Tested Applications
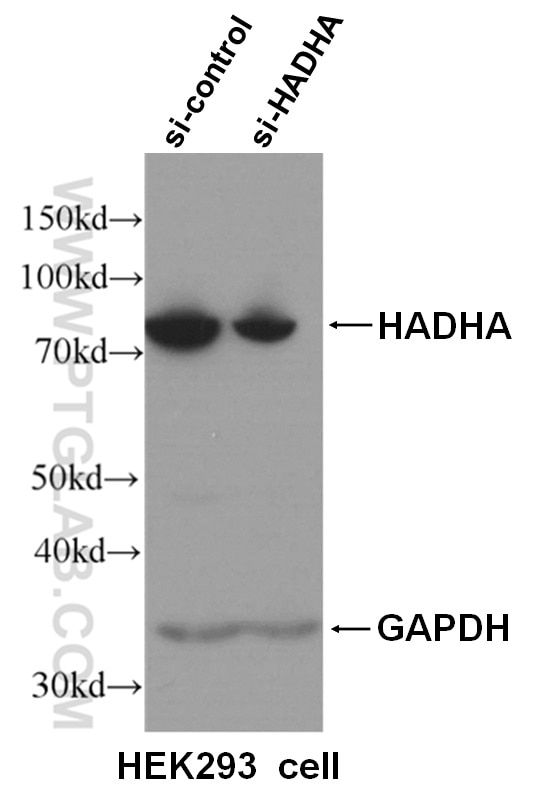
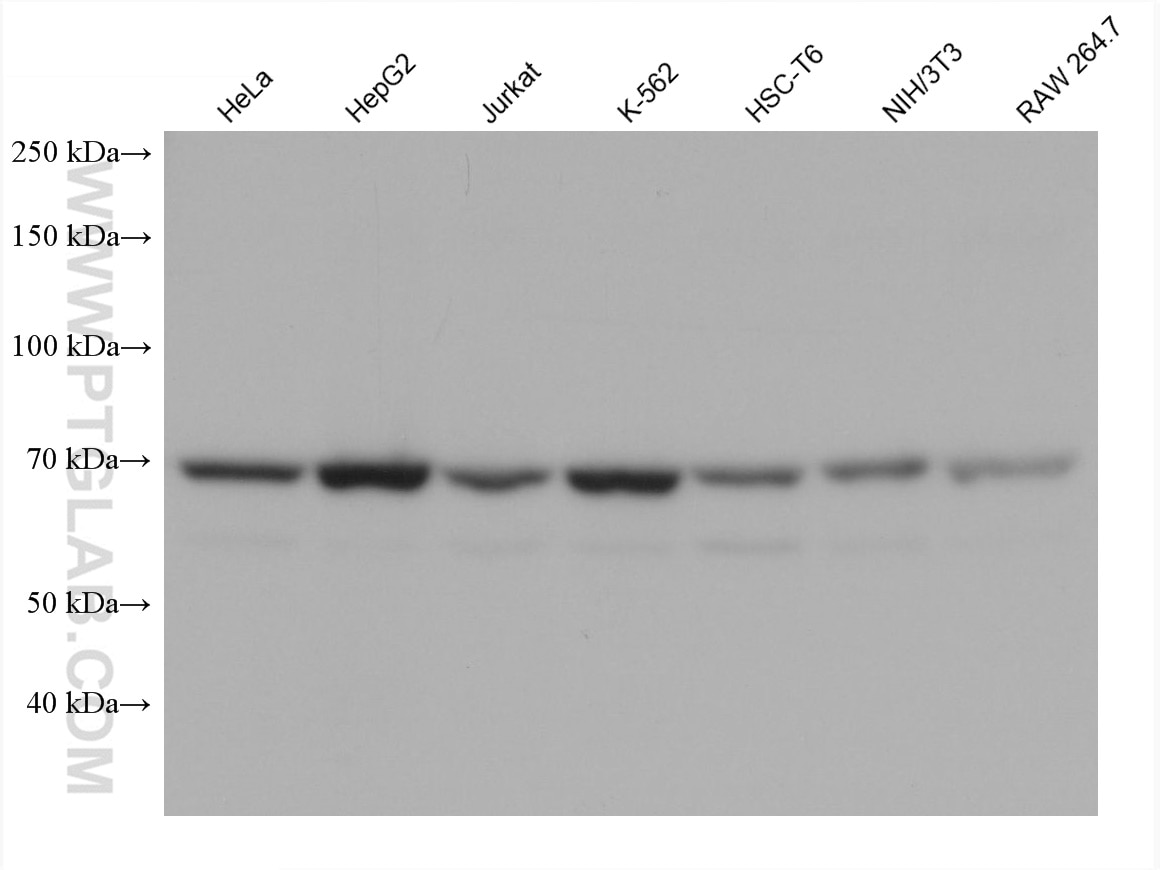
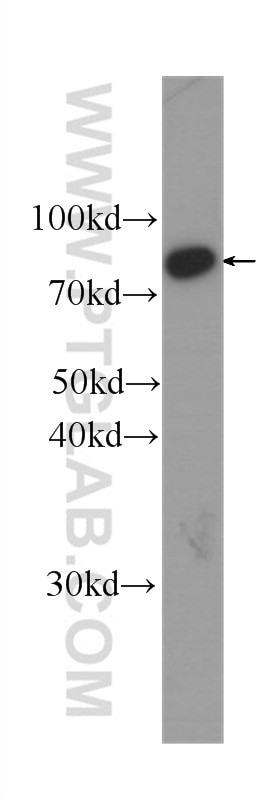
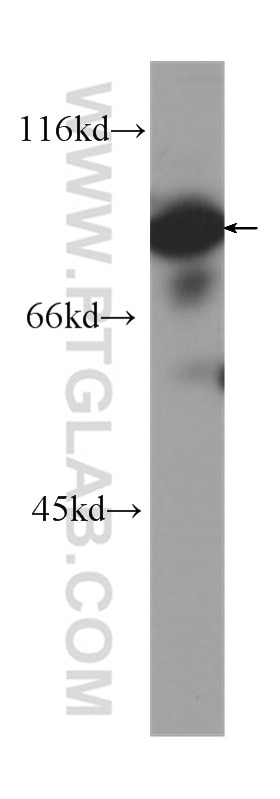
| Positive WB detected in | HeLa cells, Jurkat cells, HepG2 cells, HEK293 cells, K-562 cells, HSC-T6 cells, NIH/3T3 cells, RAW 264.7 cells |
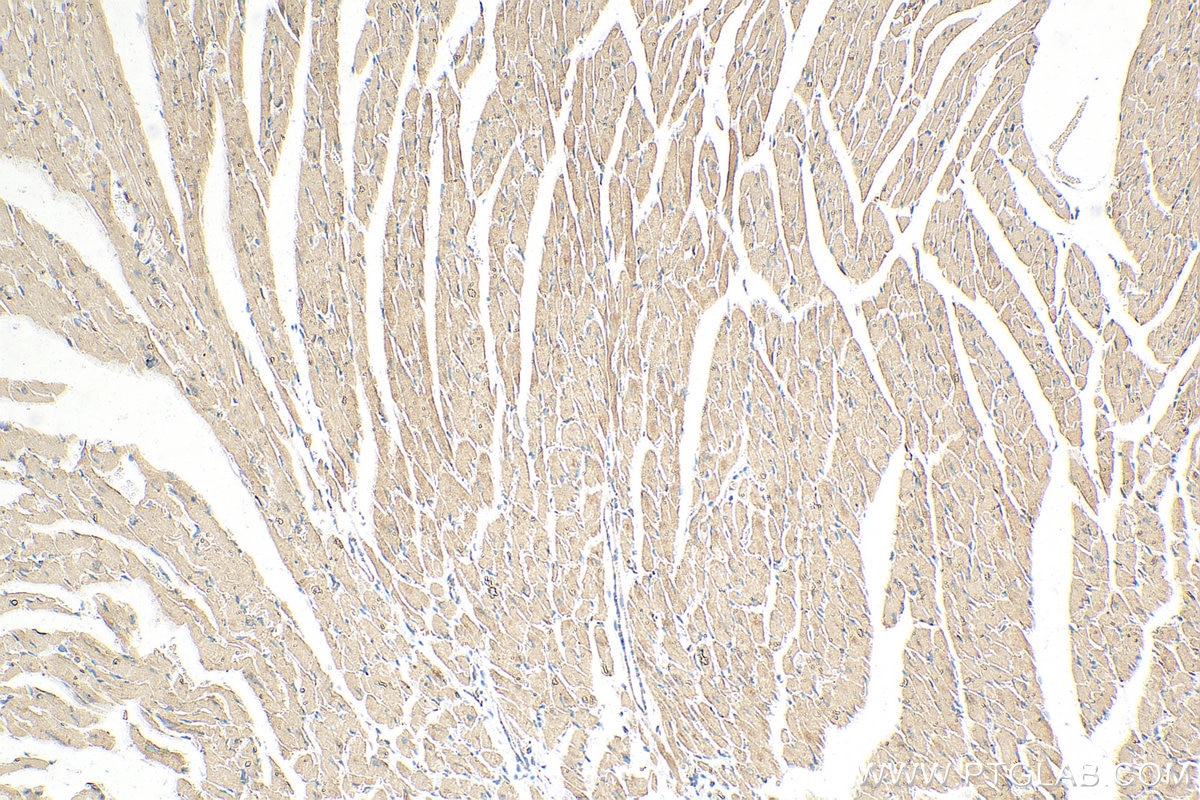
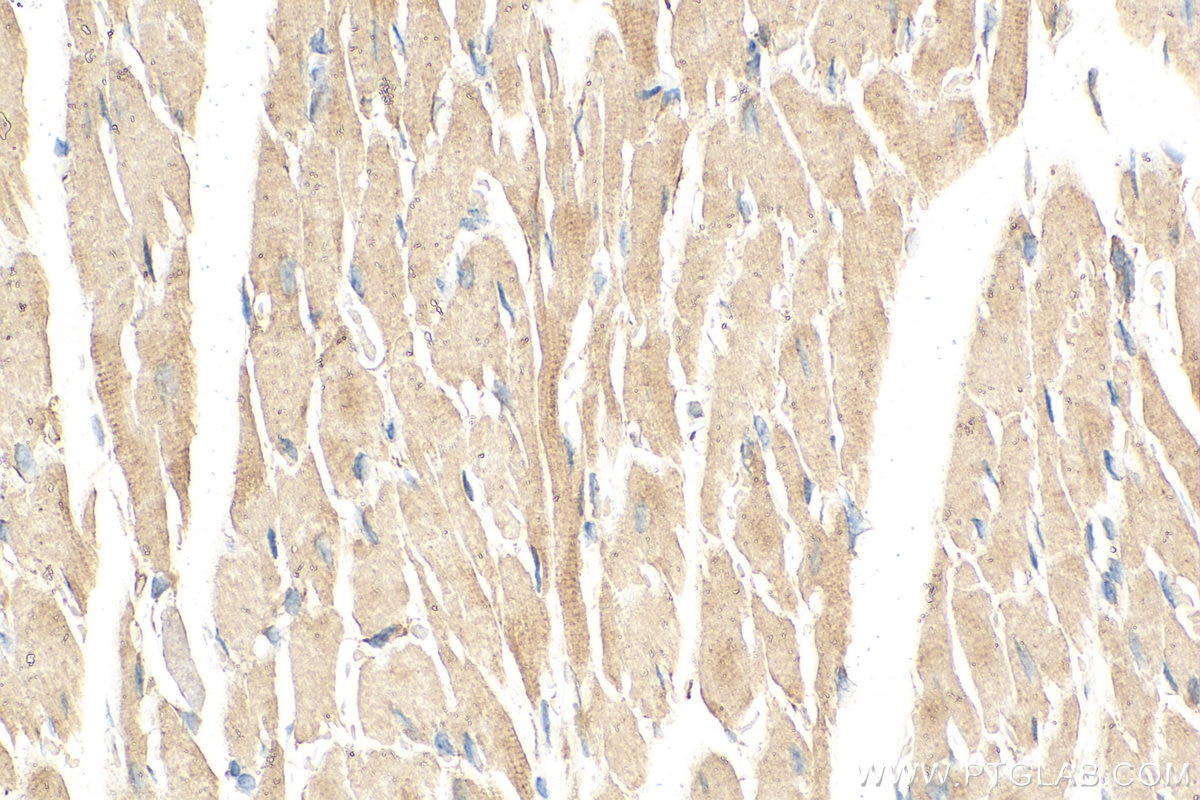
| Positive IHC detected in | mouse heart tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
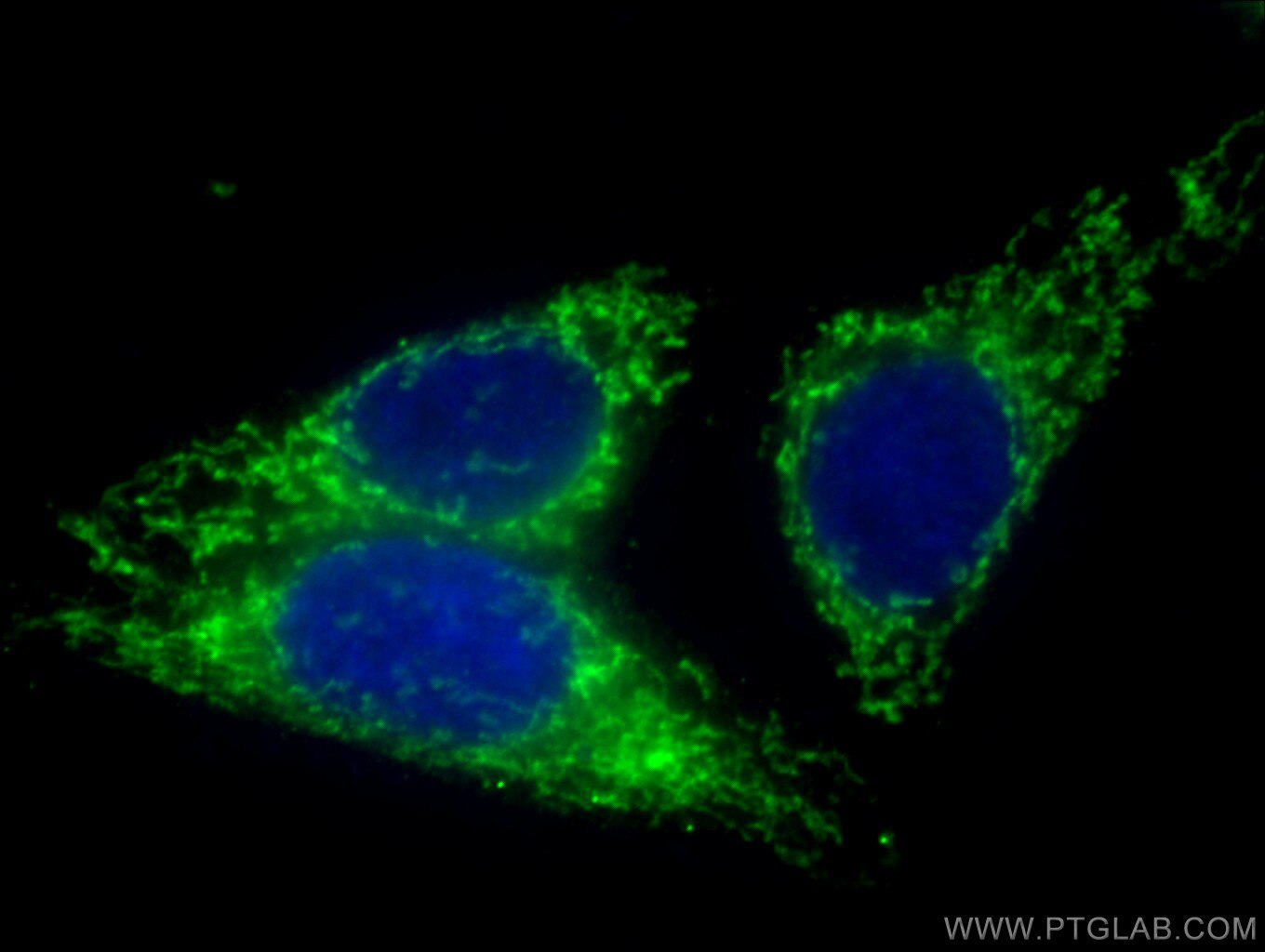
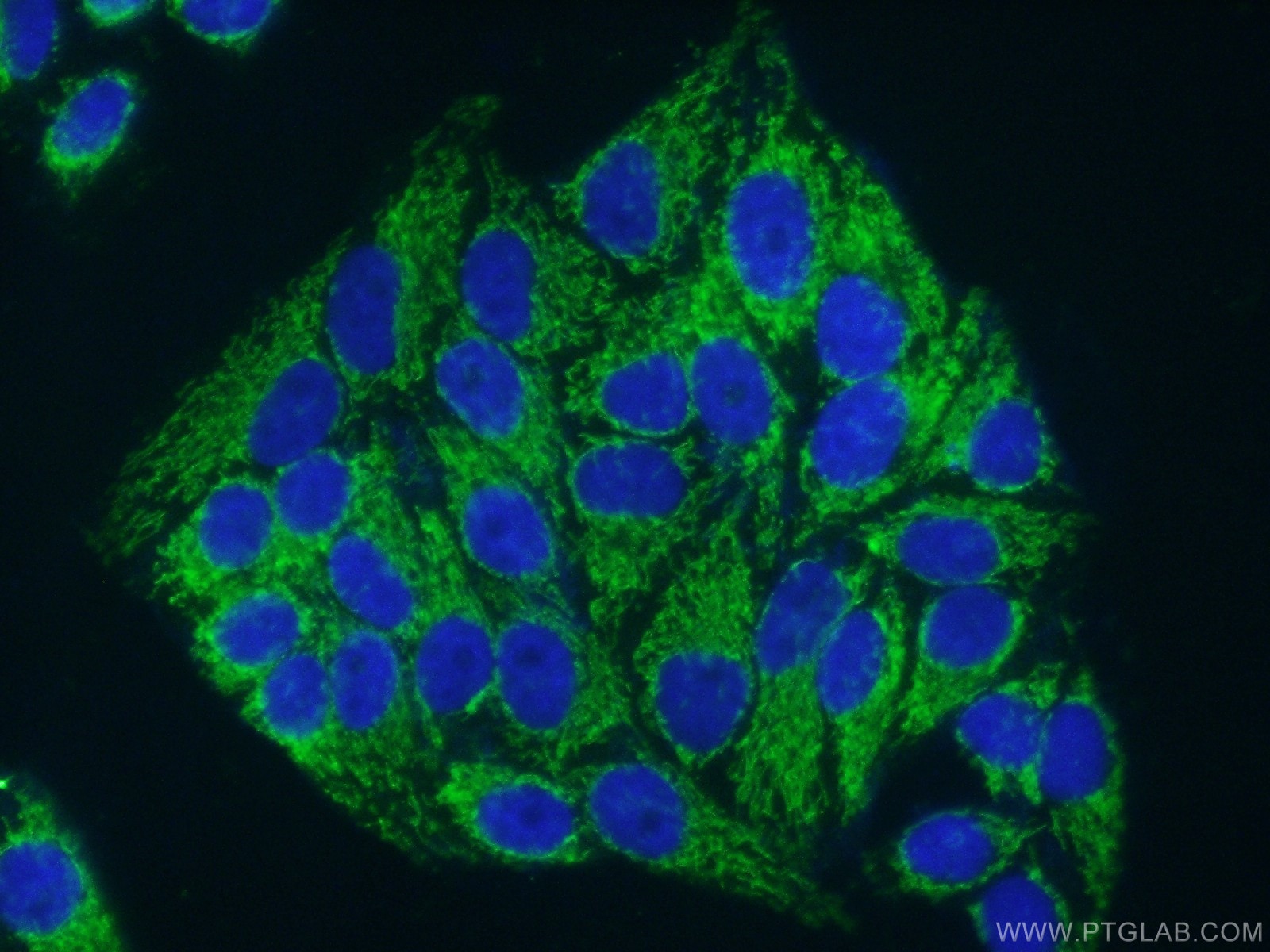
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HepG2 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:250-1:1000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 9 publications below |
Product Information
60250-1-Ig targets HADHA in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag1211 Product name: Recombinant human HADHA protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 339-763 aa of BC009235 Sequence: LMGLYHGQVLCKKNKFGAPQKDVKHLAILGAGLMGAGIAQVSVDKGLKTILKDATLTALDRGQQQVFKGLNDKVKKKALTSFERDSIFSNLTGQLDYQGFEKADMVIEAVFEDLSLKHRVLKEVEAVIPDHCIFASNTSALPISEIAAVSKRPEKVIGMHYFSPVDKMQLLEIITTEKTSKDTSASAVAVGLKQGKVIIVVKDGPGFYTTRCLAPMMSEVIRILQEGVDPKKLDSLTTSFGFPVGAATLVDEVGVDVAKHVAEDLGKVFGERFGGGNPELLTQMVSKGFLGRKSGKGFYIYQEGVKRKDLNSDMDSILASLKLPPKSEVSSDEDIQFRLVTRFVNEAVMCLQEGILATPAEGDIGAVFGLGFPPCLGGPFRFVDLYGAQKIVDRLKKYEAAYGKQFTPCQLLADHANSPNKKFYQ Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | hydroxyacyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase/3-ketoacyl-Coenzyme A thiolase/enoyl-Coenzyme A hydratase (trifunctional protein), alpha subunit |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 83 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 79 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC009235 |
| Gene Symbol | HADHA |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3030 |
| RRID | AB_2881371 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P40939 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
HADHA(Trifunctional enzyme subunit alpha, mitochondrial) is also named as HADH,78 kDa gastrin-binding protein.It belongs to the enoyl-CoA hydratase/isomerase family in the N-terminal section and the 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase family in the central section.It harbors the 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase and enoyl-CoA hydratase activities.Defects in HADHA are a cause of trifunctional protein deficiency (TFP deficiency) and long-chain 3-hydroxyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (LCHAD deficiency) and maternal acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for HADHA antibody 60250-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for HADHA antibody 60250-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for HADHA antibody 60250-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Commun Biol A G1528C Hadha knock-in mouse model recapitulates aspects of human clinical phenotypes for long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency | ||
Proteomics Quantitative Proteomic Study of Myocardial Mitochondria in Urea Transporter B Knockout Mice.
| ||
Cell Biosci Exosomes from hyperglycemia-stimulated vascular endothelial cells contain versican that regulate calcification/senescence in vascular smooth muscle cells. | ||
JCI Insight Mitochondrial bioenergetics and cardiolipin remodeling abnormalities in mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency | ||
J Cancer Knockdown of HOXD13 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Inhibited its Proliferation, Migration, and Influenced Fatty Acid Metabolism |