Tested Applications
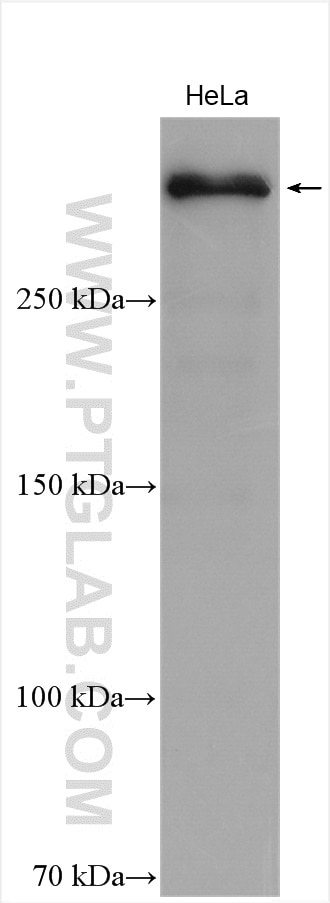
| Positive WB detected in | HeLa cells, HepG2 cells |
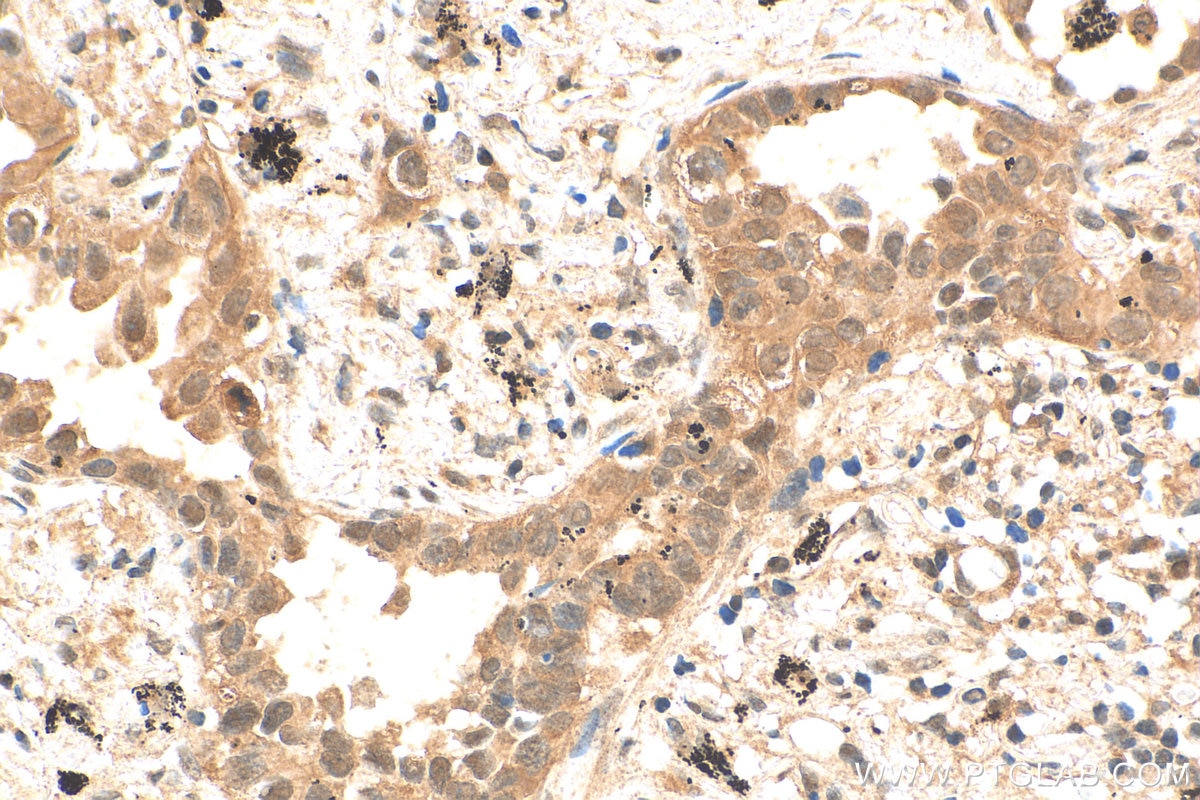
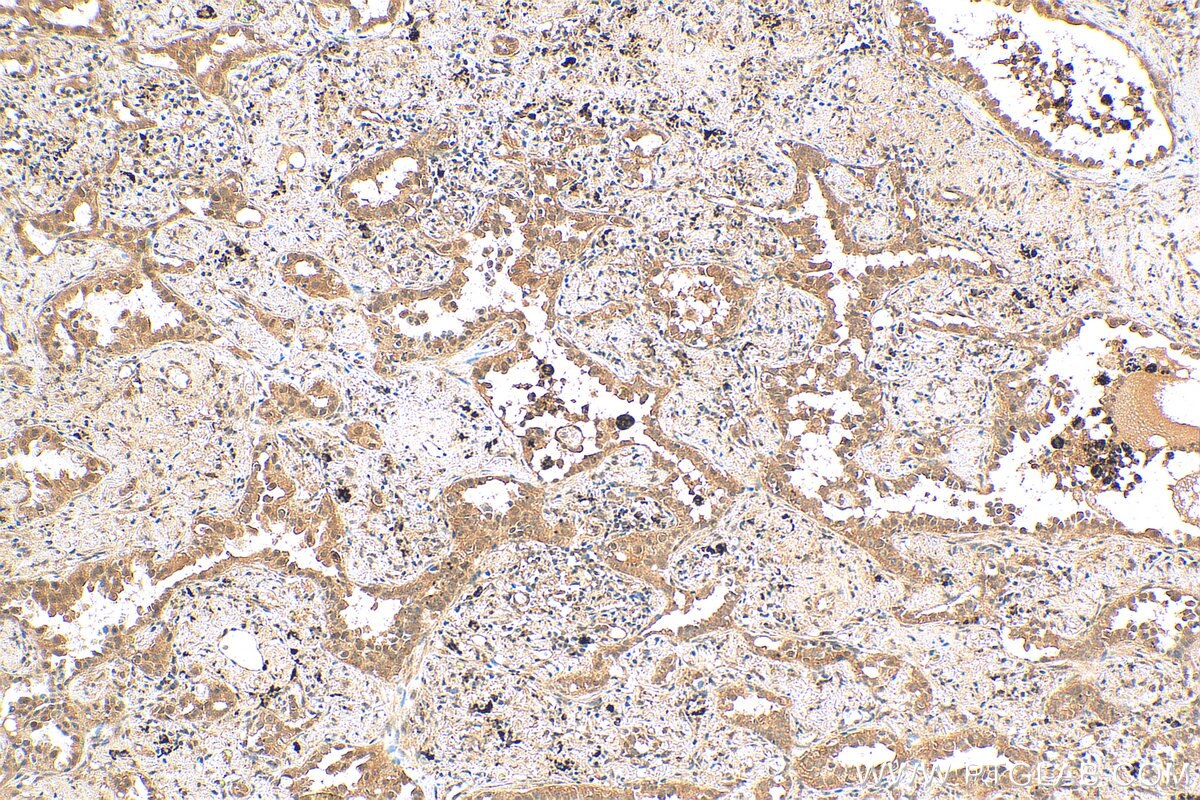
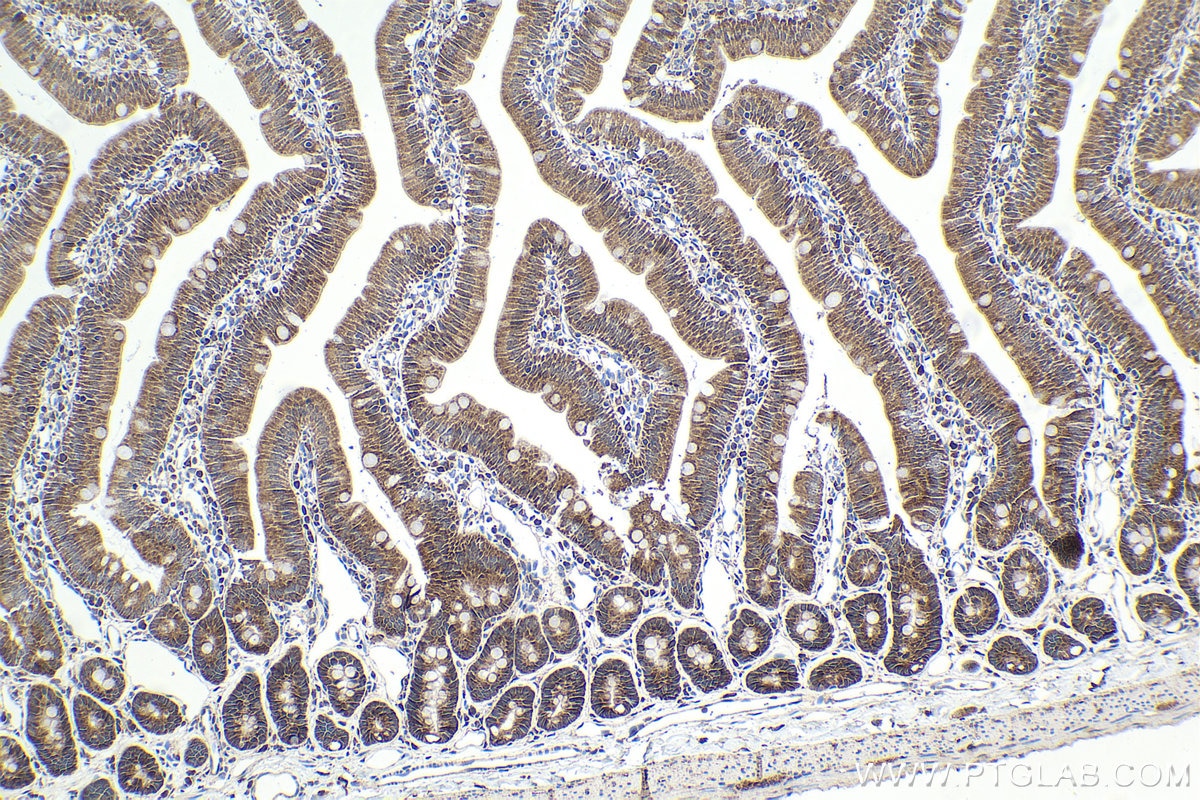
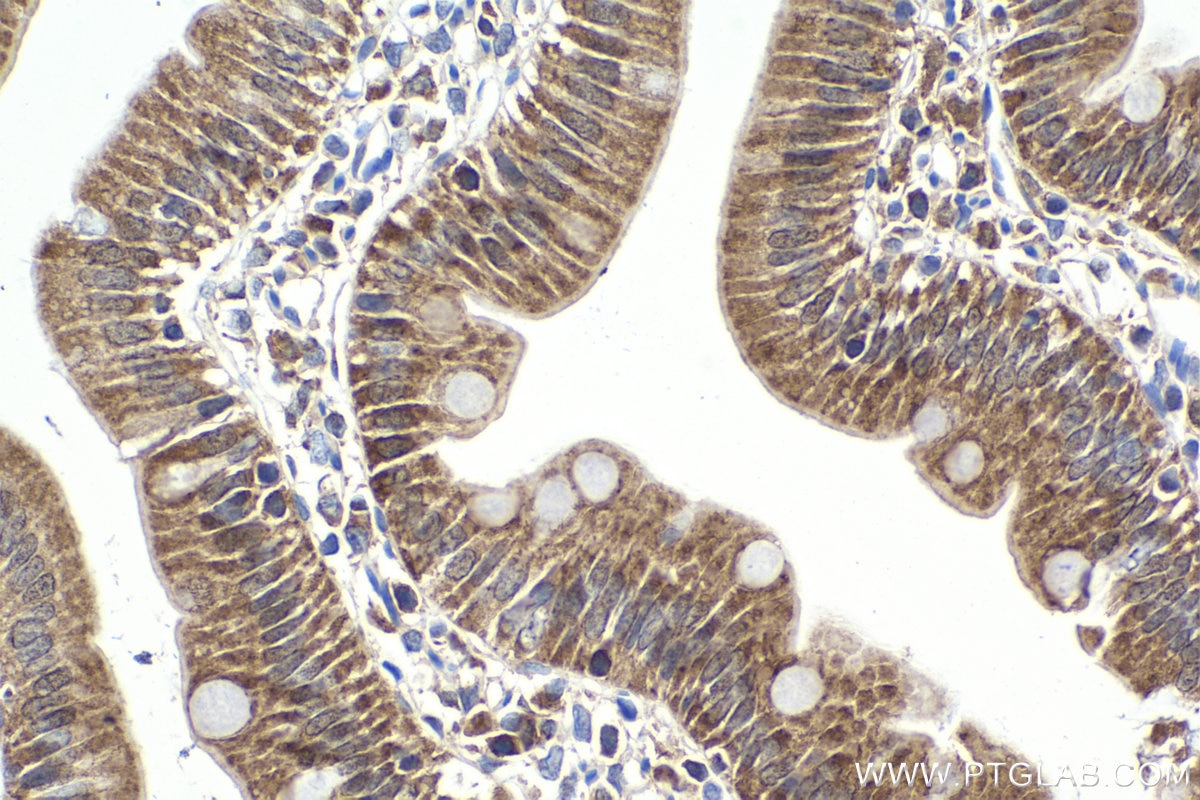
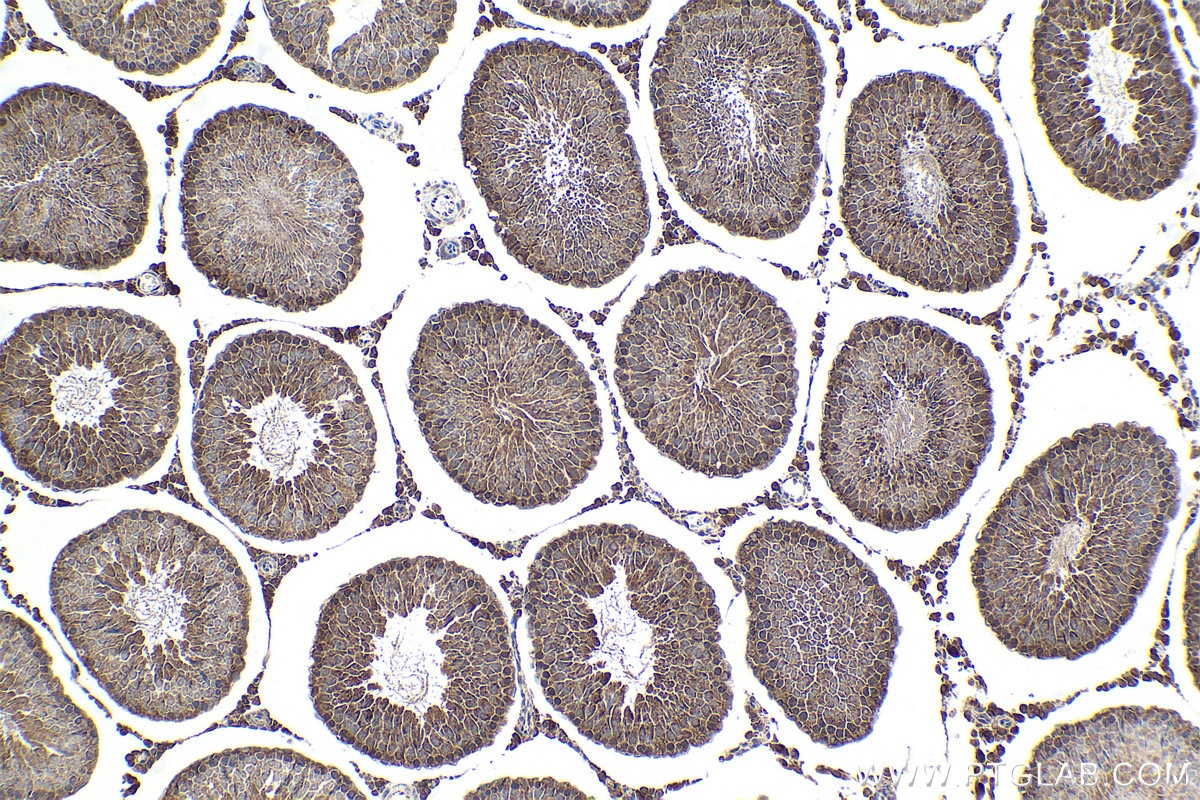
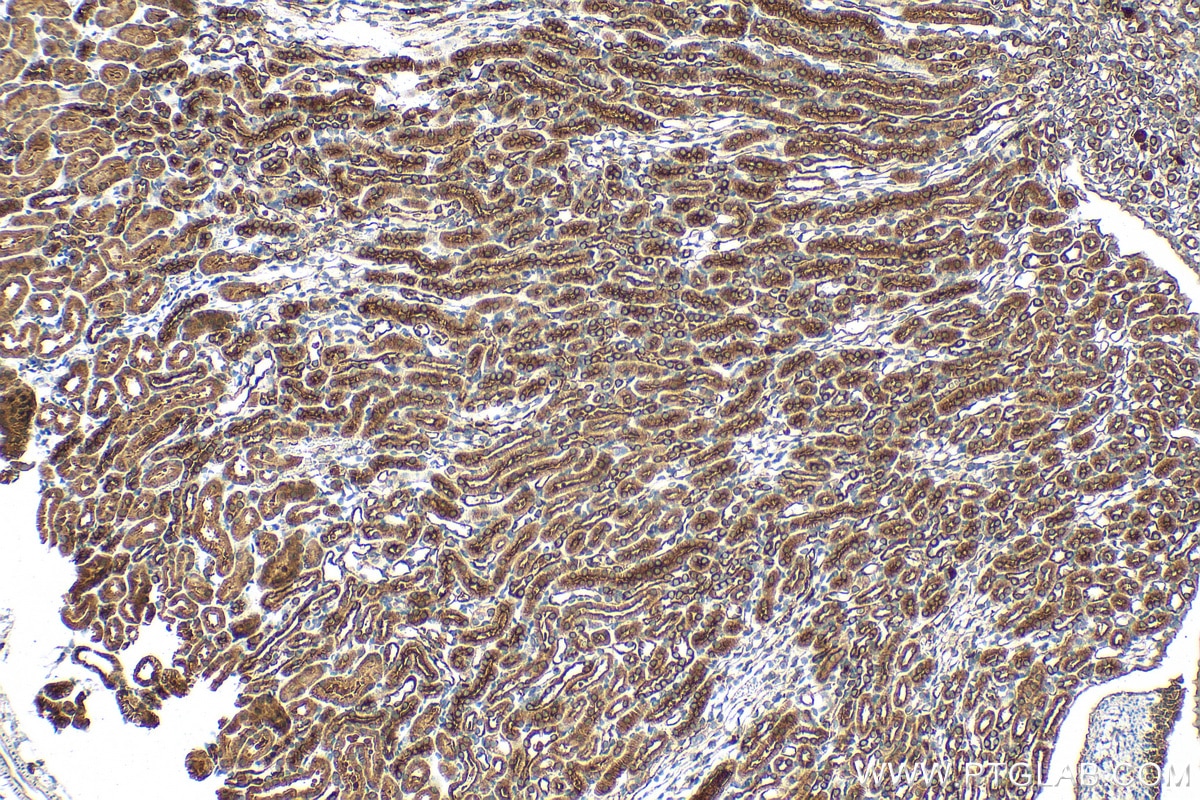
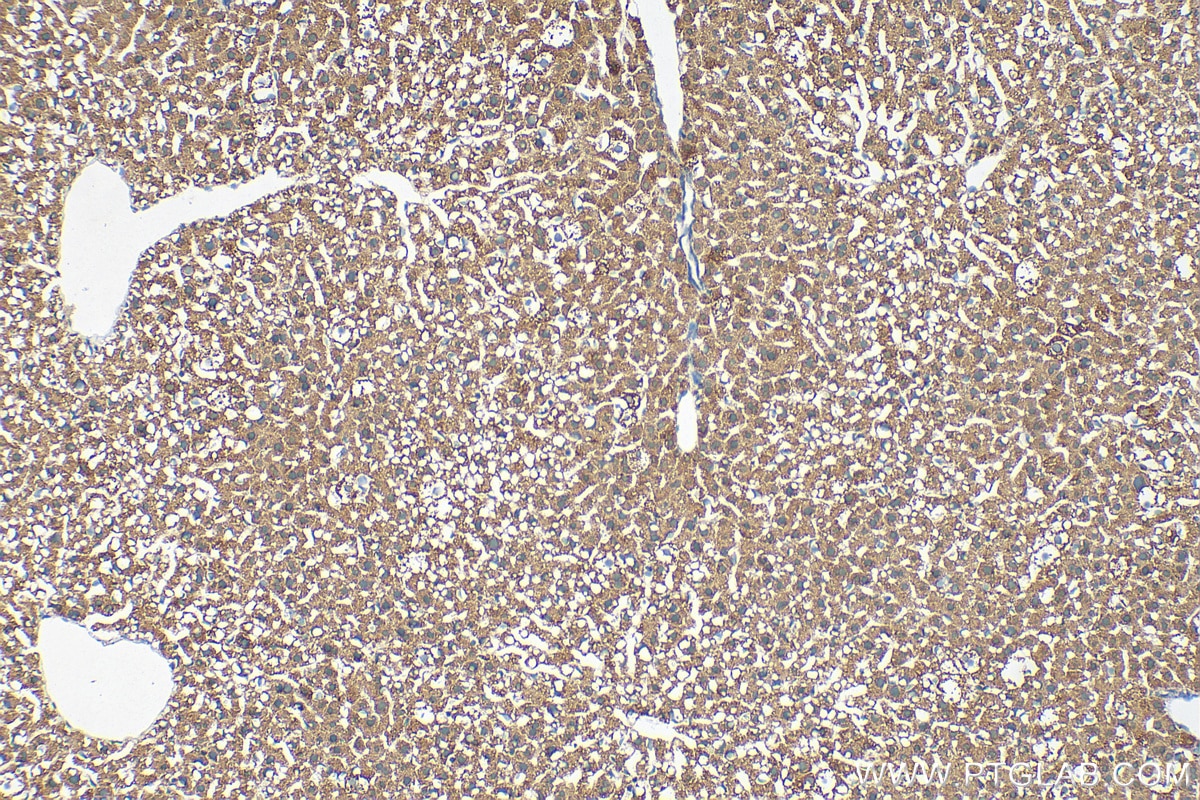
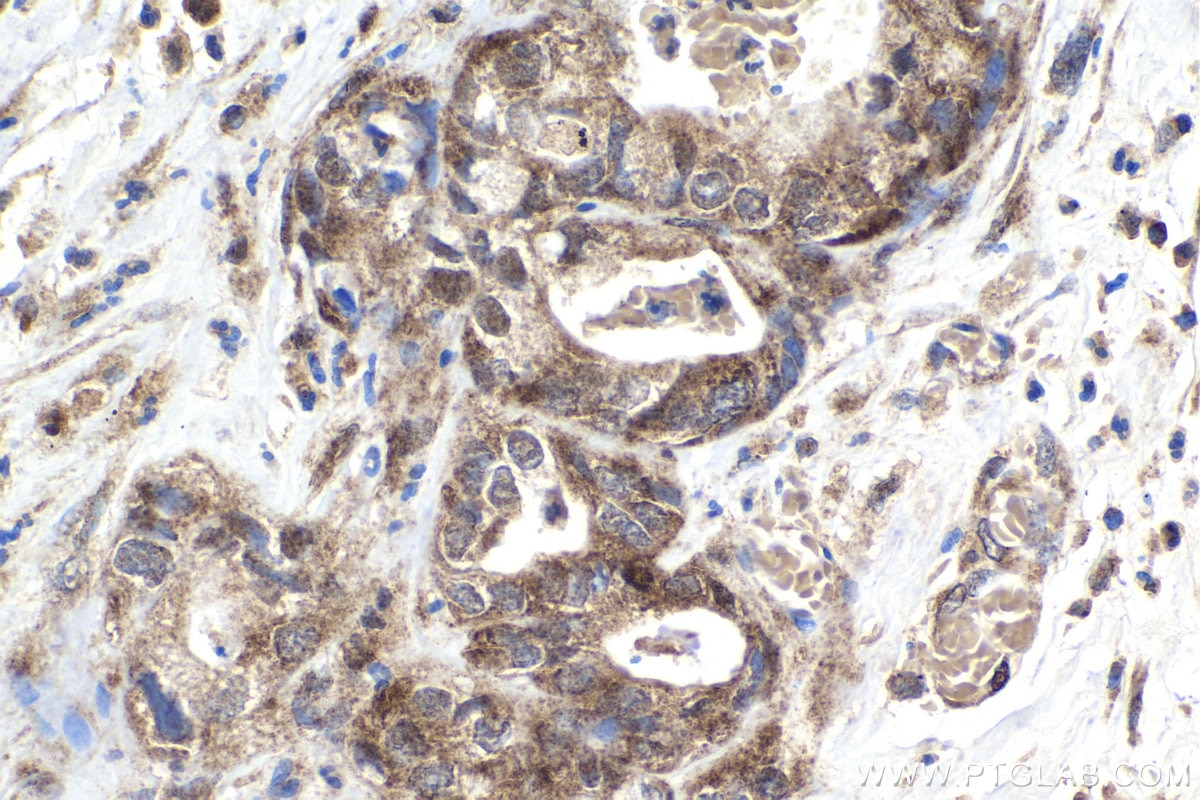
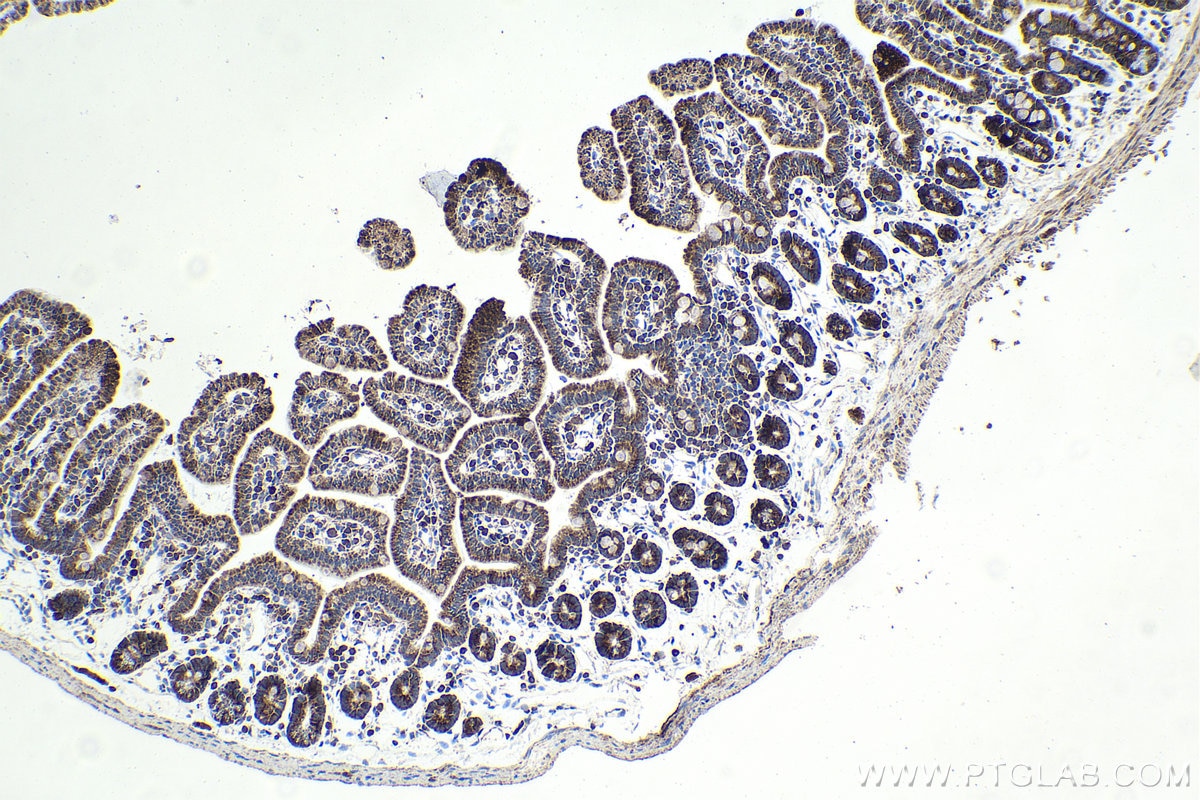
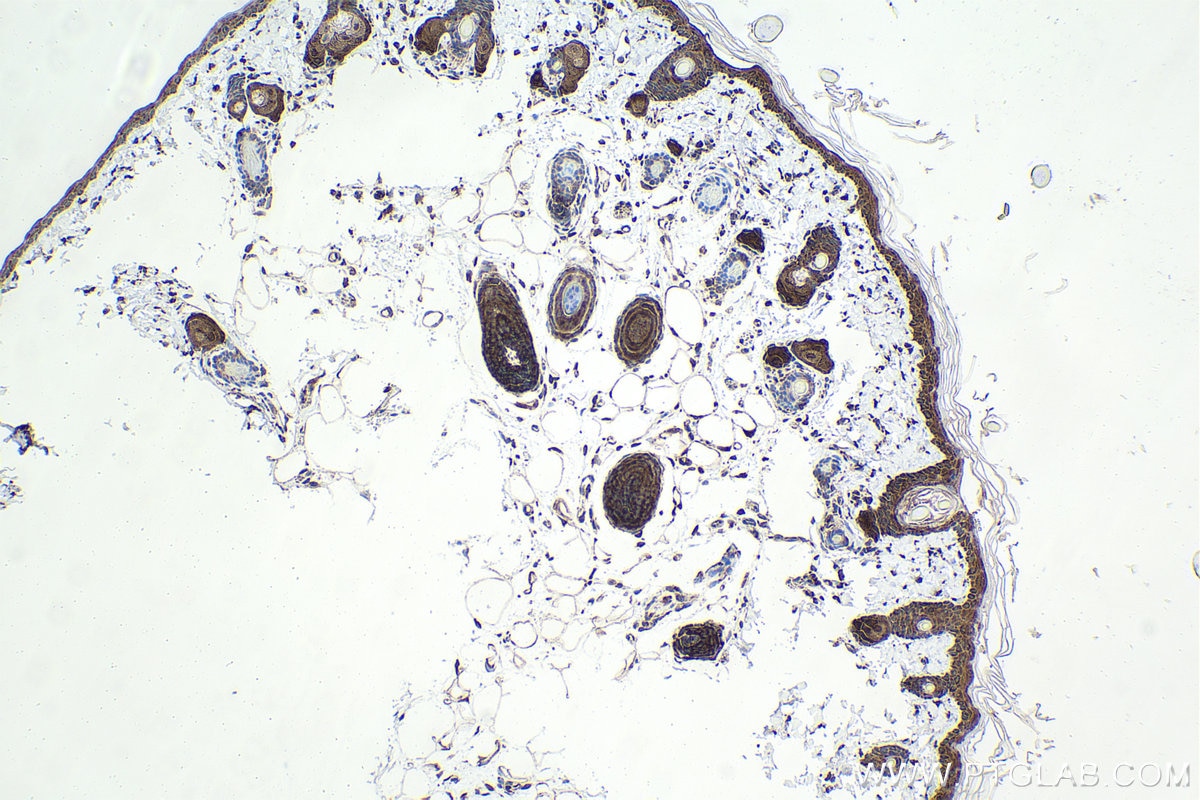
| Positive IHC detected in | rat small intestine tissue, human lung cancer tissue, mouse liver tissue, mouse kidney tissue, human pancreas cancer tissue, mouse small intestine tissue, rat skin tissue, rat testis tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
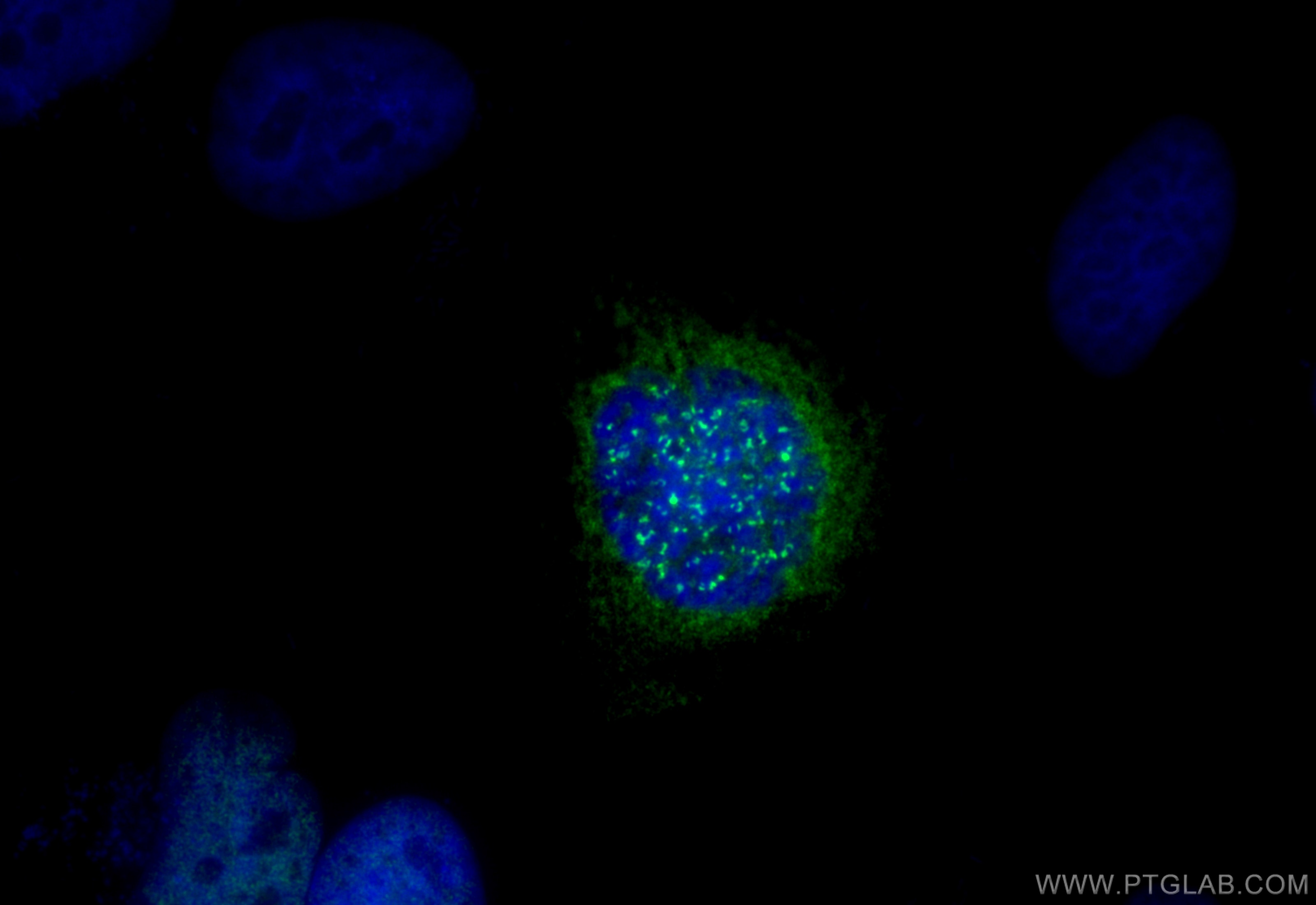
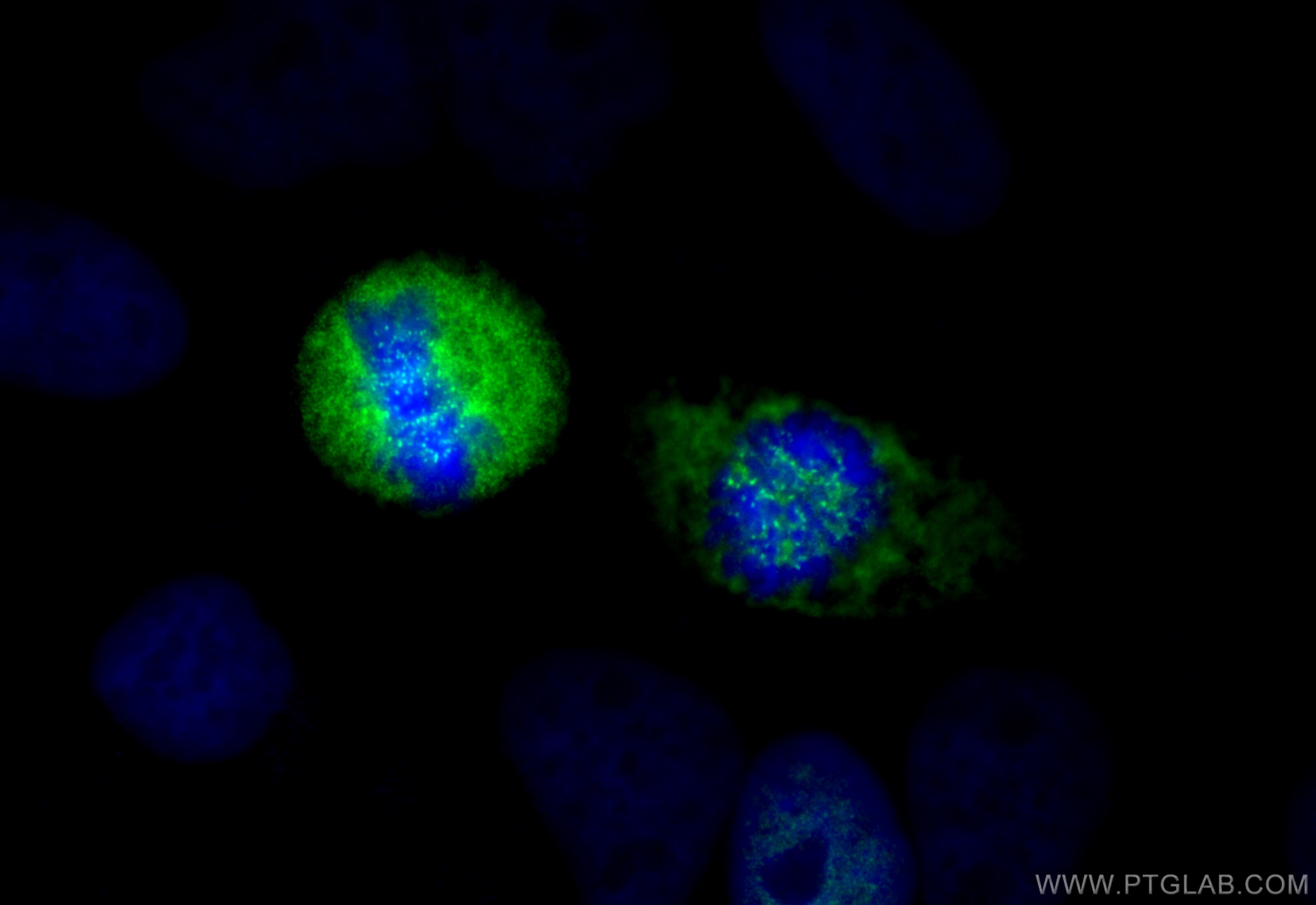
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HeLa cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:6000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:250-1:1000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 3 publications below |
| IHC | See 2 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
28568-1-AP targets CENPF in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag29665 Product name: Recombinant human CENPF protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 3011-3210 aa of NM_016343 Sequence: SVTEKRLSSGQNKASGKRQRSSGIWENGRGPTPATPESFSKKSKKAVMSGIHPAEDTEGTEFEPEGLPEVVKKGFADIPTGKTSPYILRRTTMATRTSPRLAAQKLALSPLSLGKENLAESSKPTAGGSRSQKVKVAQRSPVDSGTILREPTTKSVPVNNLPERSPTDSPREGLRVKRGRLVPSPKAGLESNGSENCKVQ Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | centromere protein F, 350/400ka (mitosin) |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 368 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 350 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | NM_016343 |
| Gene Symbol | CENPF |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1063 |
| RRID | AB_2918176 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P49454 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
CENPF, also named as mitosin and centromere protein F (PMID: 22912832), belongs to centromere protein F family. During the cell cycle, CENPF localizes in multiple cellular structures including the nuclear envelope in late G2/early prophase and kinetochores throughout mitosis (PMID: 30198378). CENPF is required for kinetochore function and chromosome segregation in mitosis and required for kinetochore localization of dynein, LIS1, NDE1 and NDEL1 (PMID: 17600710)(PMID: 7542657). It regulates recycling of the plasma membrane by acting as a link between recycling vesicles and the microtubule network though its association with STX4 and SNAP25. Acts as a potential inhibitor of pocket protein-mediated cellular processes during development by regulating the activity of RB proteins during cell division and proliferation (PMID: 26125848). The calculated molecular weight of CENPF is ~358 kDa and CENPF can be detected as ~367 kDa (PMID: 7542657).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for CENPF antibody 28568-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for CENPF antibody 28568-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for CENPF antibody 28568-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Transl Androl Urol CENPF promotes the proliferation of renal cell carcinoma in vitro
| ||
Cancer Cell Int CENPF interaction with PLA2G4A promotes glioma growth by modulating mTORC1 and NF-κB pathways | ||
Nat Commun CSTF2 mediated mRNA N6-methyladenosine modification drives pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma m6A subtypes | ||
Oncol Lett FOXM1 and CENPF are associated with a poor prognosis through promoting proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma |