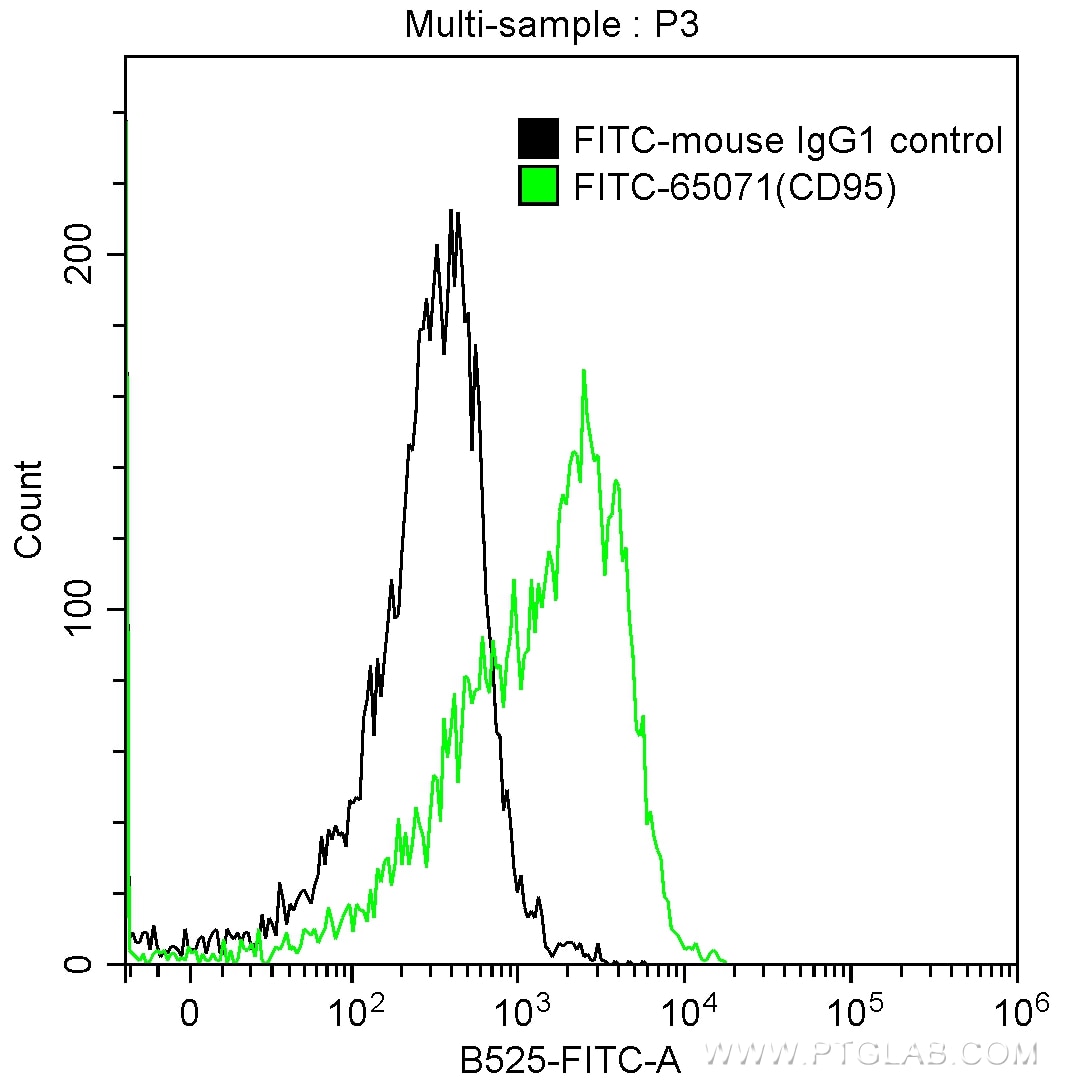
Tested Applications
| Positive FC detected in | human peripheral blood lymphocytes |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry (FC) | FC : 0.2 ug per 10^6 cells in 100 μl suspension |
| This reagent has been pre-titrated and tested for flow cytometric analysis. The suggested use of this reagent is 10 µl per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension or 10 µl per 100 µl of whole blood. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
FITC-65071 targets CD95 in FC applications and shows reactivity with Human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | Human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1, kappa |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
Human CD95 transfected L cells Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | Fas (TNF receptor superfamily, member 6) |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 35-38 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC012479 |
| Gene Symbol | Fas/CD95 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 355 |
| RRID | AB_2920494 |
| Conjugate | FITC Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission Maxima Wavelengths | 498 nm / 526 nm |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P25445 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.09% sodium azide, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at 2-8°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. |
Background Information
Fas (CD95/APO-1) is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily. It can mediate apoptosis by ligation with an agonistic anti-Fas antibody or Fas ligand. Stimulation of Fas results in the aggregation of its intracellular death domains, leading to the formation of the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC). FAS-mediated apoptosis may have a role in the induction of peripheral tolerance, in the antigen-stimulated suicide of mature T-cells, or both.