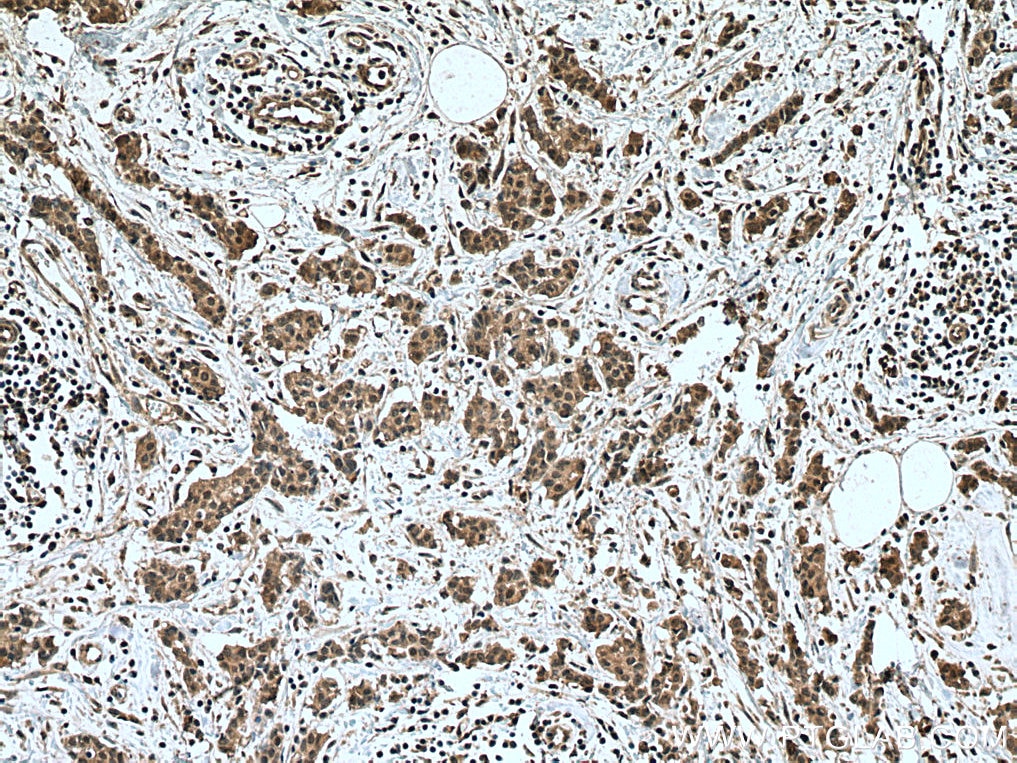
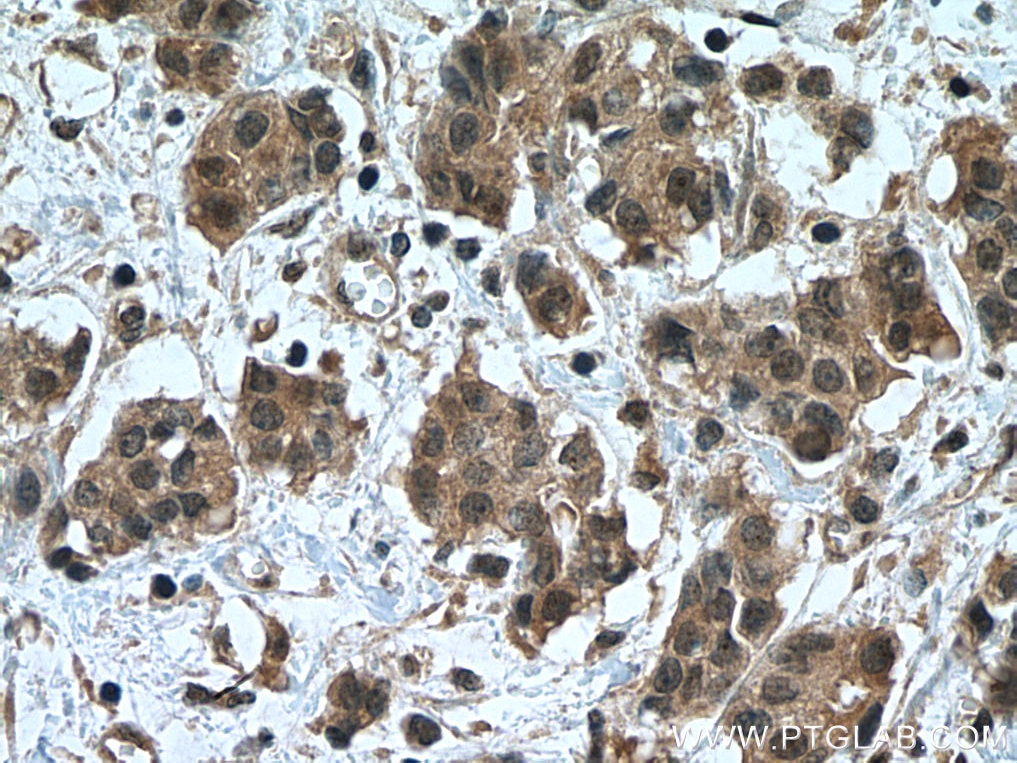
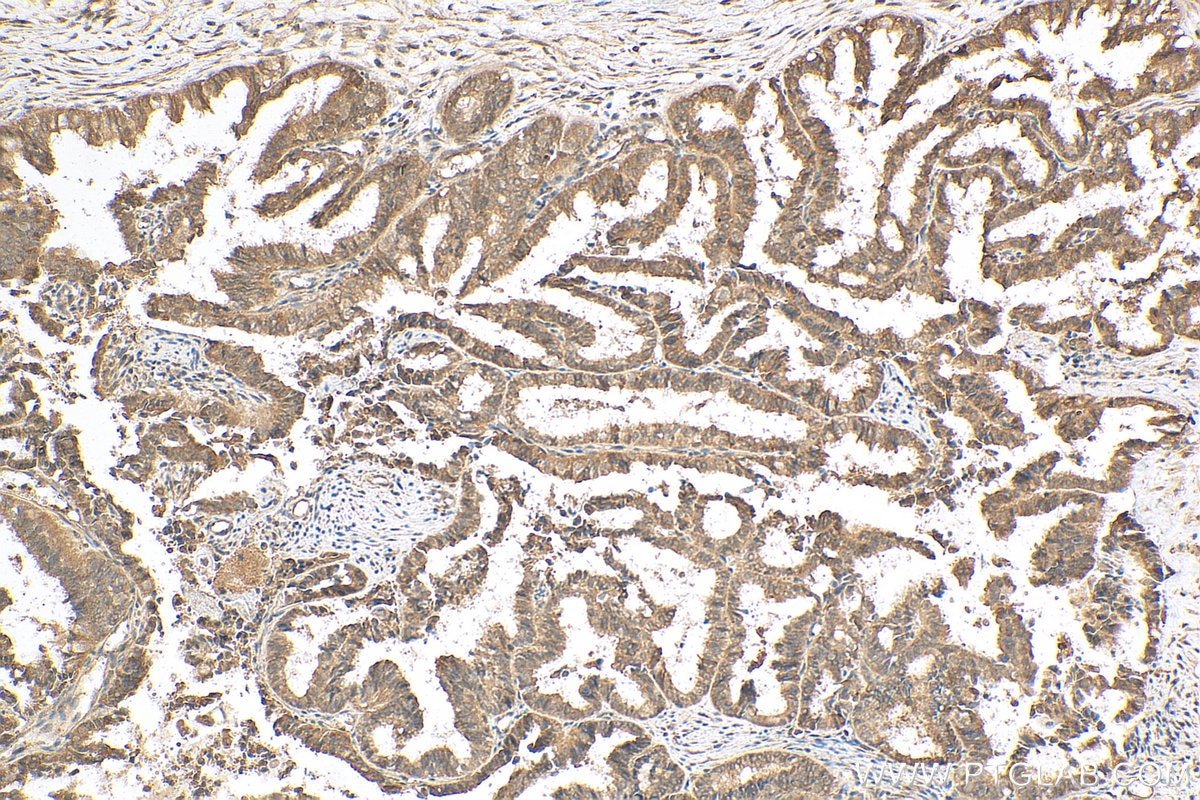
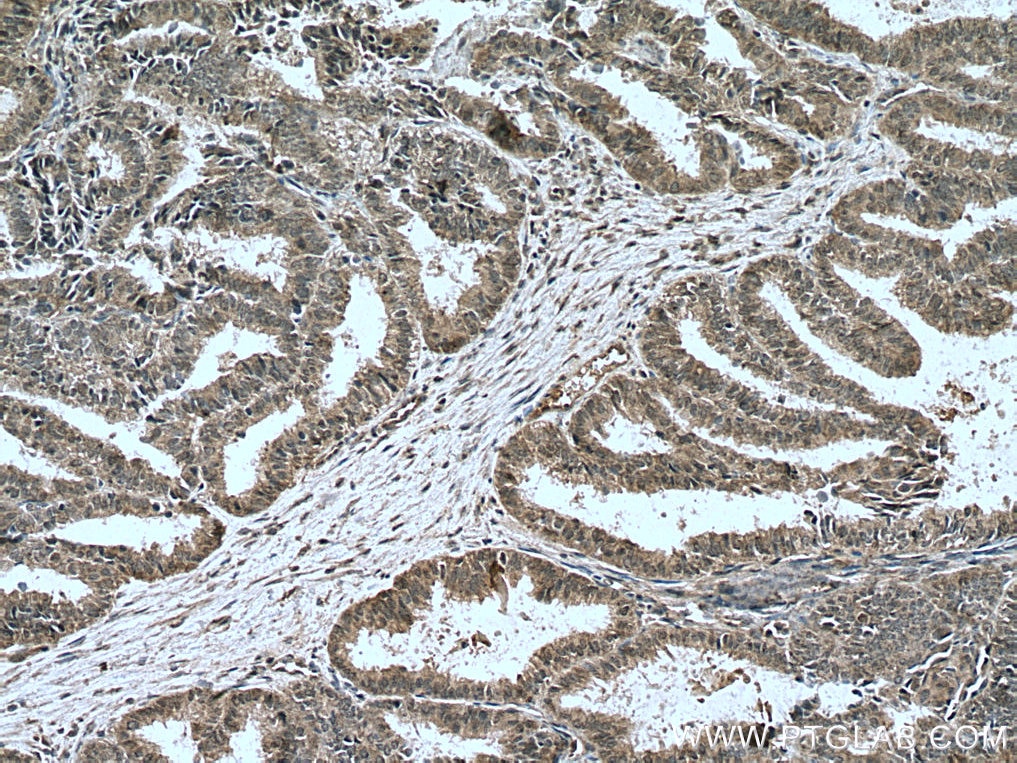
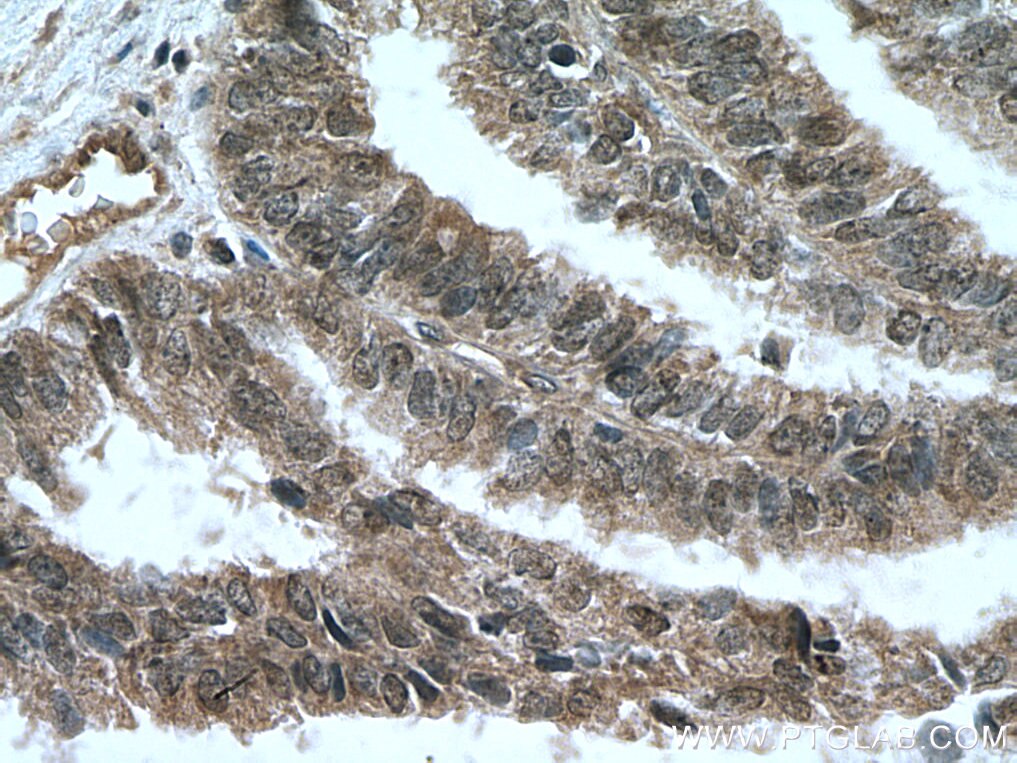
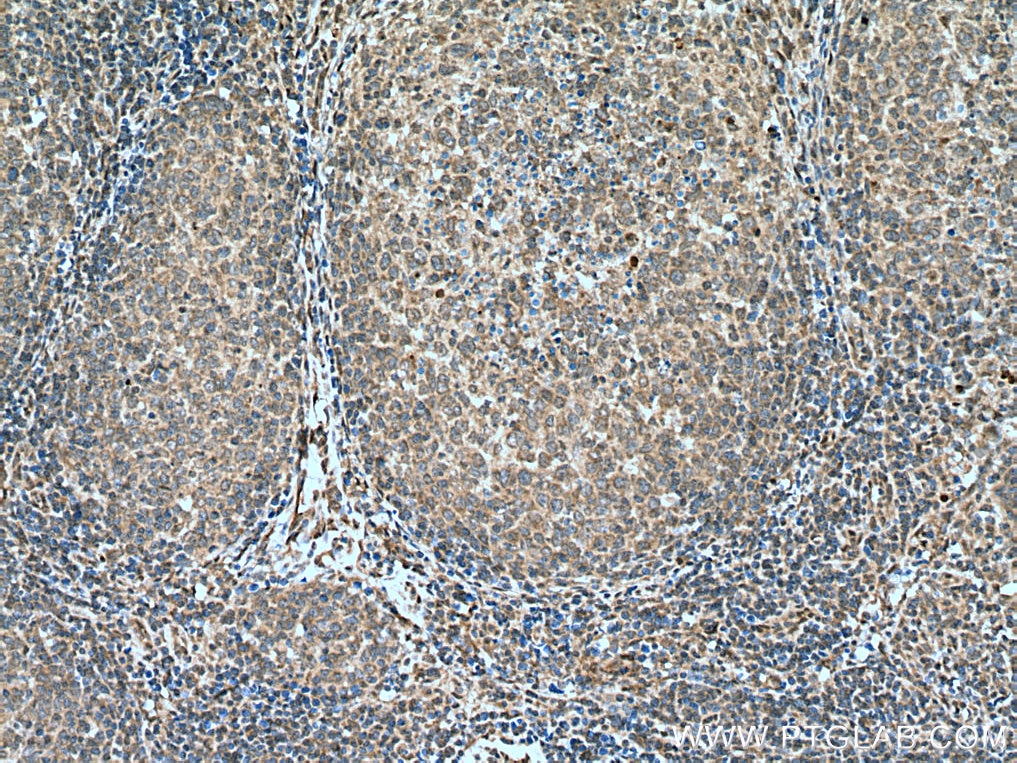
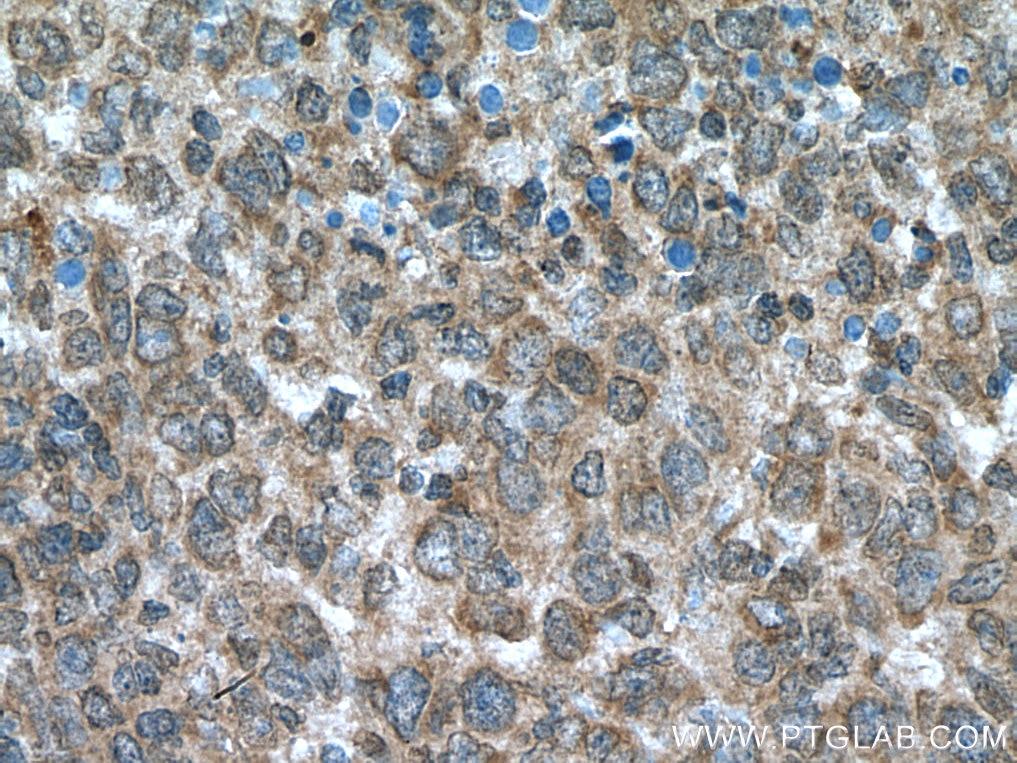
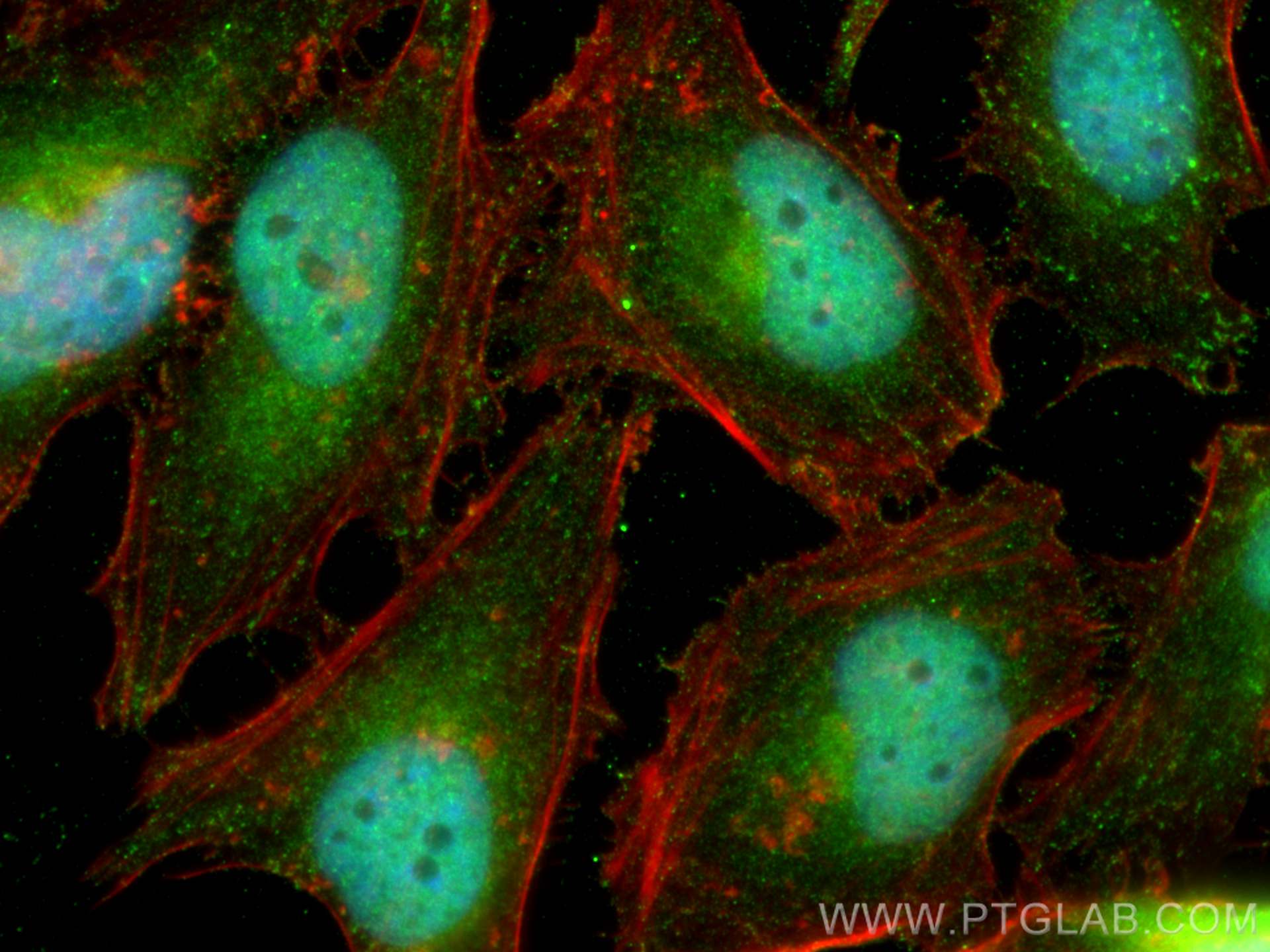
Product Information
20687-1-PBS targets NOTCH1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
Peptide Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | Notch homolog 1, translocation-associated (Drosophila) |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 273 kDa |
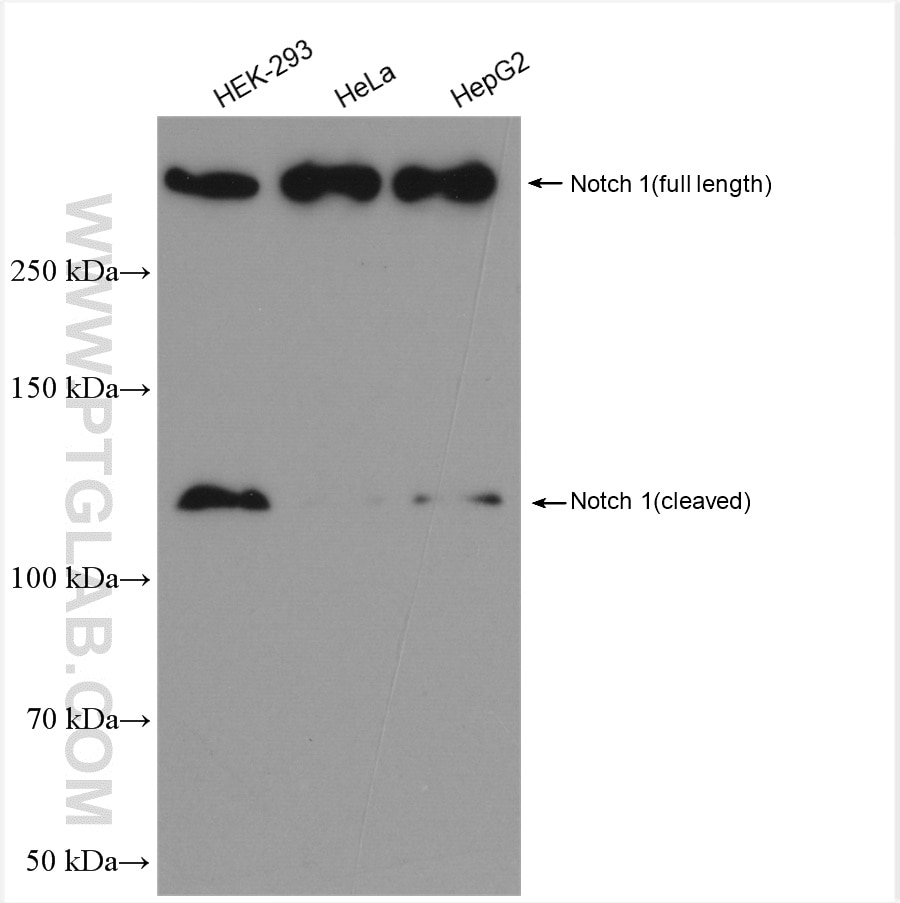
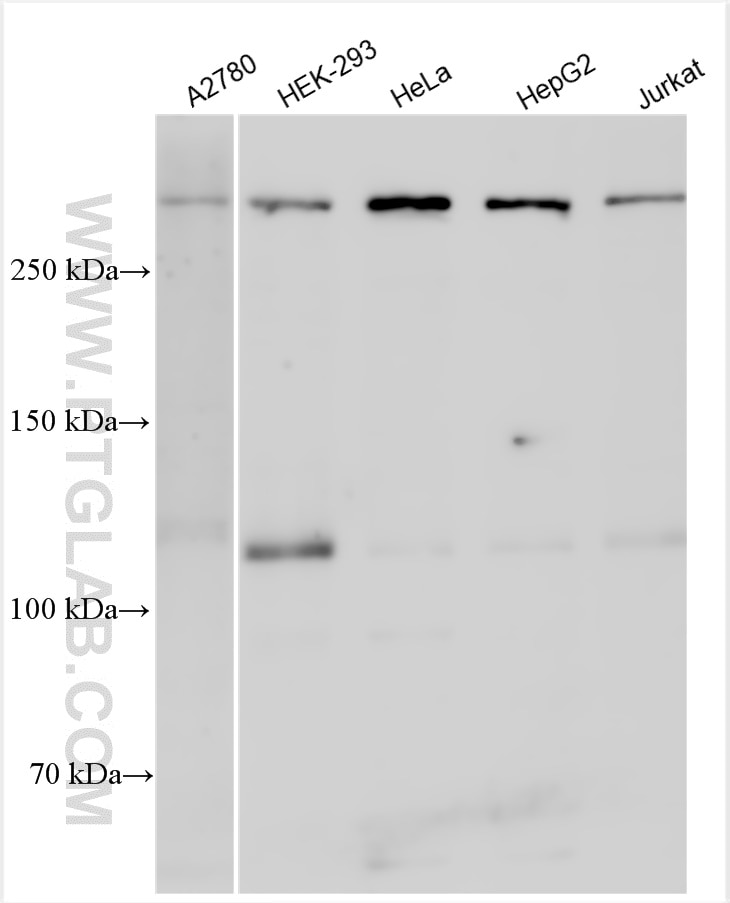
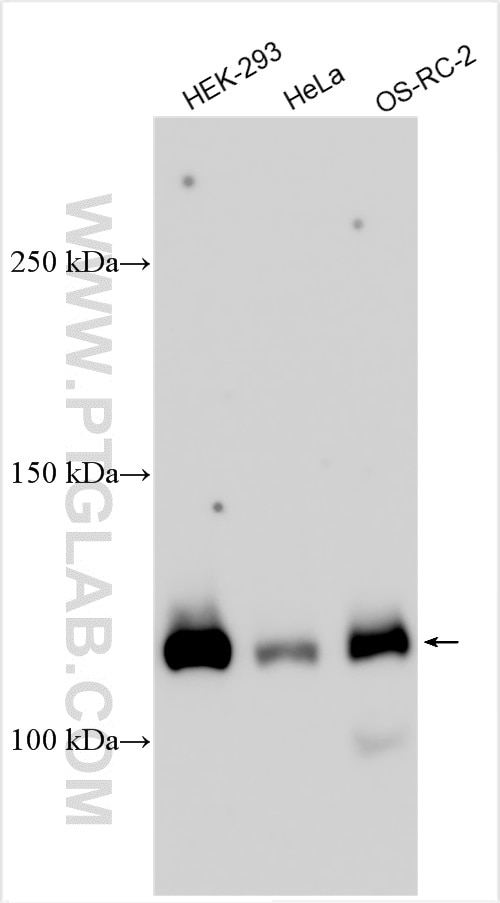
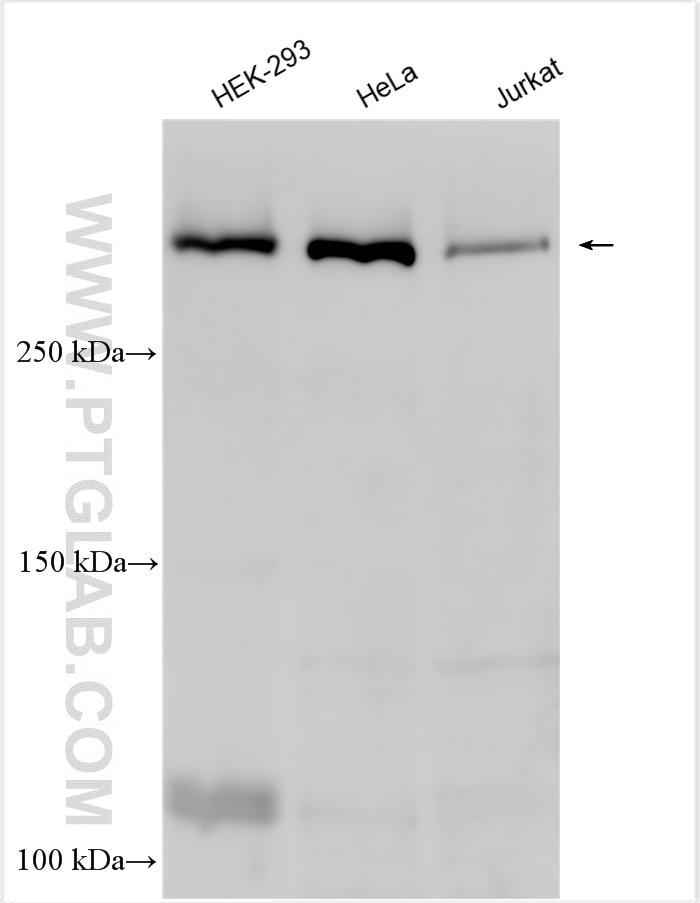
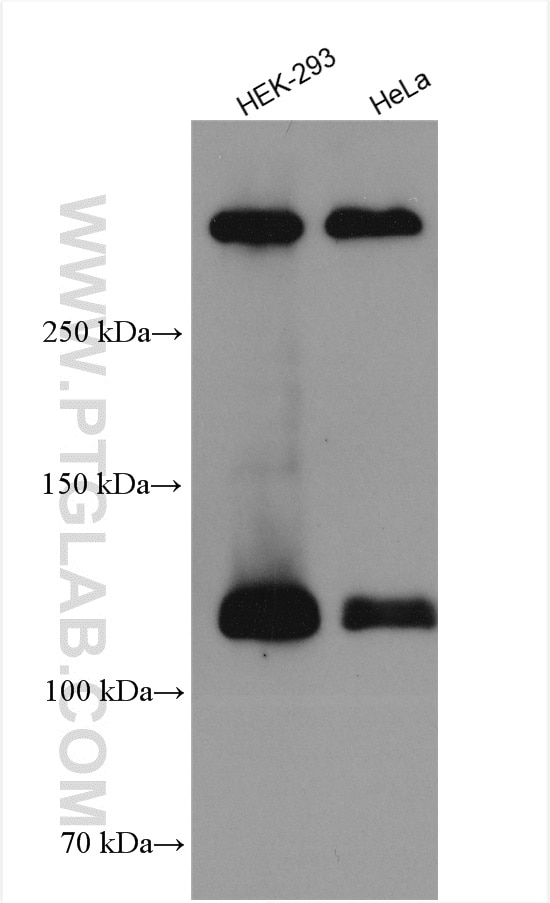
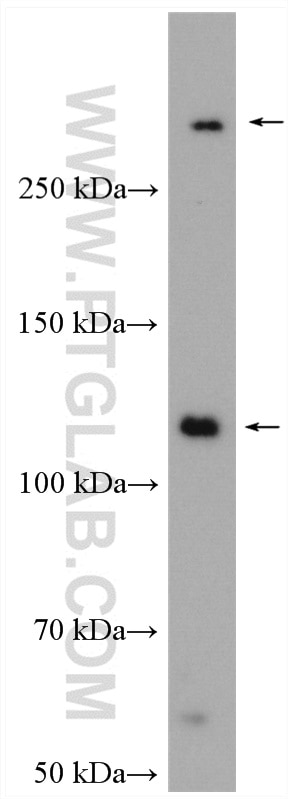
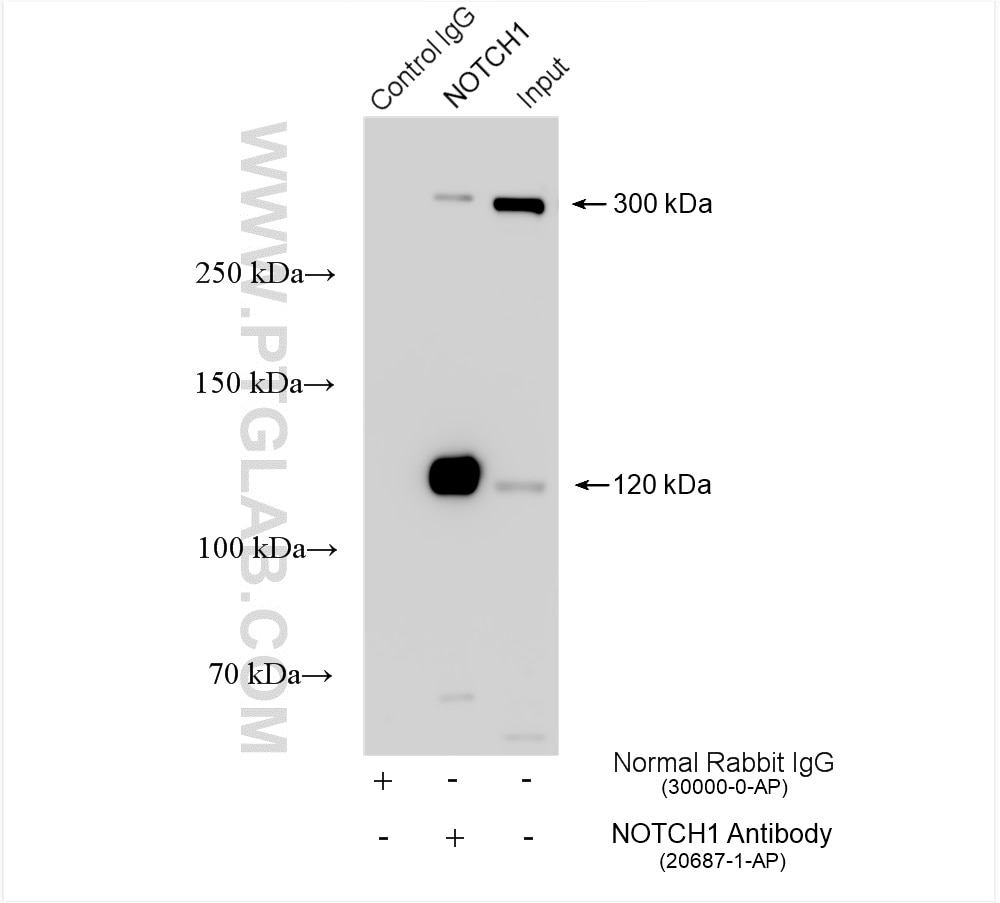
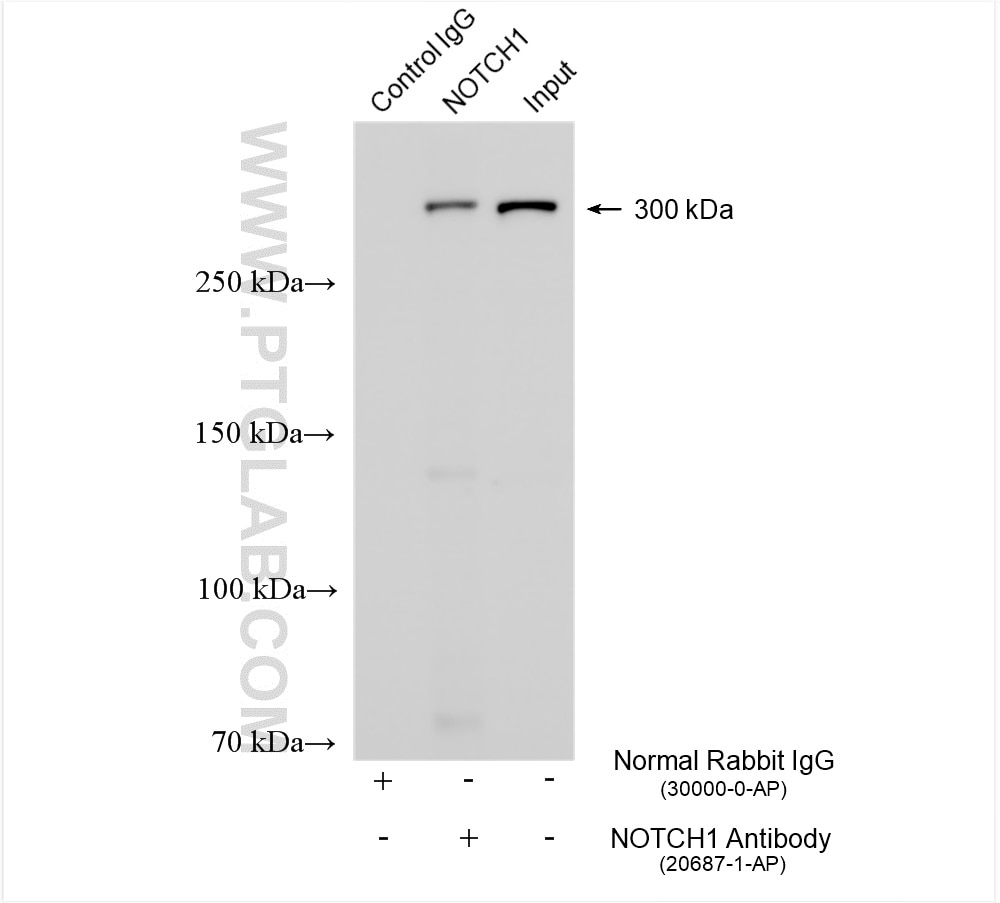
| Observed Molecular Weight | 273-300 kDa, 120 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | NM_017617 |
| Gene Symbol | NOTCH1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4851 |
| RRID | AB_10700012 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P46531 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
NOTCH1, also named as TAN1, belongs to the NOTCH family. NOTCH1 functions as a receptor for membrane-bound ligands Jagged1, Jagged2 and Delta1 to regulate cell-fate determination. Upon ligand activation through the released notch intracellular domain (NICD) it forms a transcriptional activator complex with RBP-J kappa and activates genes of the enhancer of split locus. NOTCH1 affects the implementation of differentiation, proliferation and apoptotic programs. It may be important for normal lymphocyte function. In altered form, may contribute to transformation or progression in some T-cell neoplasms. NOTCH1 is involved in the maturation of both CD4+ and CD8+ cells in the thymus. May be important for follicular differentiation and possibly cell fate selection within the follicle. During cerebellar development, may function as a receptor for neuronal DNER and may be involved in the differentiation of Bergmann glia. Defects in NOTCH1 are a cause of bicuspid aortic valve (BAV).
Notch is synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum as an inactive form which is proteolytically cleaved by a furin-like convertase (S1 cleavage) in the trans-golgi network before it reaches the plasma membrane to yield an active, ligand-accessible form. Cleavage results in a C-terminal fragment N(TM) and a N-terminal fragment N(EC). Following ligand binding, it is cleaved (S2 cleavage) by TNF-alpha converting enzyme (TACE) to yield a membrane-associated intermediate fragment called Notch extracellular truncation (NEXT). This fragment is then cleaved by presenilin-dependent gamma-secretase (S3 cleavage) to release the intracellular domain (NICD) from the membrane. The antibody is specific to NOTCH1. It can recognize the full length NOTCH1(270 kDa) and cleaved NOTCH1 form (120 kDa).