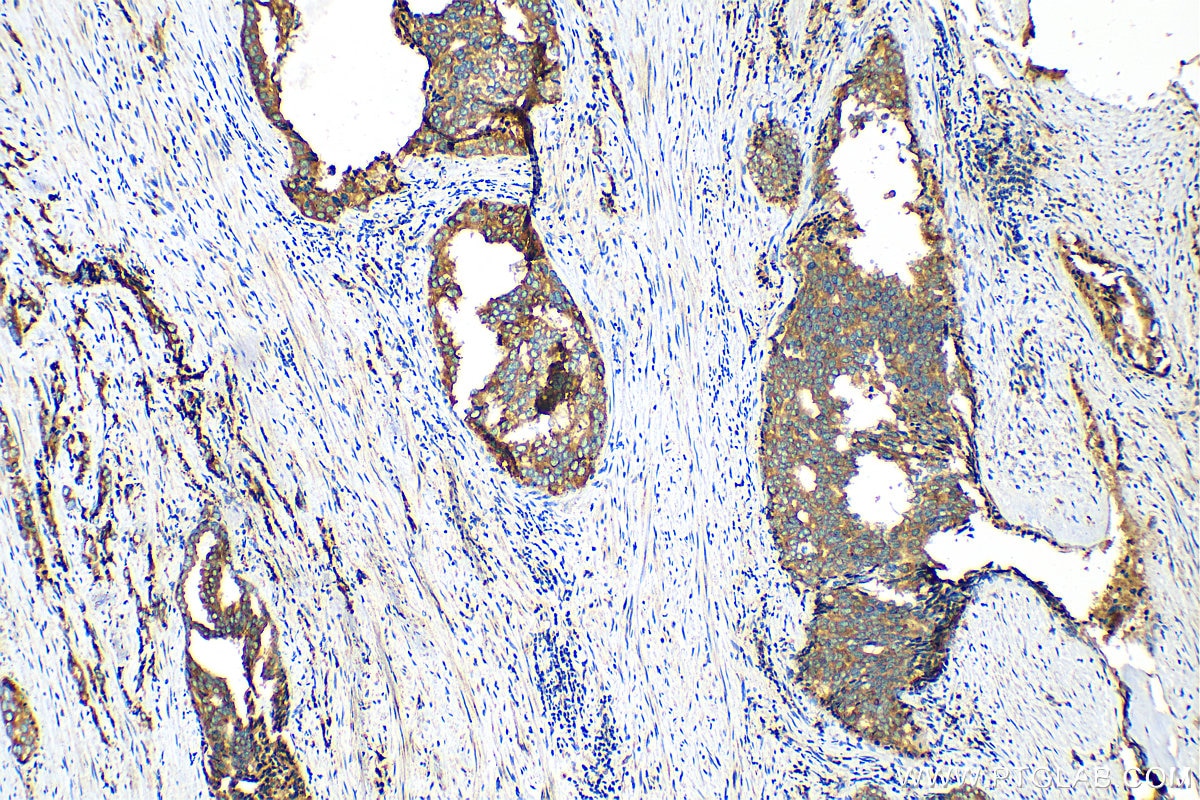
15518-1-PBS targets Beta Galactosidase in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag7792 Product name: Recombinant human Beta galactosidase protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 329-677 aa of BC007493 Sequence: TSYDYDAPLSEAGDLTEKYFALRNIIQKFEKVPEGPIPPSTPKFAYGKVTLEKLKTVGAALDILCPSGPIKSLYPLTFIQVKQHYGFVLYRTTLPQDCSNPAPLSSPLNGVHDRAYVAVDGIPQGVLERNNVITLNITGKAGATLDLLVENMGRVNYGAYINDFKGLVSNLTLSSNILTDWTIFPLDTEDAVRSHLGGWGHRDSGHHDEAWAHNSSNYTLPAFYMGNFSIPSGIPDLPQDTFIQFPGWTKGQVWINGFNLGRYWPARGPQLTLFVPQHILMTSAPNTITVLELEWAPCSSDDPELCAVTFVDRPVIGSSVTYDHPSKPVEKRLMPPPPQKNKDSWLDHV Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | galactosidase, beta 1 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 76 kDa |
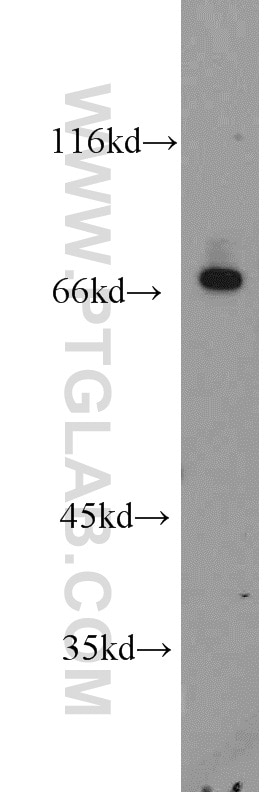
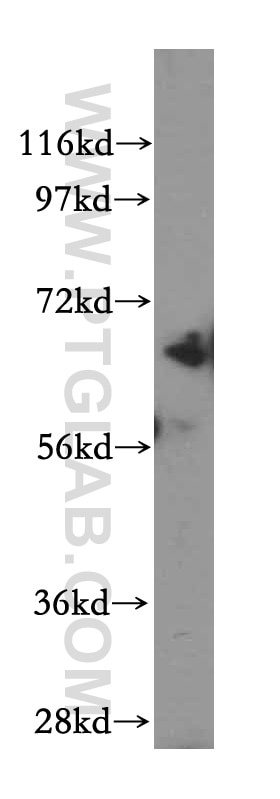
| Observed Molecular Weight | 67 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC007493 |
| Gene Symbol | GLB1/Beta-galactosidase |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2720 |
| RRID | AB_2263448 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P16278 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
What is the molecular weight of β-galactosidase (GLB1)?
The molecular weight of GLB1 is 76 kD, although this protein is known to have multiple isoforms with lower
molecular weight values.
What is the function of GLB1?
The common name of β-galactosidase is lactase. This enzyme is responsible for catalyzing the hydrolysis of
lactose to monosaccharide glucose and galactose. GLB1 also catalyzes hydrolysis of polymeric D-galactosyl
residues (PMID: 23526073, doi: 10.1088/1757-899x/263/2/022046).
How is GLB1 used in our food?
GLB1 isolated from bacteria, fungi, yeast, plants, and other sources has been applied to the manufacturing
of lactose-hydrolyzed products (PMID: 28500401).
How is GLB1 part of a positive feedback loop?
GLB1 transgalactosylates lactose, resulting in allolactose. Allolactose is the inducer for the lac operon and
binds to the lac repressor, prompting GLB1 synthesis (PMIDs: 23526073, 28500401, 26394634).
What organisms express GLB1?
GLB1 is ubiquitous in nature and is produced across kingdoms in plants, microorganisms, and animals.
Properties, such as optimal pH range and temperature preference, vary between species; fungal GLB1
prefers acidic conditions, while yeast and bacteria have optimal conditions at more neutral pH values
(PMID: 28500401).
How is GLB1 utilized in transgenic animals?
Bacterial GLB1 is a widely used reporter gene in transgenic or knockout animals. The lacZ gene of E. coli
has been used to identify cis-acting DNA elements that play a key role for the regulation of gene expression
in mice. The lacZ gene can be incorporated into an endogenous gene, and it is frequently a used to indicate
the success of Cre-loxP recombination events, which allows temporal control of lacZ expression. Mice a
part of the Rosa26R line that also express Cre ubiquitously express Cre-inducible lacZ (PMID: 26394634).