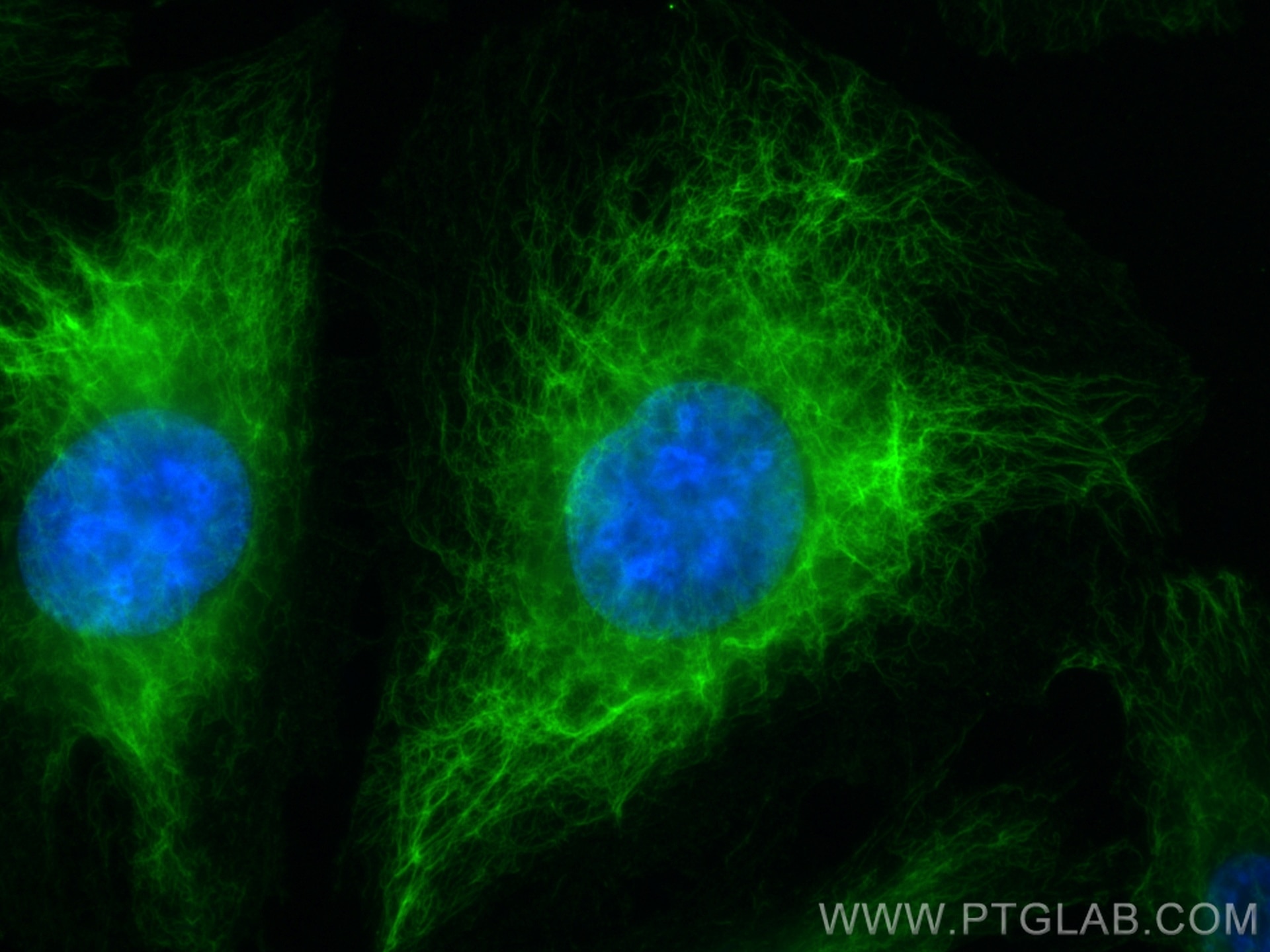
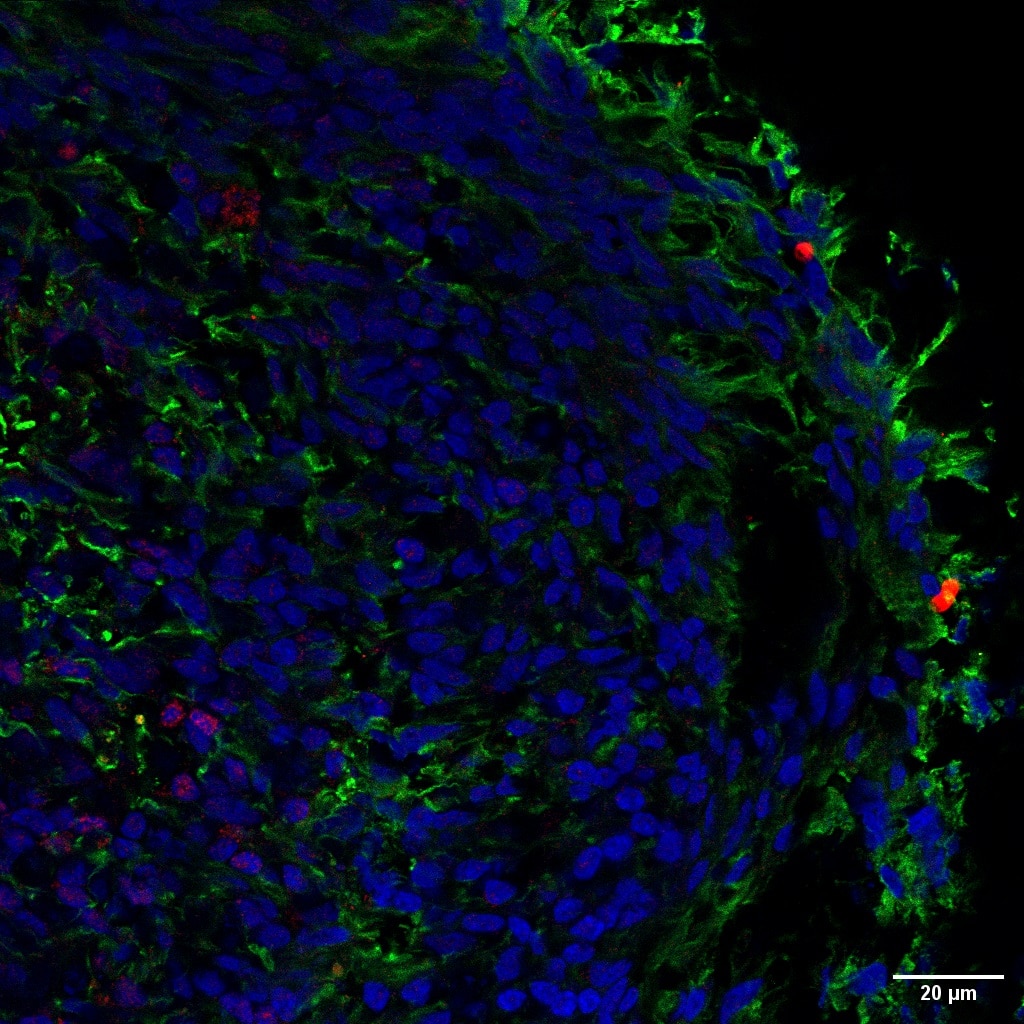
Tested Applications
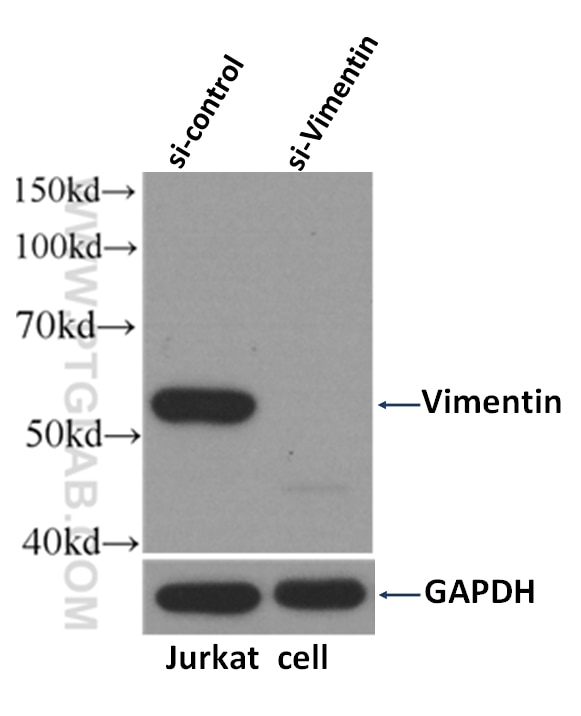
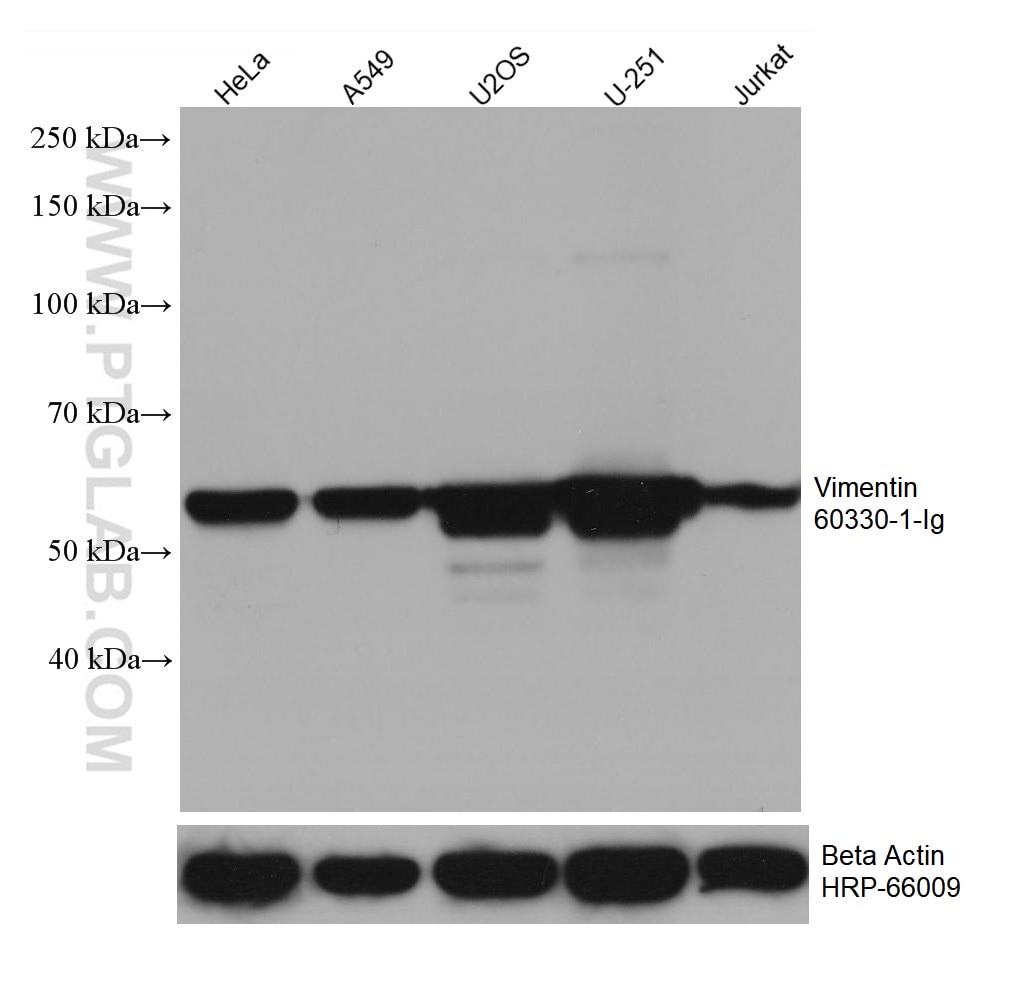
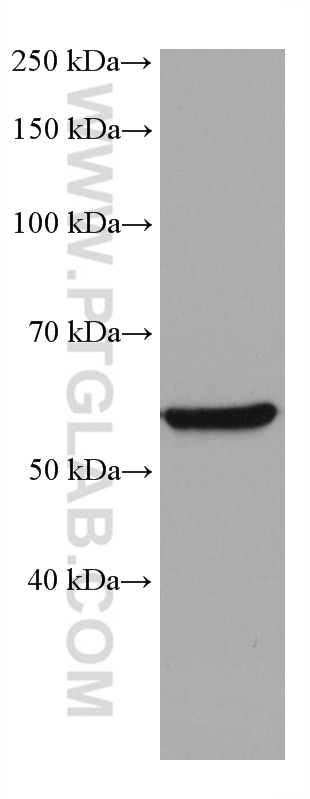
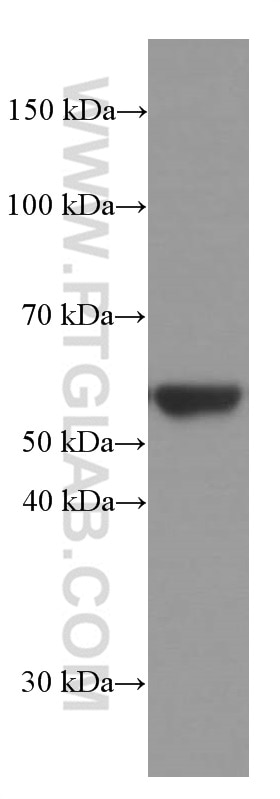
| Positive WB detected in | HeLa cells, NIH/3T3 cells, ROS1728 cells, Jurkat cells, A549 cells, U2OS cells, U-251 cells |
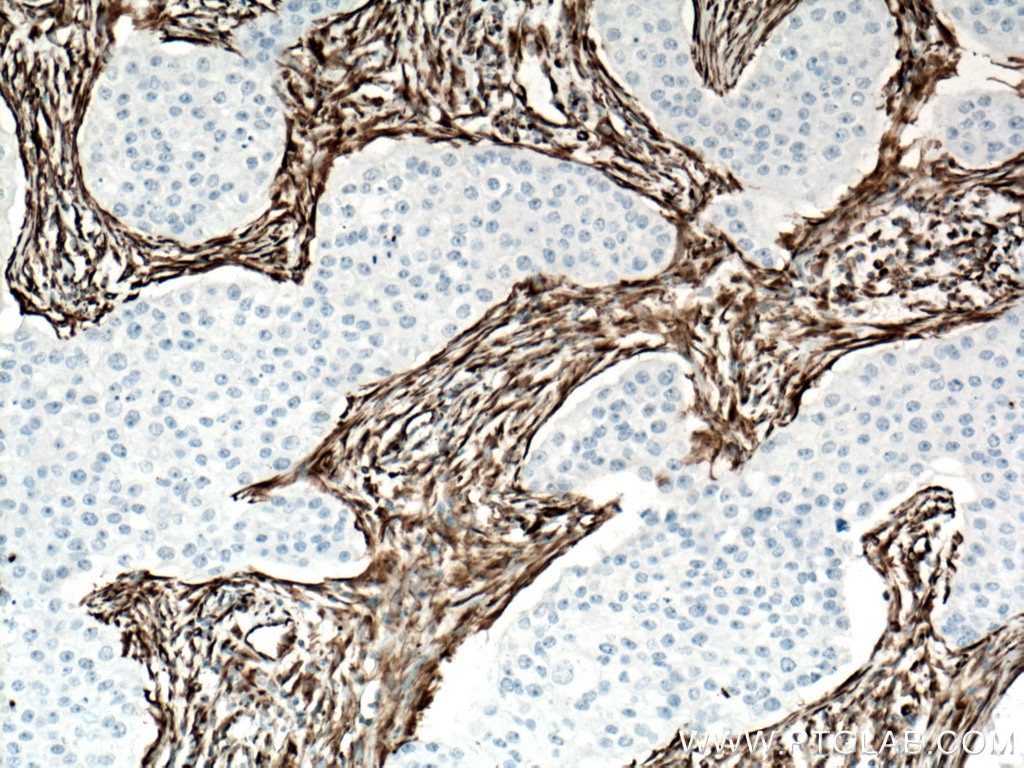
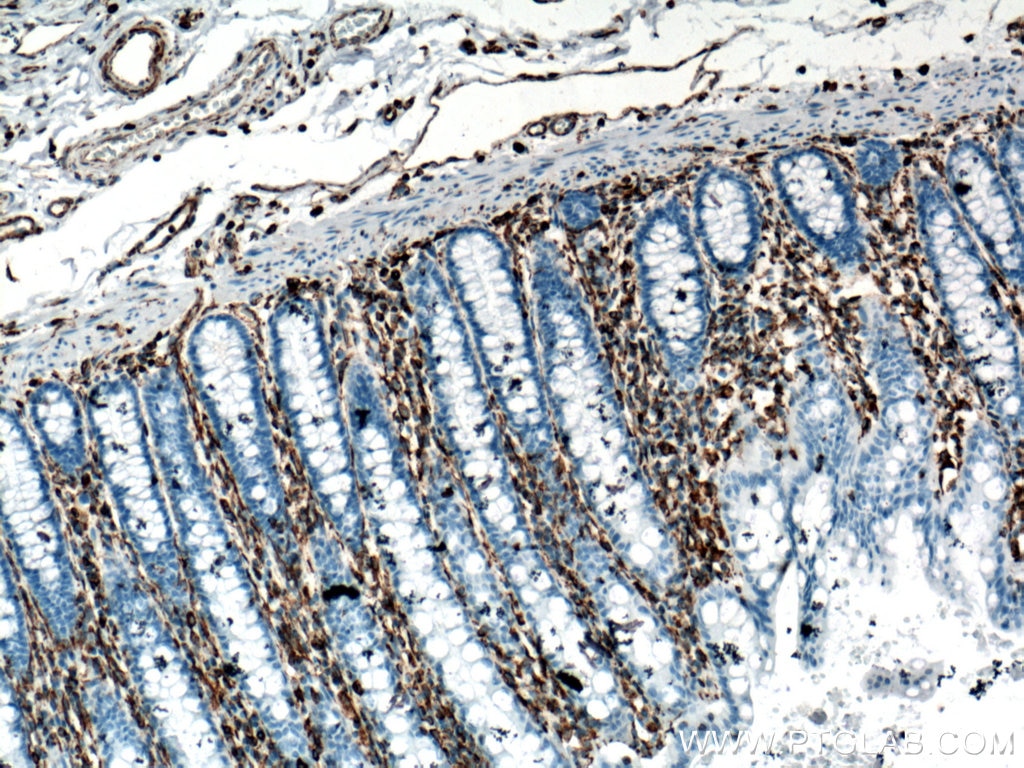
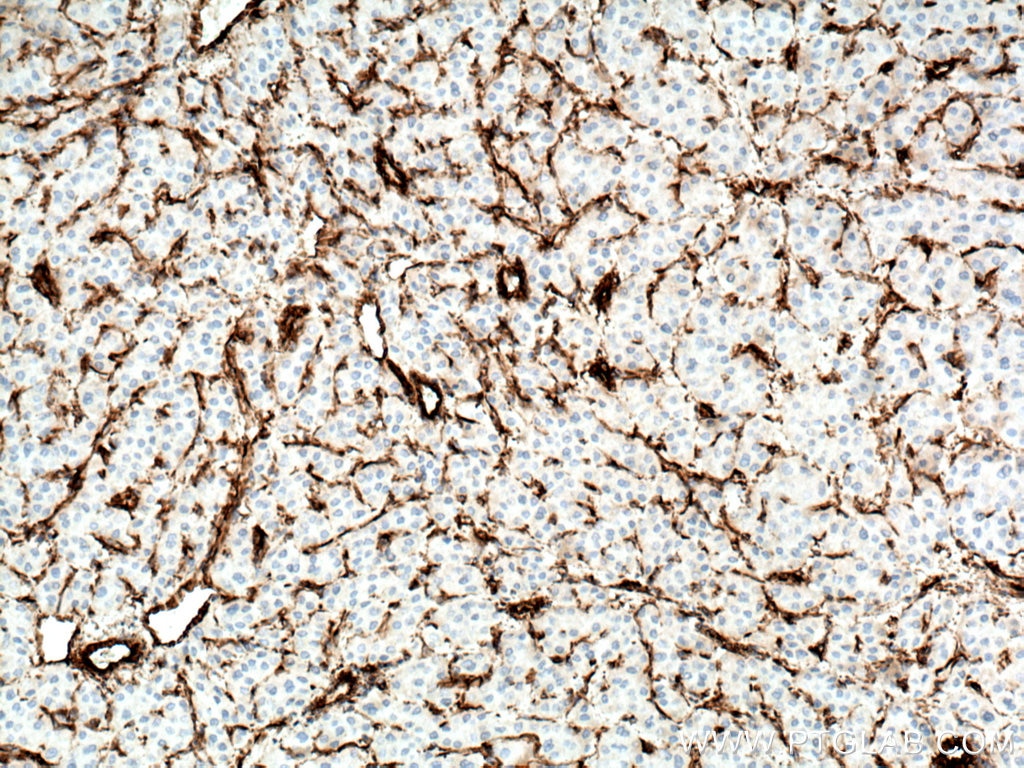
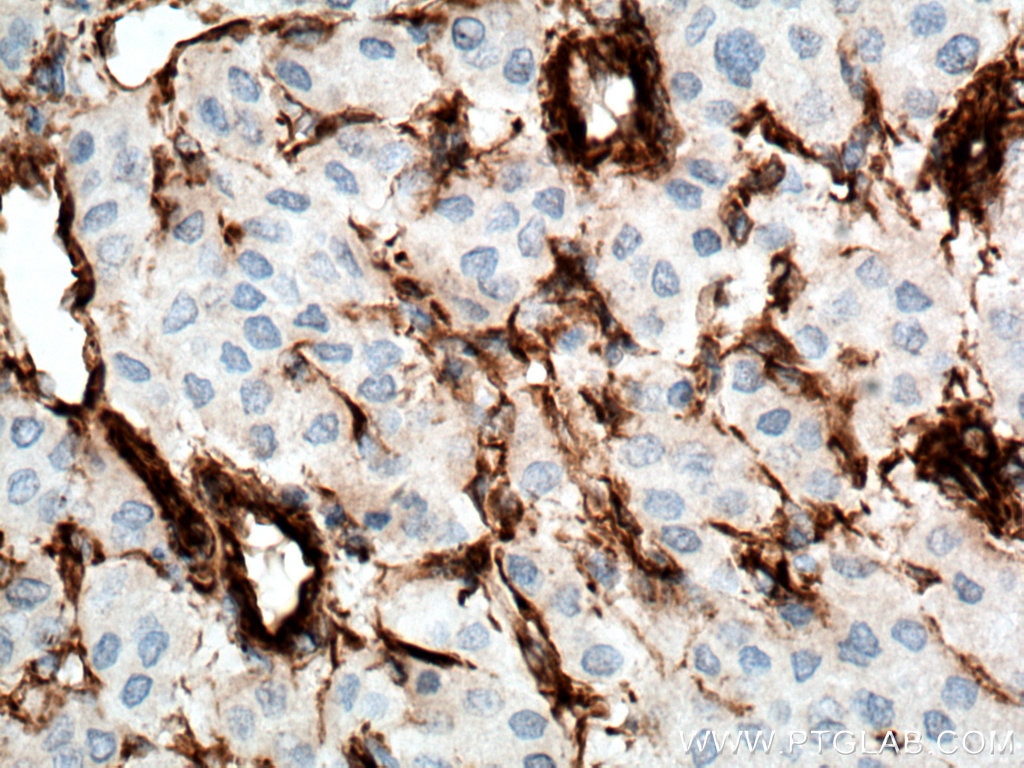
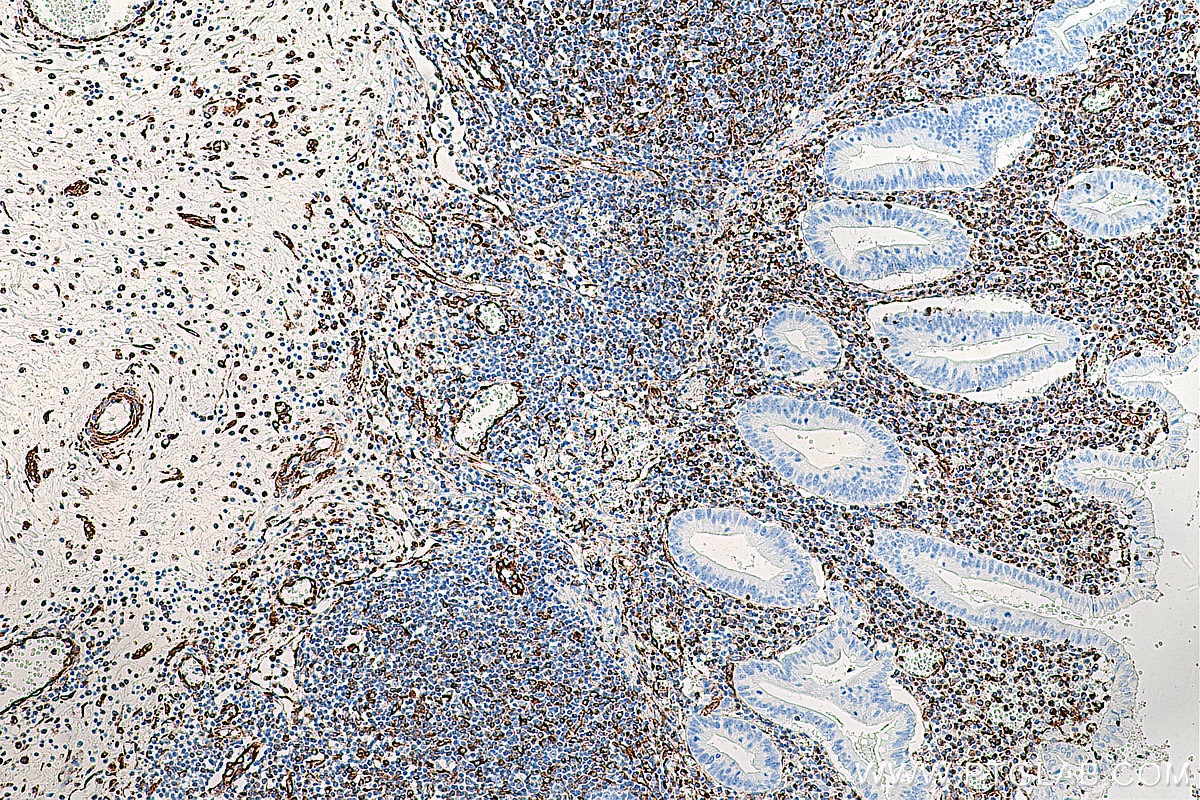
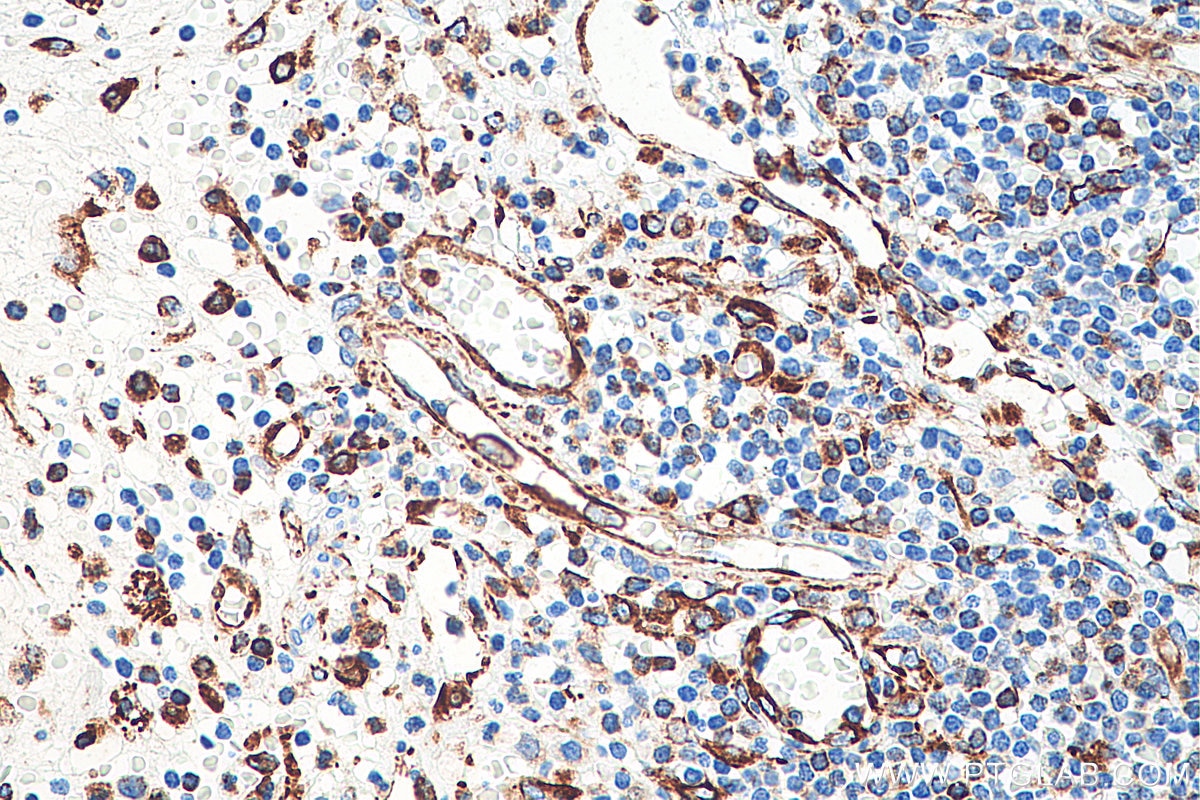
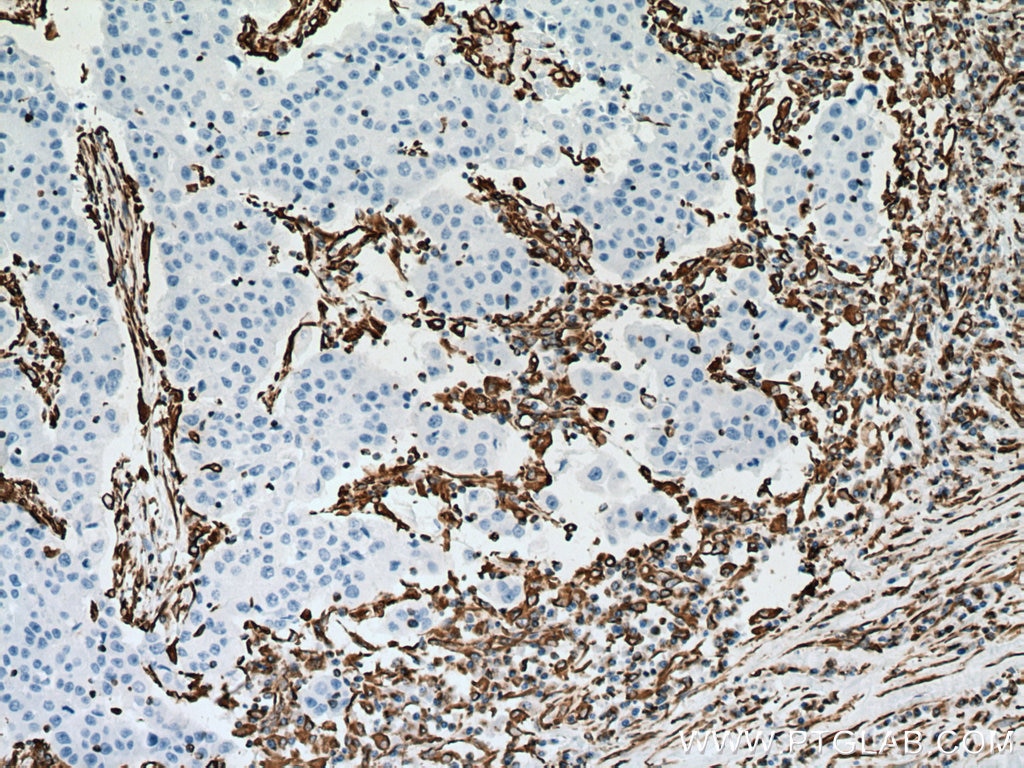
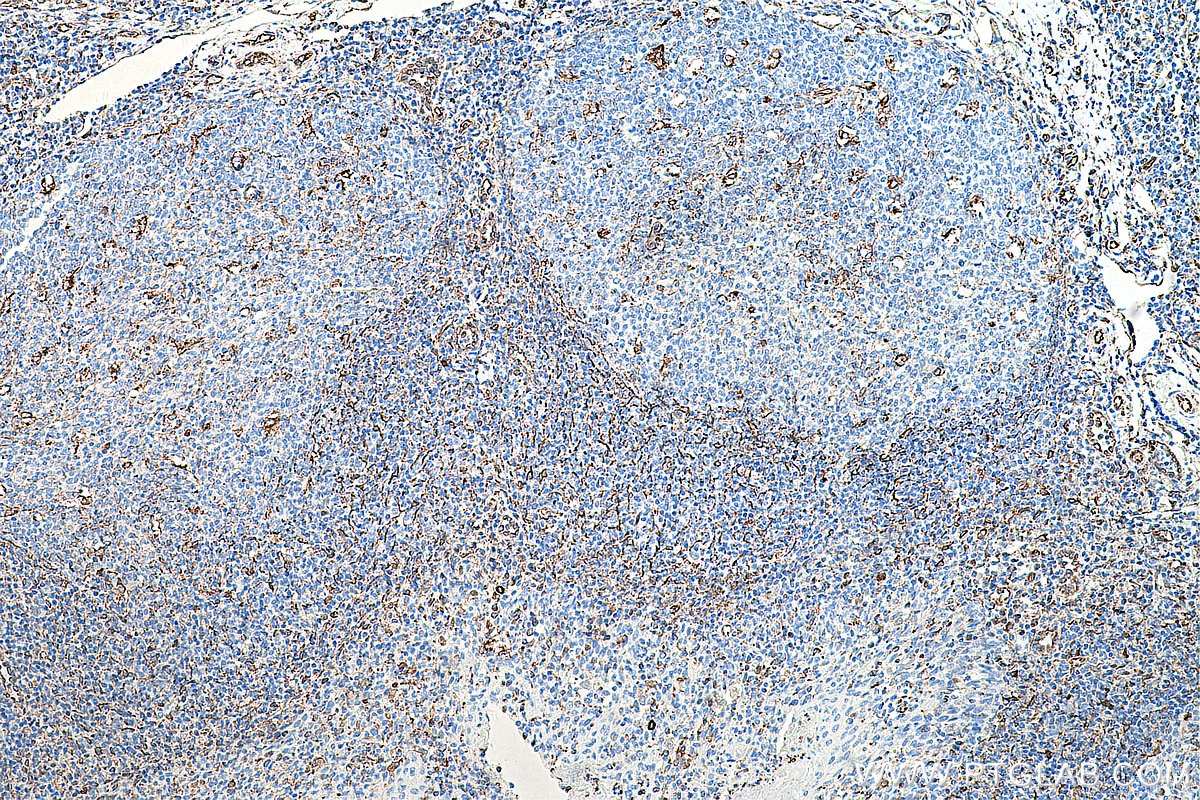
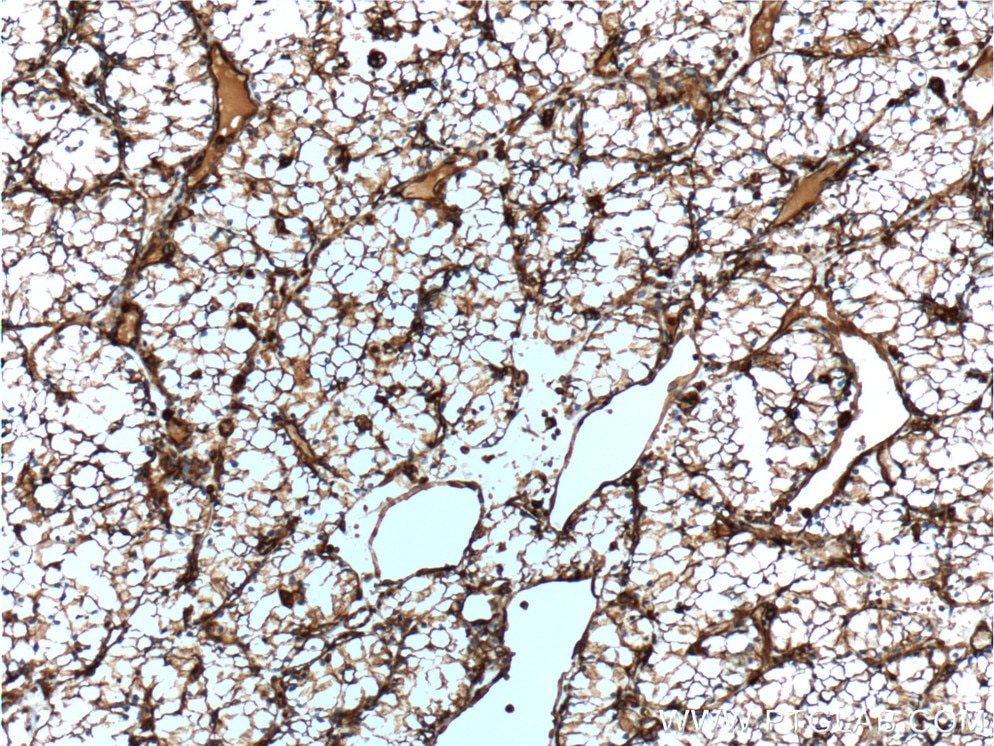
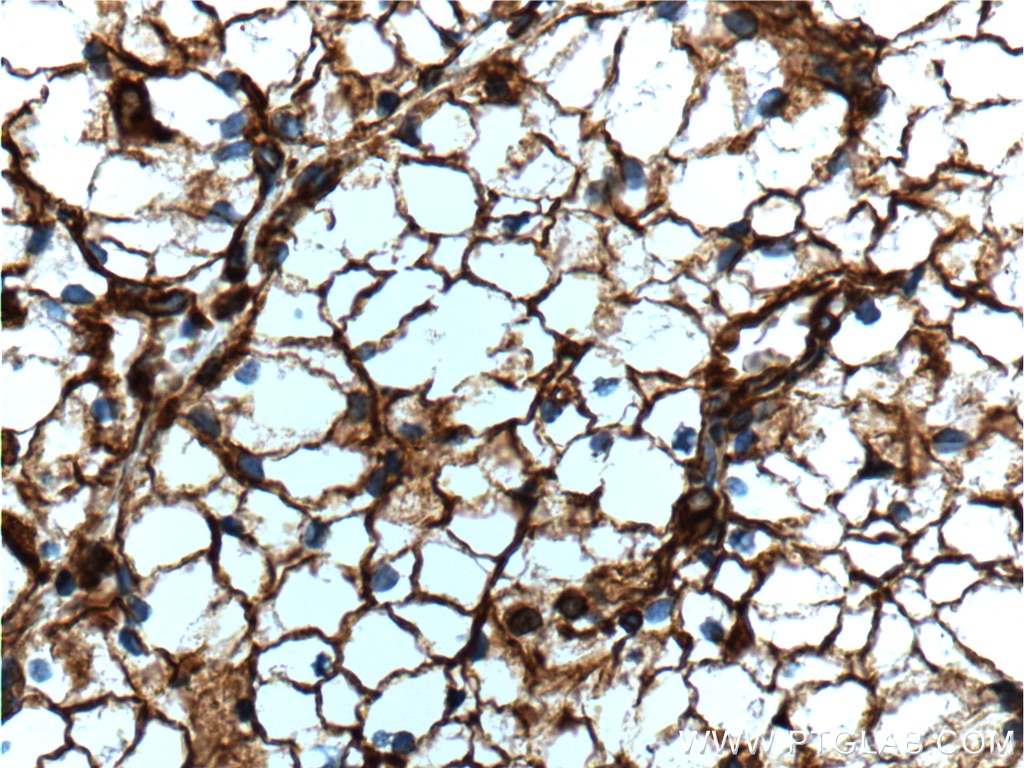
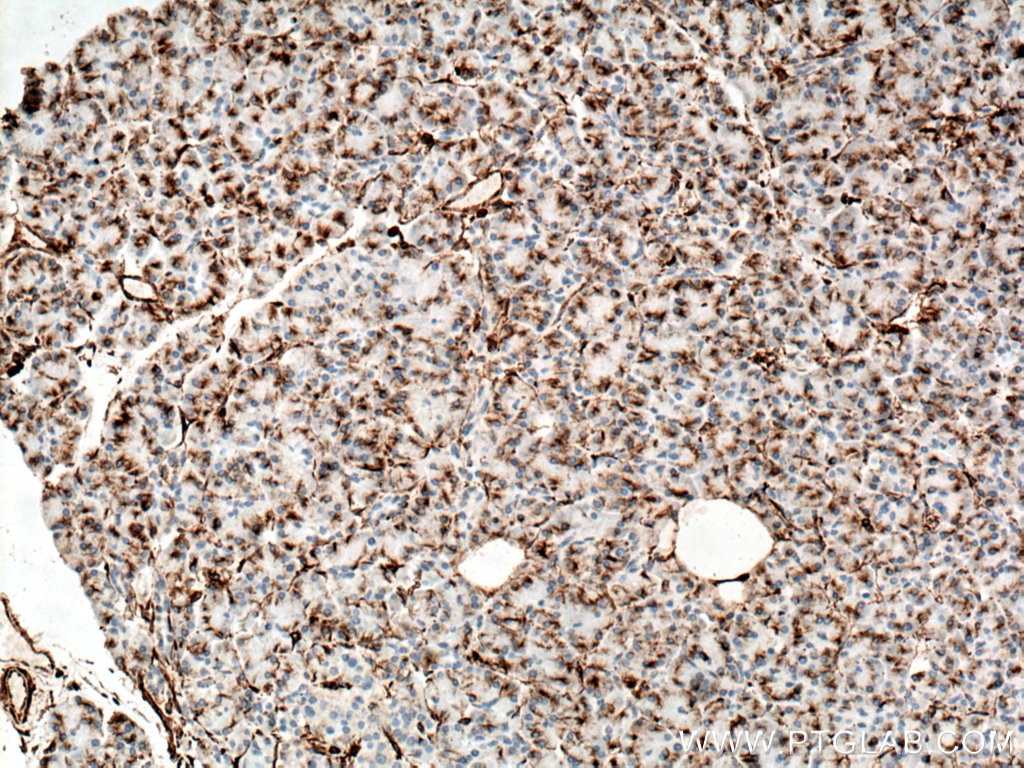
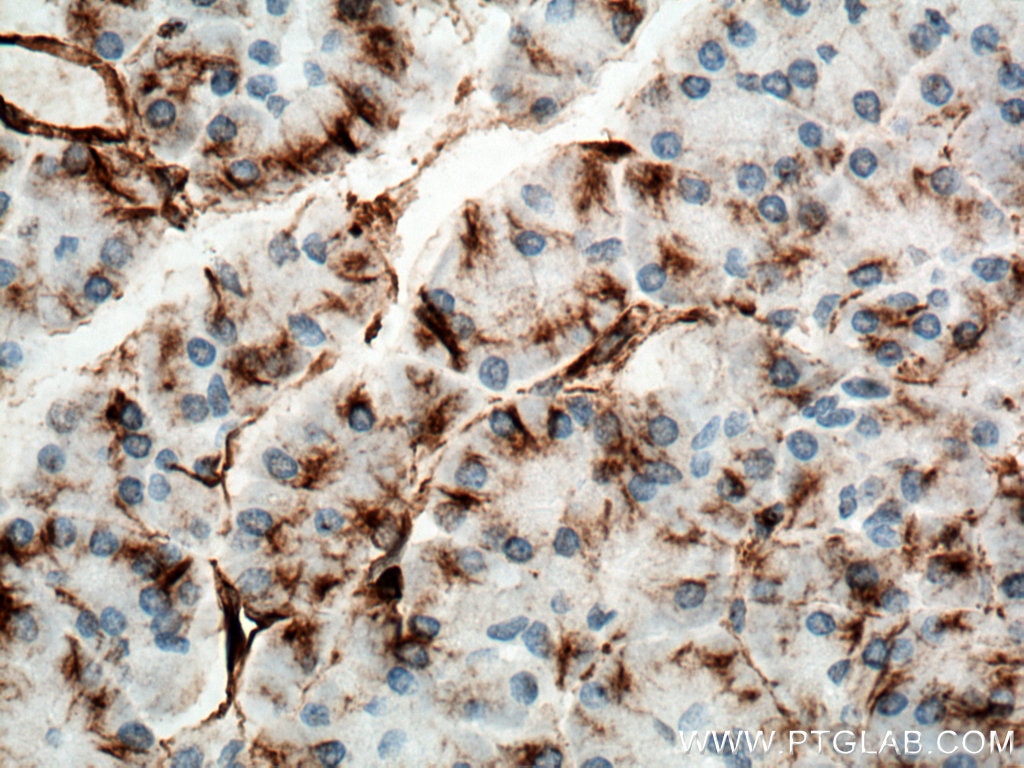
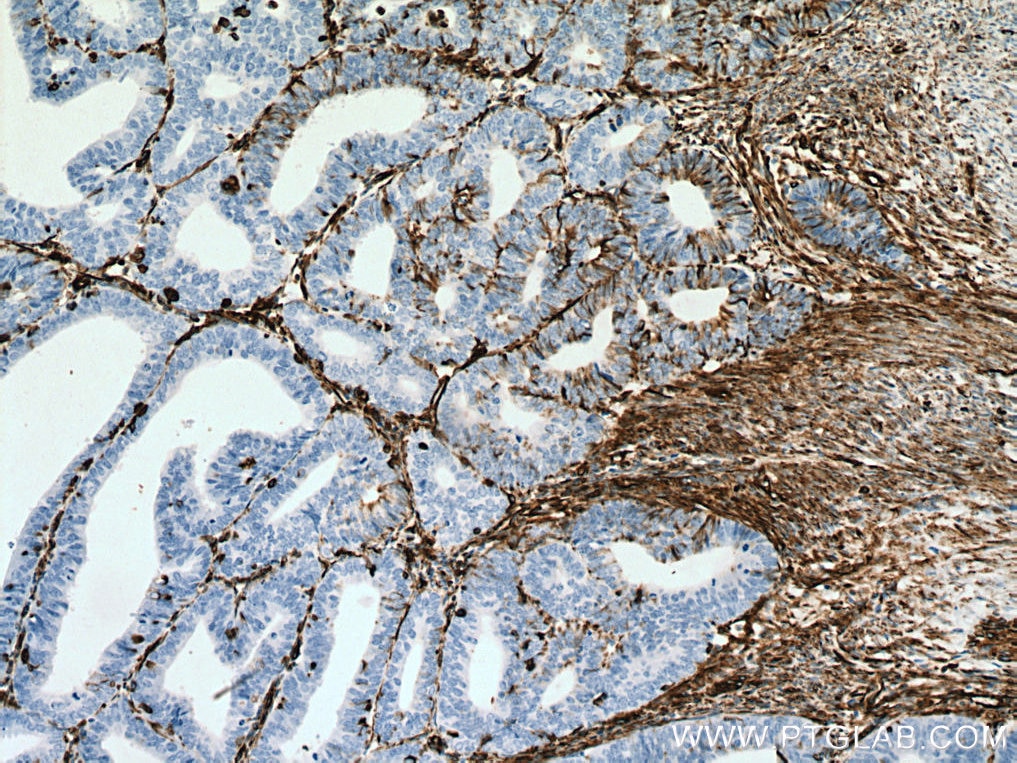
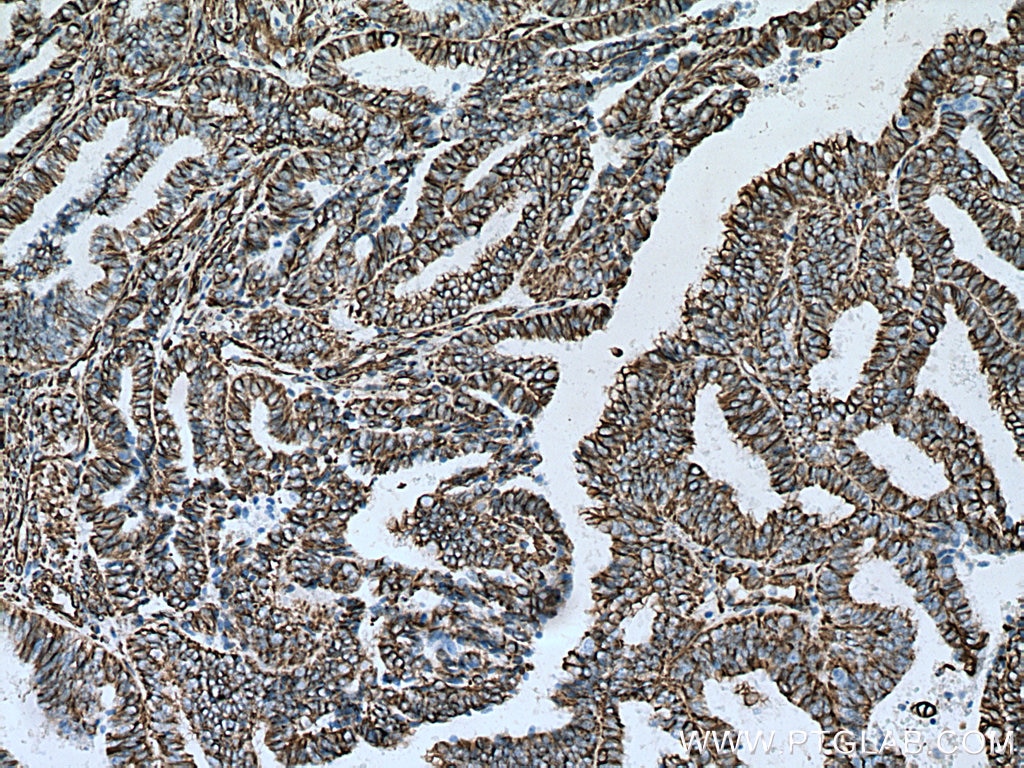
| Positive IHC detected in | human appendicitis tissue, human breast cancer tissue, human colon tissue, human endometrial cancer tissue, human liver cancer tissue, human ovary tumor tissue, human pancreas tissue, human renal cell carcinoma tissue, human tonsillitis tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
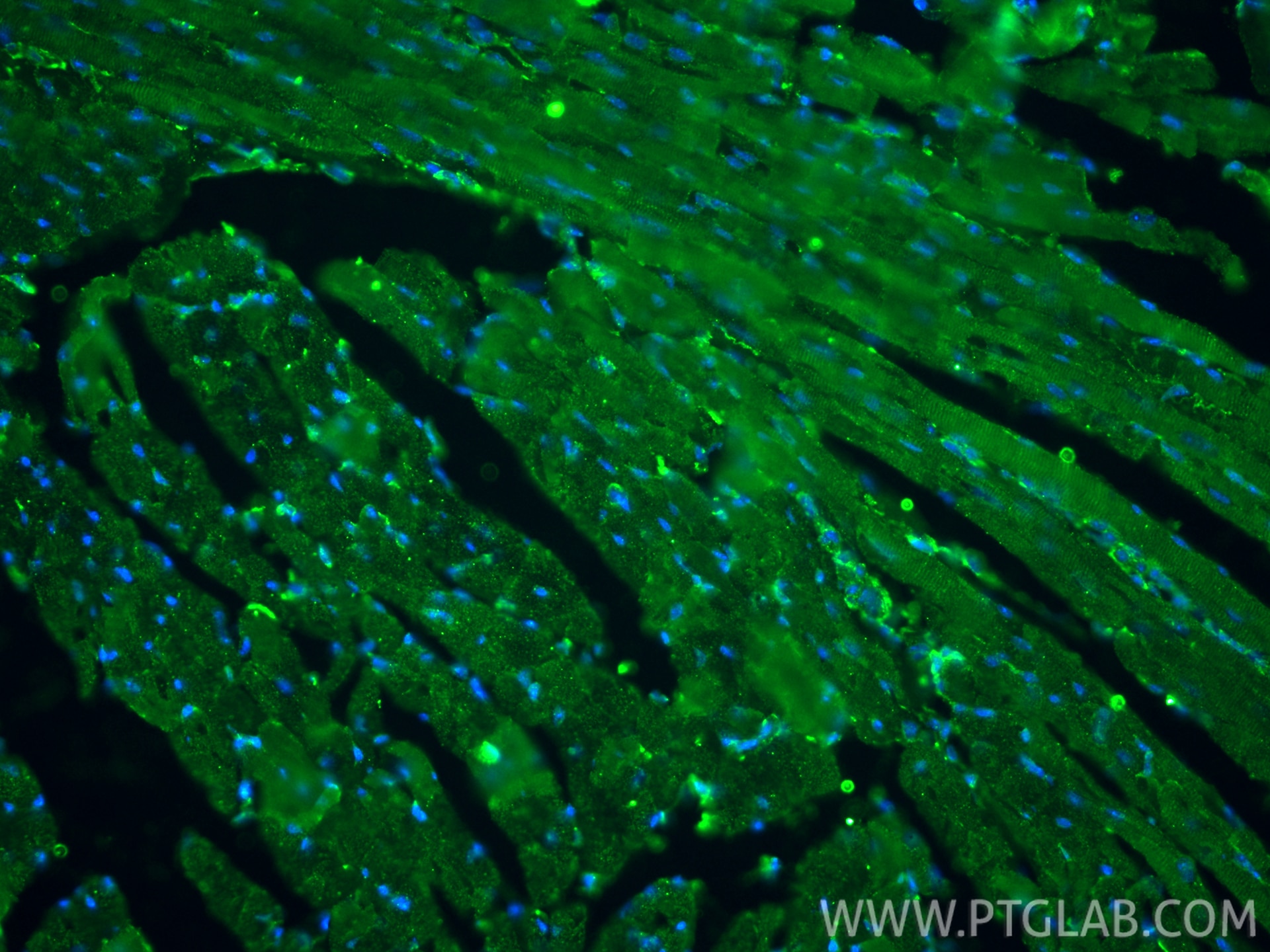
| Positive IF-P detected in | Customer Sample customer |
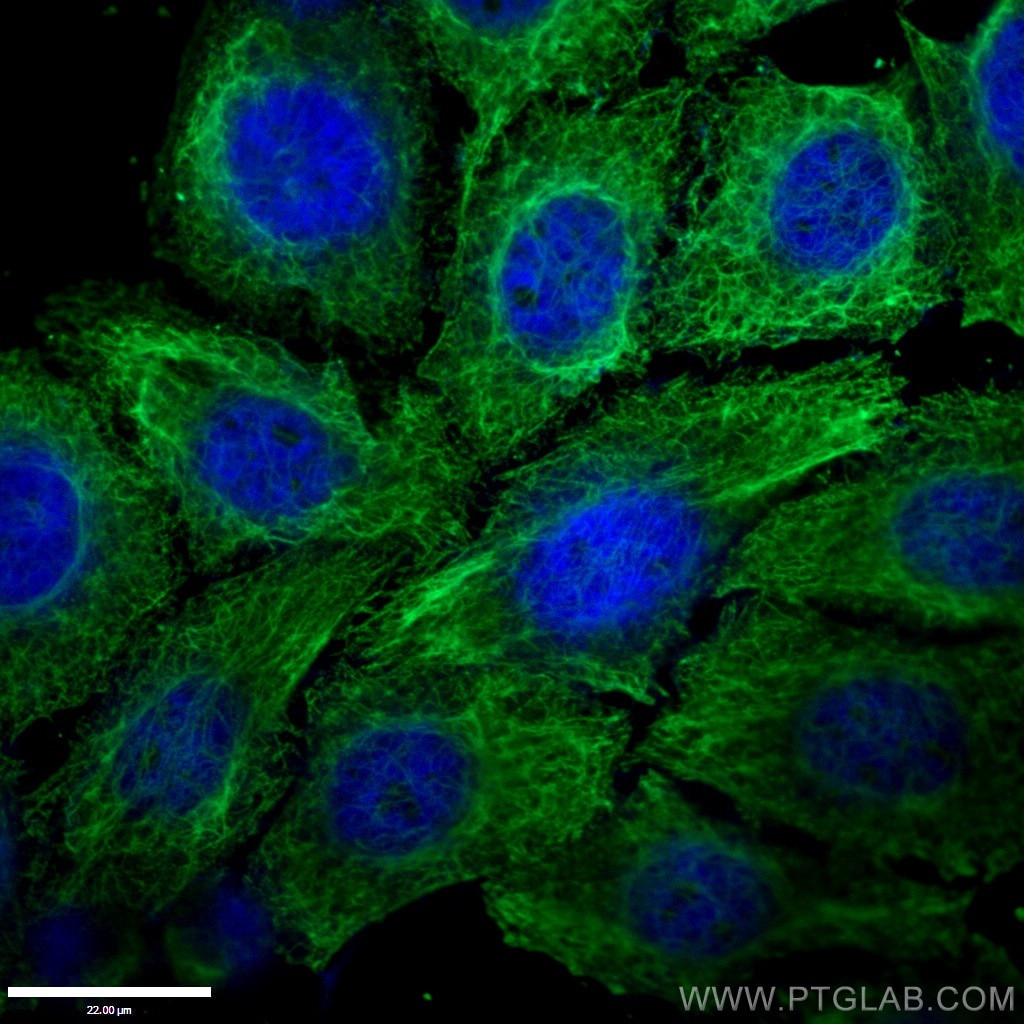
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HUVEC cells, HepG2 cells, Retinal organoids |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:20000-1:100000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:4000-1:16000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:400-1:1600 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:500-1:2000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 250 publications below |
| IHC | See 42 publications below |
| IF | See 127 publications below |
| IP | See 2 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
60330-1-Ig targets Vimentin in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, IP, CoIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, pig, rabbit, zebrafish |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag0489 Product name: Recombinant human Vimentin protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-466 aa of BC000163 Sequence: MSTRSVSSSSYRRMFGGPGTASRPSSSRSYVTTSTRTYSLGSALRPSTSRSLYASSPGGVYATRSSAVRLRSSVPGVRLLQDSVDFSLADAINTEFKNTRTNEKVELQELNDRFANYIDKVRFLEQQNKILLAELEQLKGQGKSRLGDLYEEEMRELRRQVDQLTNDKARVEVERDNLAEDIMRLREKLQEEMLQREEAENTLQSFRQDVDNASLARLDLERKVESLQEEIAFLKKLHEEEIQELQAQIQEQHVQIDVDVSKPDLTAALRDVRQQYESVAAKNLQEAEEWYKSKFADLSEAANRNNDALRQAKQESTEYRRQVQSLTCEVDALKGTNESLERQMREMEENFAVEAANYQDTIGRLQDEIQNMKEEMARHLREYQDLLNVKMALDIEIATYRKLLEGEESRISLPLPNFSSLNLRETNLDSLPLVDTHSKRTLLIKTVETRDGQVINETSQHHDDLE Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | vimentin |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 466 aa, 54 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 55-60 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC000163 |
| Gene Symbol | VIM |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7431 |
| ENSEMBL Gene ID | ENSG00000026025 |
| RRID | AB_2881439 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P08670 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
Vimentin, also named as VIM, belongs to the intermediate filament family. Vimentin is class-III intermediate filaments found in various non-epithelial cells, especially mesenchymal cells. Vimentin is important for stabilizing the architecture of the cytoplasm. Monocyte-derived macrophages secrete vimentin into the extracellular space in vitro. Secretion of vimentin was enhanced by the proinflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFA; 191160) and inhibited by the antiinflammatory cytokine IL10 (124092), suggesting that vimentin is involved in the immune response. Vimentin has specialized functions that contribute to specific dynamic cellular processes. As a phosphoprotein, 55-60 kDa of vimentin proteins can be observed due to the different phosphorylation level.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for Vimentin antibody 60330-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for Vimentin antibody 60330-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for Vimentin antibody 60330-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Adv Mater Neonatal Tissue-derived Extracellular Vesicle Therapy (NEXT): A Potent Strategy for Precision Regenerative Medicine | ||
Adv Mater Glycated ECM Derived Carbon Dots Inhibit Tumor Vasculogenic Mimicry by Disrupting RAGE Nuclear Translocation and Its Interaction With HMGB1 | ||
Mol Cancer CircNR3C2 promotes HRD1-mediated tumor-suppressive effect via sponging miR-513a-3p in triple-negative breast cancer. | ||
Adv Sci (Weinh) Inflammatory Fibroblast-Like Synoviocyte-Derived Exosomes Aggravate Osteoarthritis via Enhancing Macrophage Glycolysis | ||
Acta Pharm Sin B Celastrol induces ferroptosis in activated HSCs to ameliorate hepatic fibrosis via targeting peroxiredoxins and HO-1. | ||
J Pineal Res Melatonin and verteporfin synergistically suppress the growth and stemness of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through the regulation of mitochondrial dynamics |
Reviews
The reviews below have been submitted by verified Proteintech customers who received an incentive for providing their feedback.
FH Alessandro (Verified Customer) (12-09-2023) | good IF antibody. no unspecific staining
|
FH Aarushi (Verified Customer) (04-15-2023) | Primary antibody worked well after methanol treatment in a dilution of 1:200.
 |
FH Saba (Verified Customer) (03-03-2022) | The antibody worked perfectly!! The band was sharp and no unspecefic bands were seen.
|