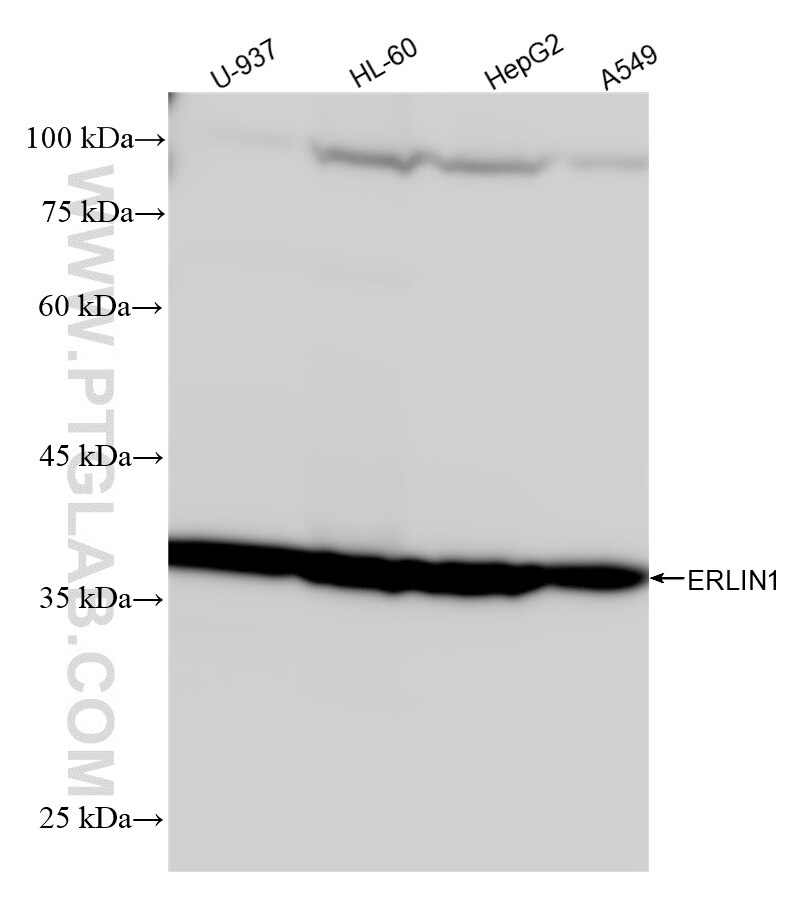
Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | U-937 cells, HL-60 cells, HepG2 cells, A549 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:10000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
85377-1-RR targets ERLIN1 in WB, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag11393 Product name: Recombinant human ERLIN1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 29-346 aa of BC031791 Sequence: GHLAVYYRGGALLTSPSGPGYHIMLPFITTFRSVQTTLQTDEVKNVPCGTSGGVMIYIDRIEVVNMLAPYAVFDIVRNYTADYDKTLIFNKIHHELNQFCSAHTLQEVYIELFDQIDENLKQALQKDLNLMAPGLTIQAVRVTKPKIPEAIRRNFELMEAEKTKLLIAAQKQKVVEKEAETERKKAVIEAEKIAQVAKIRFQQKVMEKETEKRISEIEDAAFLAREKAKADAEYYAAHKYATSNKHKLTPEYLELKKYQAIASNSKIYFGSNIPNMFVDSSCALKYSDIRTGRESSLPSKEALEPSGENVIQNKESTG Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | ER lipid raft associated 1 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 346 aa, 39 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 39 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC031791 |
| Gene Symbol | ERLIN1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 10613 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O75477 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
ERLIN1, also known as Erlin-1 or SPFH1, stands for "ER lipid raft-associated protein 1." It is a protein-coding gene that plays a significant role in cellular processes, particularly in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The ER is a crucial organelle involved in protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and calcium homeostasis. ERLIN1 is part of the SPFH (stomatin, prohibitin, flotillin, and HflK/C) domain-containing family of proteins, which are often associated with lipid rafts-microdomains within cellular membranes that are enriched in cholesterol and sphingolipids. ERLIN1 is involved in the regulation of protein degradation, particularly through the ER-associated degradation (ERAD) pathway (PMID: 37683630).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for ERLIN1 antibody 85377-1-RR | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |