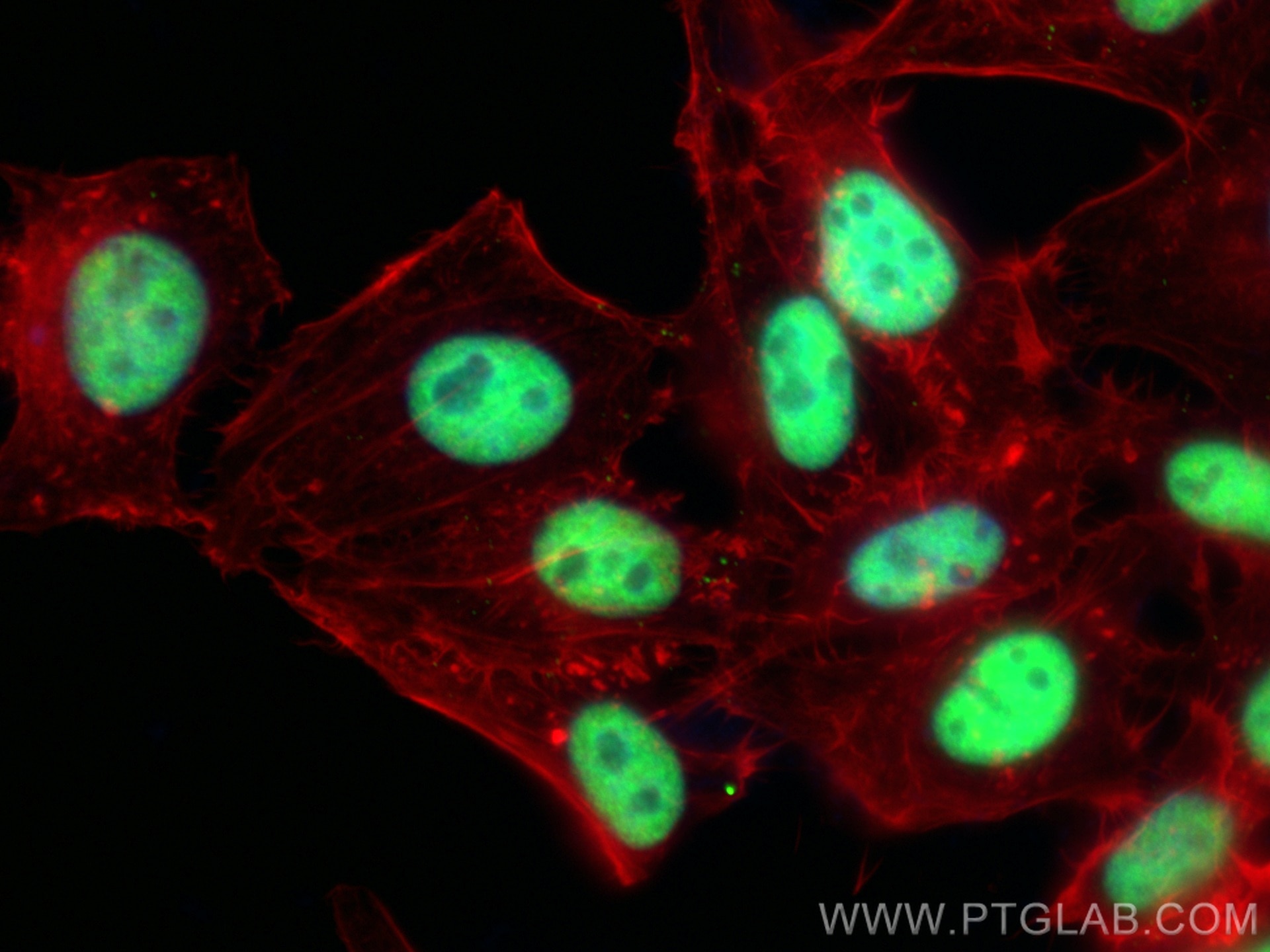
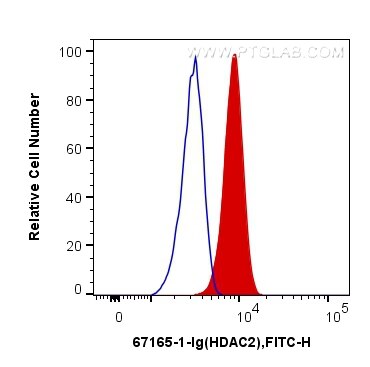
Product Information
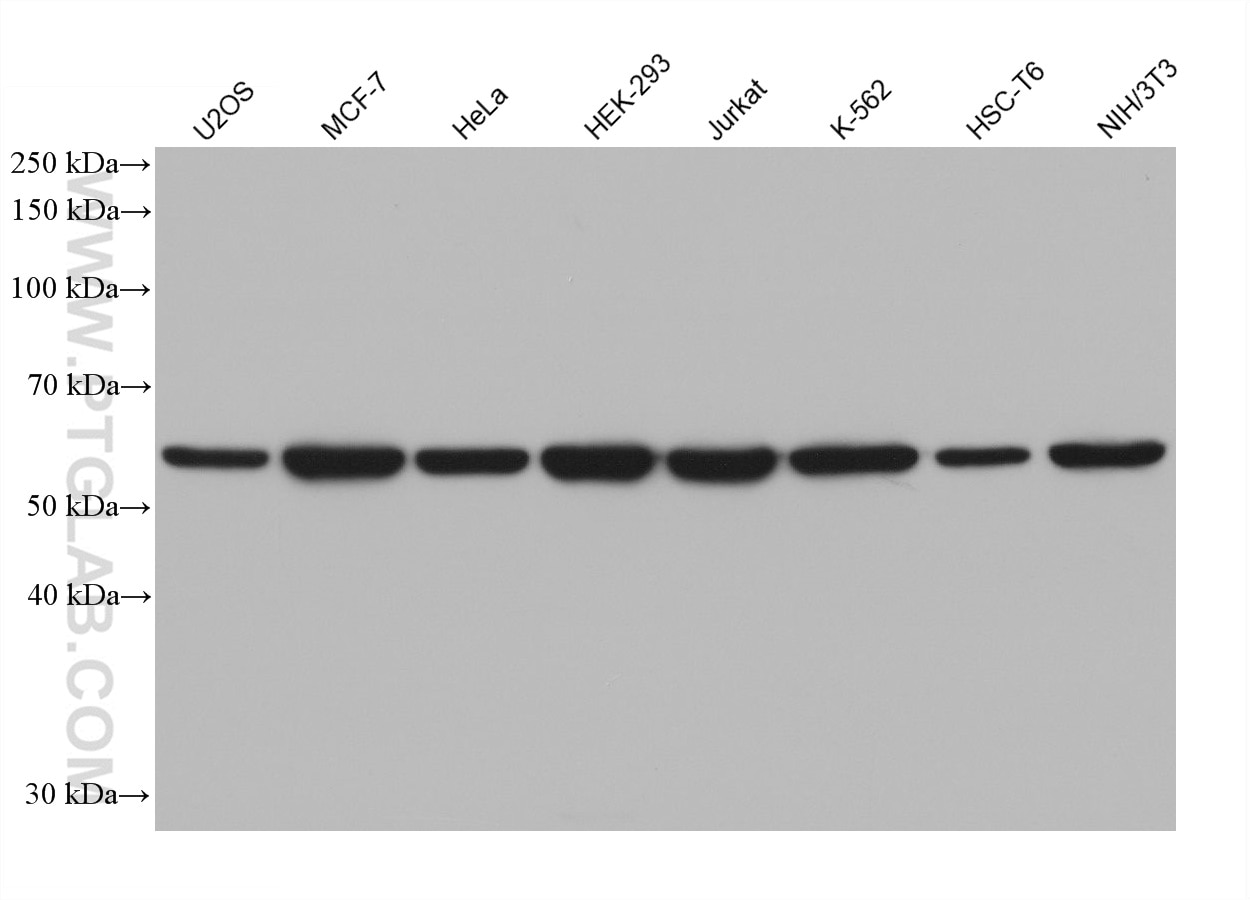
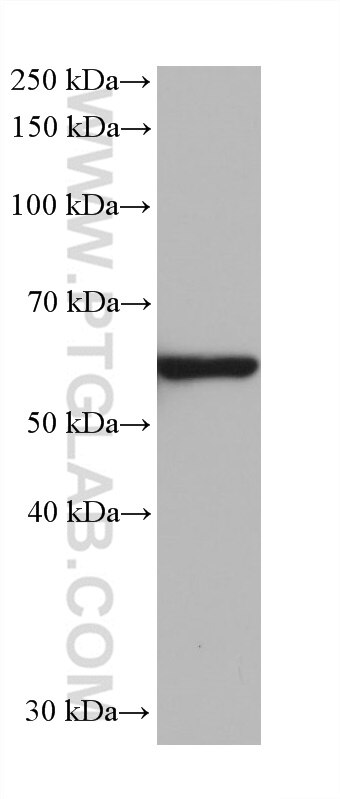
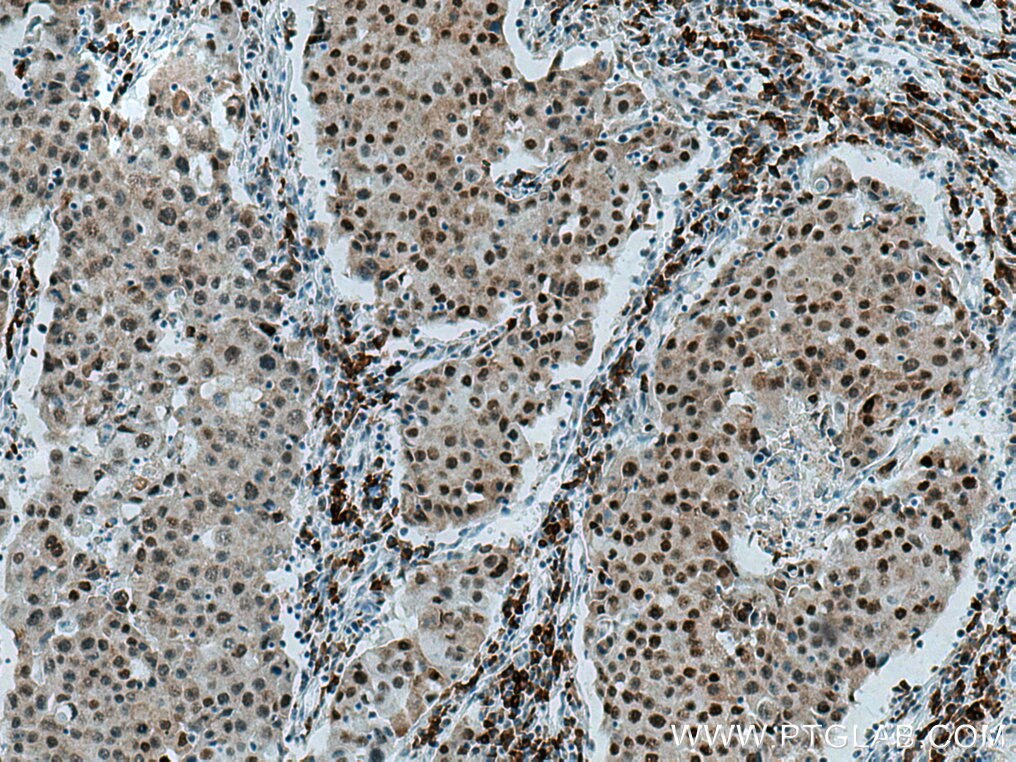
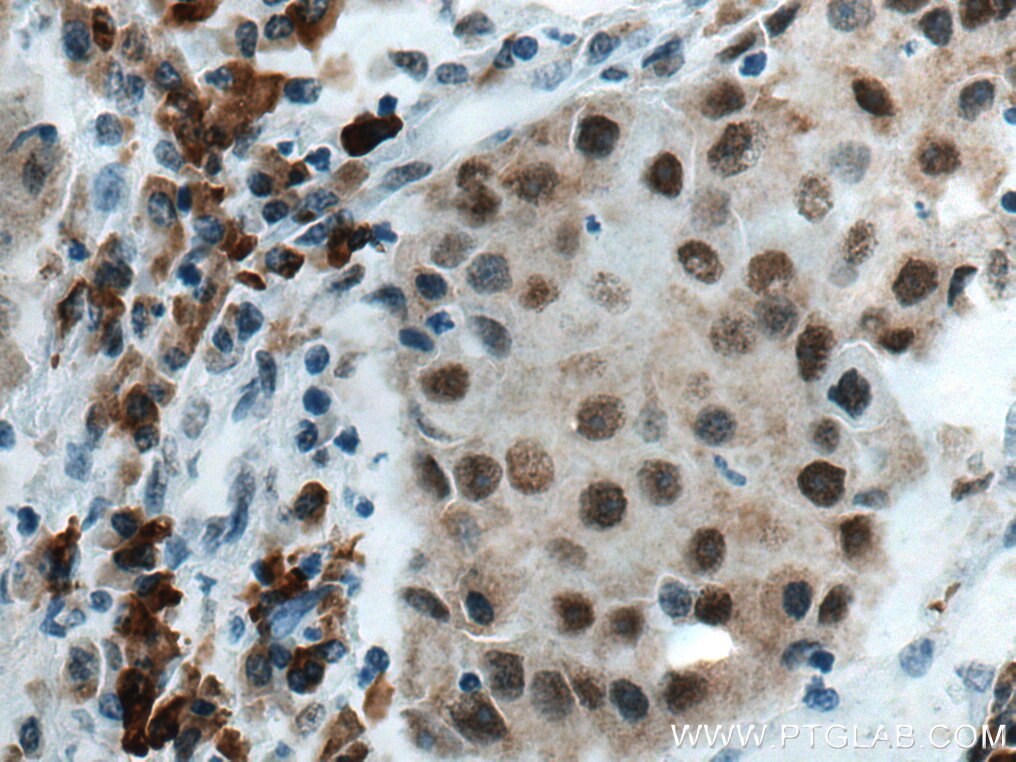
67165-1-PBS targets HDAC2 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), ELISA applications and shows reactivity with Human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | Human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag21288 Product name: Recombinant human HDAC2 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 274-571 aa of BC031055 Sequence: TDRVMTVSFHKYGEYFPGTGDLRDIGAGKGKYYAVNFPMRDGIDDESYGQIFKPIISKVMEMYQPSAVVLQCGADSLSGDRLGCFNLTVKGHAKCVEVVKTFNLPLLMLGGGGYTIRNVARCWTHETAVALDCEIPNELPYNDYFEYFGPDFKLHISPSNMTNQNTPEYMEKIKQRLFENLRMLPHAPGVQMQAIPEDAVHEDSGDEDGEDPDKRISIRASDKRIACDEEFSDSEDEGEGGRRNVADHKKGAKKARIEEDKKETEDKKTDVKEEDKSKDNSGEKTDTKGTKSEQLSNP Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | histone deacetylase 2 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 458 aa, 52 kDa; 488 aa,55 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 55 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC031055 |
| Gene Symbol | HDAC2 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3066 |
| RRID | AB_2882461 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q92769 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Histone deacetylases(HDAC) are a class of enzymes that remove the acetyl groups from the lysine residues leading to the formation of a condensed and transcriptionally silenced chromatin.Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes, and are responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues at the N-terminal regions of core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). At least 4 classes of HDAC were identified. As a class I HDAC, HDAC2 was primarily found in the nucleus. HDAC2 forms transcriptional repressor complexes by associating with many different proteins, including YY1, a mammalian zinc-finger transcription factor. Thus, it plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. This antibody is raised against residues near the C terminus of human HDAC2.