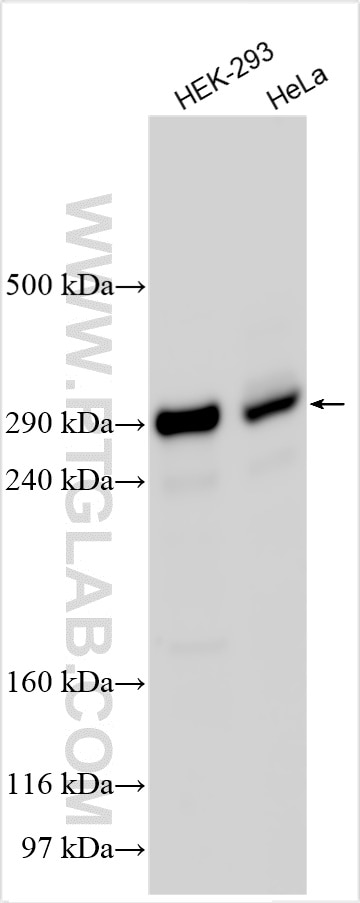
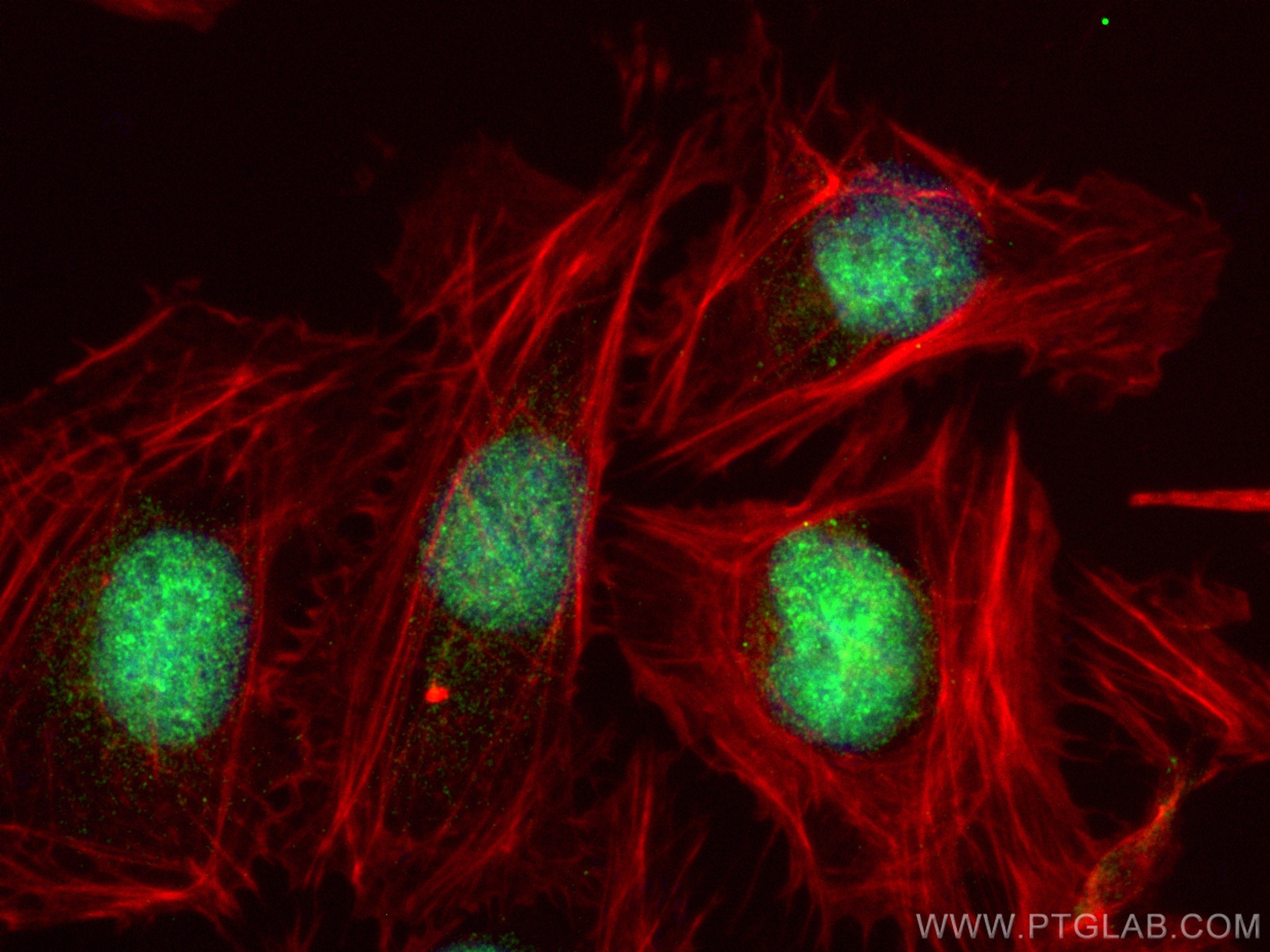
Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | HEK-293 cells, HeLa cells |
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | U2OS cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:8000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
28695-1-AP targets KNL1 in WB, IF/ICC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag29881 Product name: Recombinant human KNL1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 1746-1896 aa of NM_170589 Sequence: PDEINSSDSINIETEEKALIETYQKEISPYENKMGKTCNSQKRTWVQEEEDIHKEKKIRKNEIKFSDTTQDREIFDHHTEEDIDKSANSVLIKNLSRTPSSCSSSLDSIKADGTSLDFSTYRSSQMESQFLRDTICEESLREKLQDGRITI Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | cancer susceptibility candidate 5 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 265 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 300 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | NM_170589 |
| Gene Symbol | CASC5/KNL1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 57082 |
| RRID | AB_3086079 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q8NG31 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
KNL1 is a component of the multiprotein assembly that is required for creation of kinetochore-microtubule attachments and chromosome segregation. KNL1 functions as a scaffold for proteins that influence the spindle assembly checkpoint during the eukaryotic cell cycle and it interacts with at least five different kinetochore proteins and two checkpoint kinases. In adults, this gene is predominantly expressed in normal testes, various cancer cell lines and primary tumors from other tissues and is ubiquitously expressed in fetal tissues.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for KNL1 antibody 28695-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for KNL1 antibody 28695-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |