Recombinant Human ALK protein (rFc Tag)
Species
Human
Purity
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
rFc Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg3796
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human ALK protein Val19-Ser1038 (Accession# Q9UM73) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 238 |
| Accession | Q9UM73 |
| PredictedSize | 136.6 kDa |
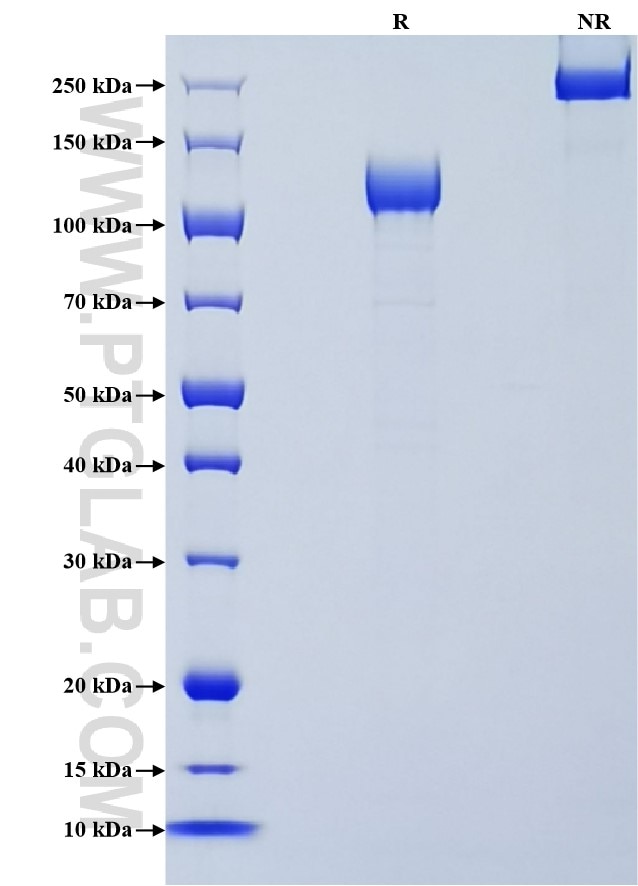
| SDS-PAGE | 125-135 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
ALK, also named as CD246, is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) that belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. ALK is usually found in the nervous system and appears to play an important role in the normal development and function of the nervous system. ALK was originally identified as part of the NPM (Nucleophosmin)-ALK oncogenic fusion protein, resulting from the (2;5)(p23;q35) translocation that is frequently associated with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL). The EML4 (echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4)-ALK fusion protein have been described in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), this transforming fusion kinase is a promising candidate for a therapeutic target as well as for a diagnostic molecular marker in NSCLC. The expression of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK, CD246) has been documented in most uIMTs.
References:
1. Soda M.et al. (2007). Nature. 448(7153):561-6. 2. Parra-Herran C. (2021). Int J Gynecol Pathol. 40(1):28-31.