Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-CD206
CD206 Polyclonal Antibody for
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
Conjugaison
APC Fluorescent Dye
N° de cat : APC-18704
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
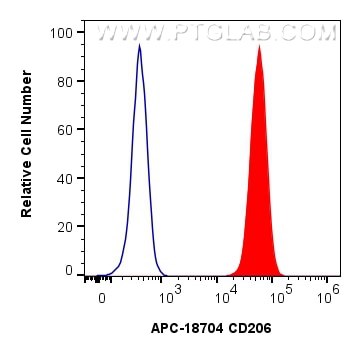
| Résultats positifs en FC (Intra) | cellules RAW 264.7, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.40 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Informations sur le produit
APC-18704 cible CD206 dans les applications de et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Peptide |
| Nom complet | mannose receptor, C type 1 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 166 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 165-180 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | NM_002438 |
| Symbole du gène | CD206 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 4360 |
| Conjugaison | APC Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission maxima wavelengths | 650 nm / 660 nm |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.09% sodium azide and 0.5% BSA |
| Conditions de stockage | Store at 2-8°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Background
CD206 (macrophage mannose receptor 1) is a lectin-type endocytic receptor expressed on selected macrophages, dendritic cells, and non-vascular endothelium and plays a role in antigen processing and presentation, phagocytosis, and intracellular signaling.
1. What is the molecular weight of CD206?
The molecular size of full-length CD206 is 170-180 kDa, depending on the exact tissue-specific glycosylation pattern (PMID: 19427834). Additionally, CD206 can be cleaved off and a soluble form (sMR) lacking the tail, with a slightly lower molecular weight, can be released to the cell medium (PMID: 9722572).
2. What is the subcellular localization of CD206?
CD206 is a type I membrane protein composed of a large extracellular multidomain, a transmembrane domain, and a short cytoplasmic tail. It is present at the plasma membrane and in endosomes, as CD206 undergoes constant recycling between the plasma membrane and endosomal compartment.
3. Is CD206 post-translationally modified?
CD206 undergoes quite extensive post-translational modifications, predominantly N-linked glycosylation that affects ligand binding recognition and affinity (PMID: 22966131).
4. Can CD206 marker be used as a marker of M2 macrophages?
The activation of macrophages with various stimuli leads to their polarization into classical (M1) or alternatively activated (M2) subtypes spectrums and both subtypes differ in their regulatory and effector functions (PMID: 24669294). Pathogens and IFN-γ promote M1 polarization, while IL-4 released during parasite infections and allergen response promotes M2 polarization. Classically, the markers of M2 macrophages include CD206, as well as arginase-1 (ARG1; https://www.ptglab.com/products/ARG1-Antibody-16001-1-AP.htm), CD163 (https://www.ptglab.com/products/CD163-Antibody-16646-1-AP.htm), and thrombospondin 1 (TSP1/ THBS1; https://www.ptglab.com/products/TSP1-Antibody-18304-1-AP.htm).
5. How can you polarize macrophages into M2 direction?
One of the most commonly used methods is stimulation by the addition of IL-4 cytokine. We recommend using our animal-free human IL-4 (https://www.ptglab.com/products/recombinant-human-il-4.htm).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for APC CD206 antibody APC-18704 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |