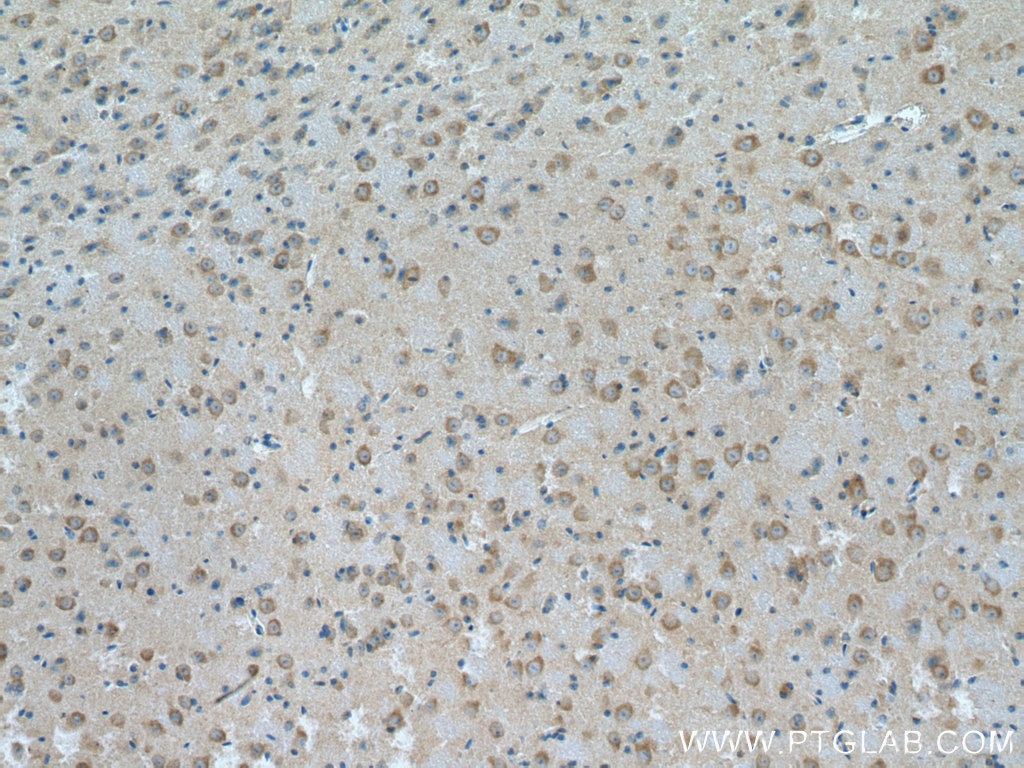
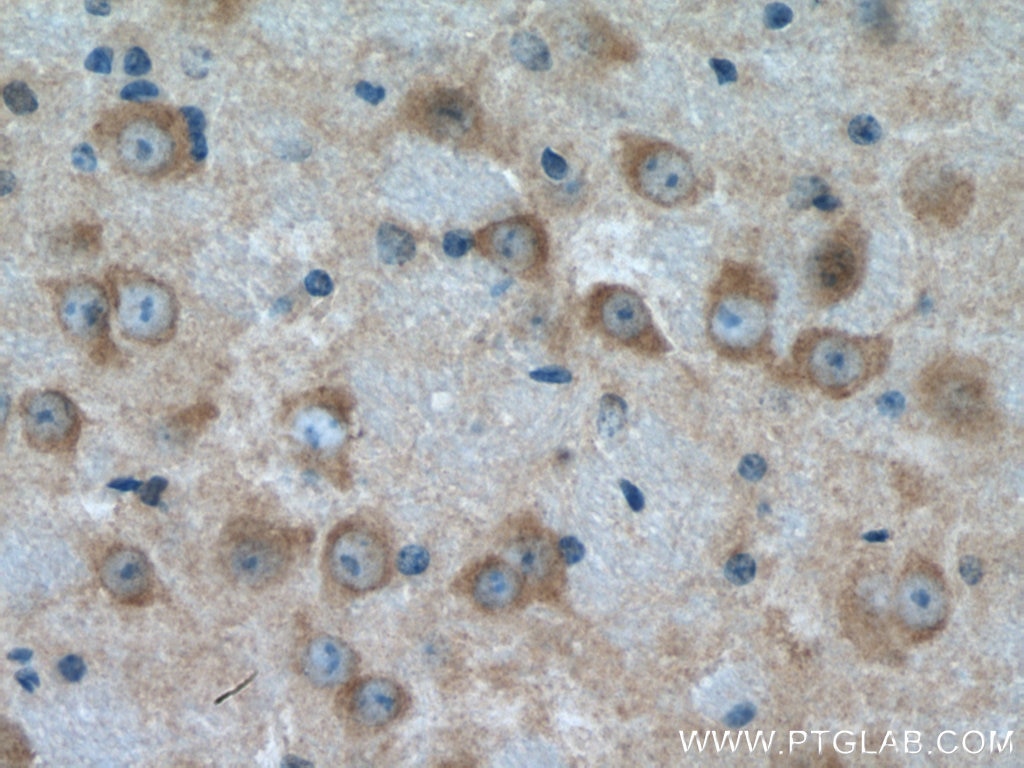
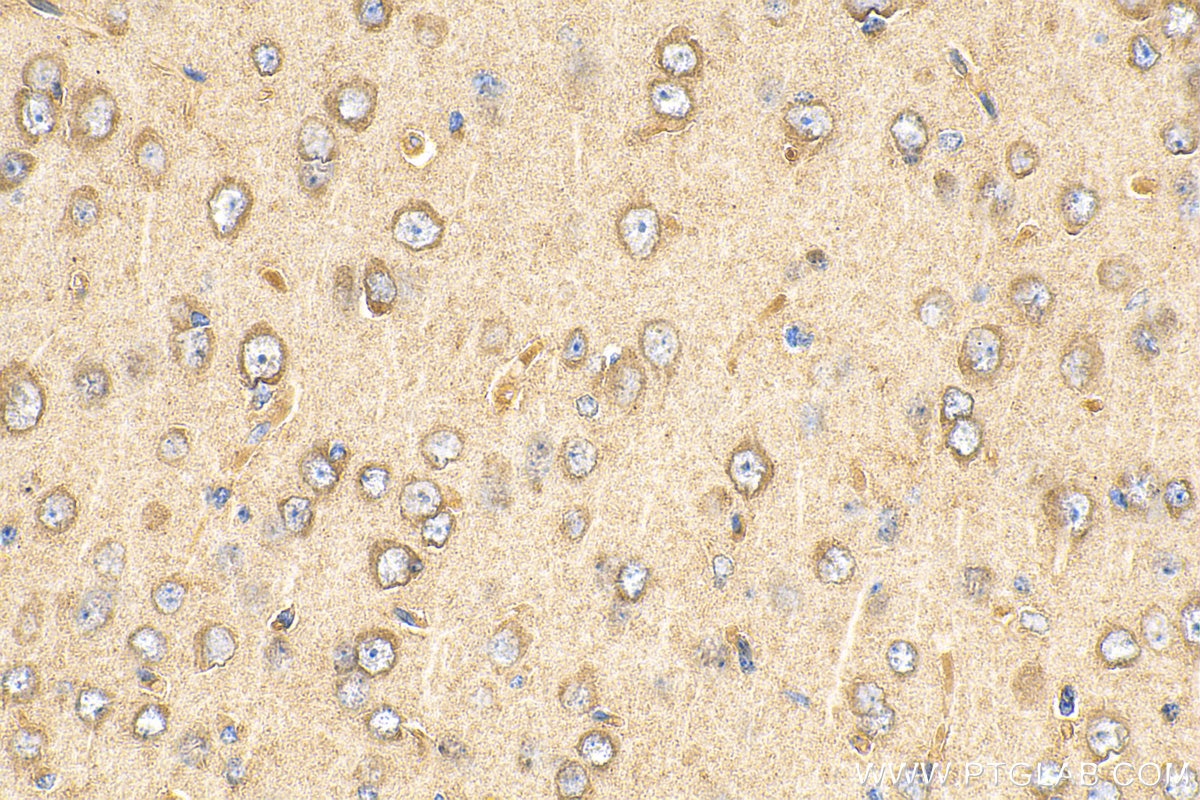
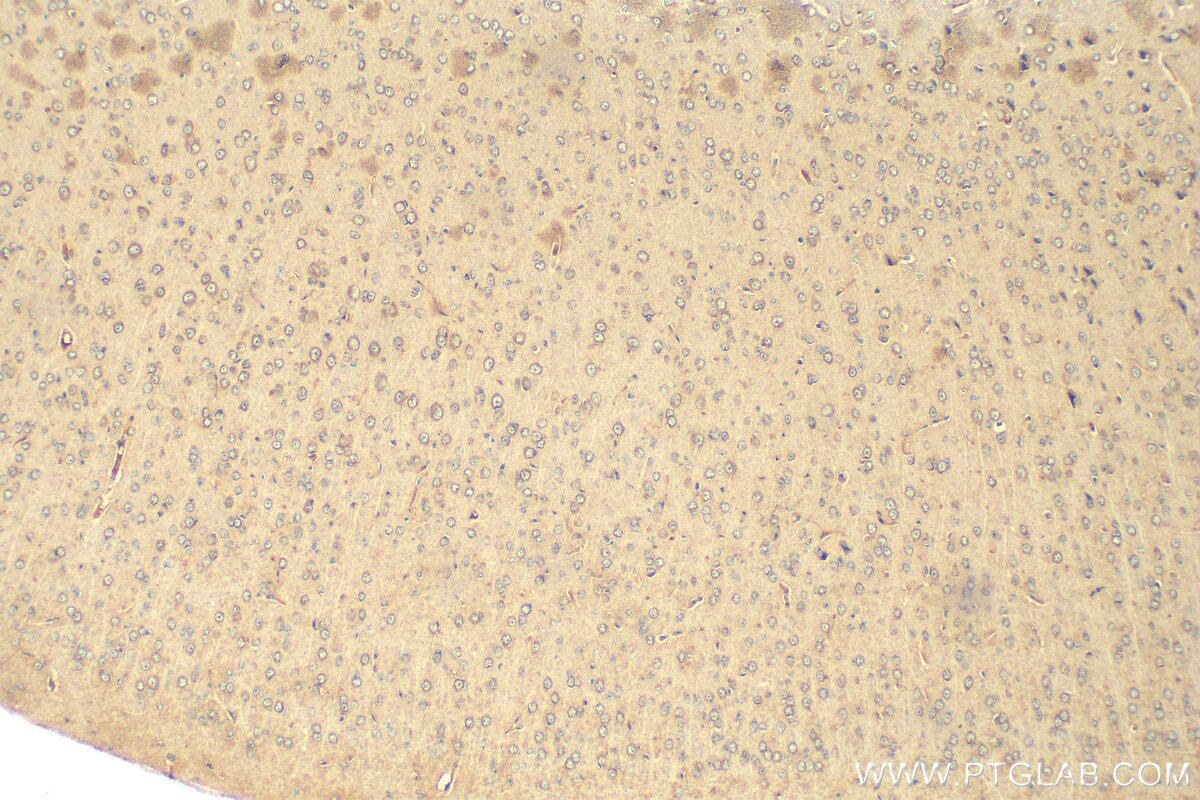
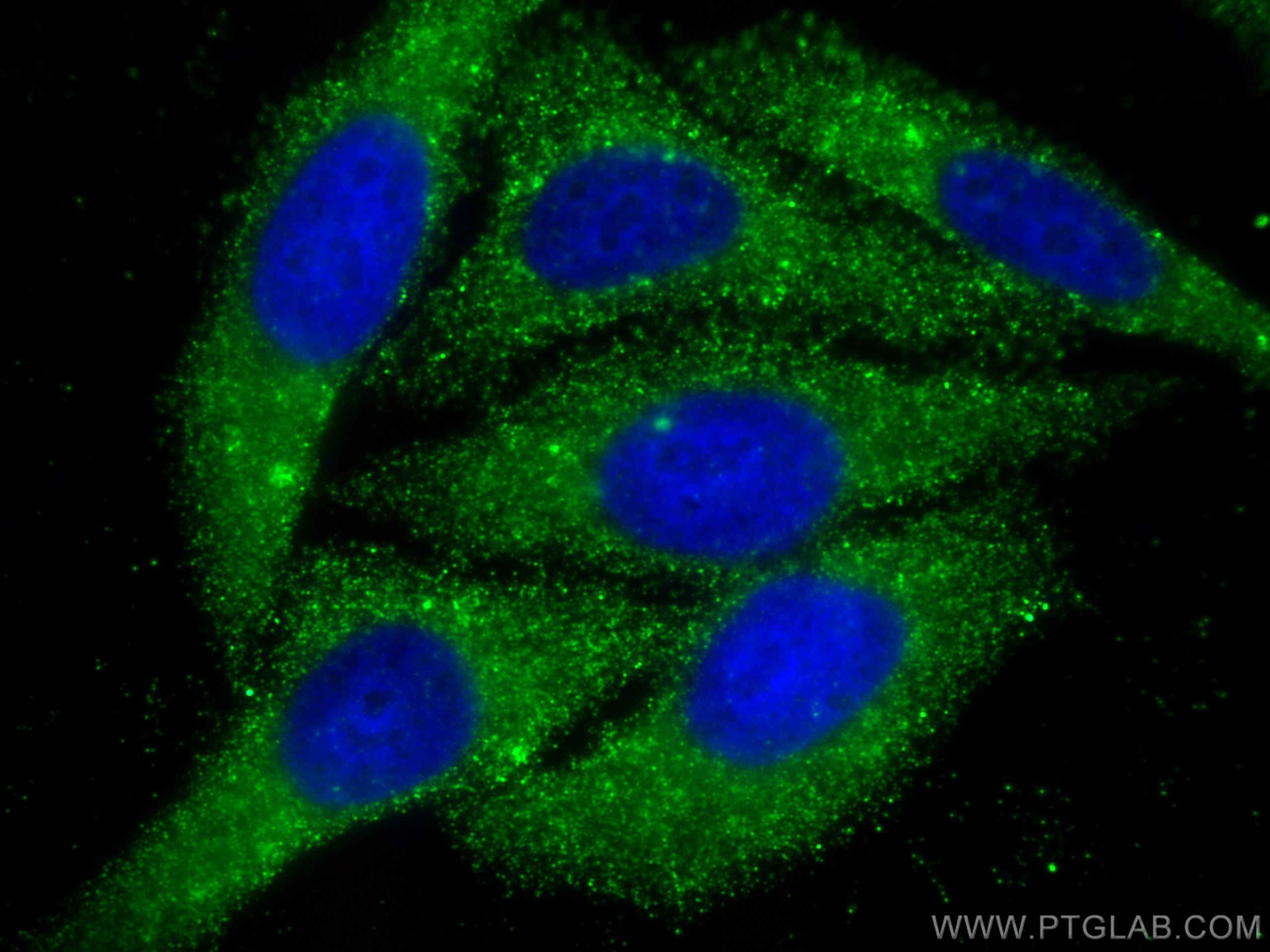
Product Information
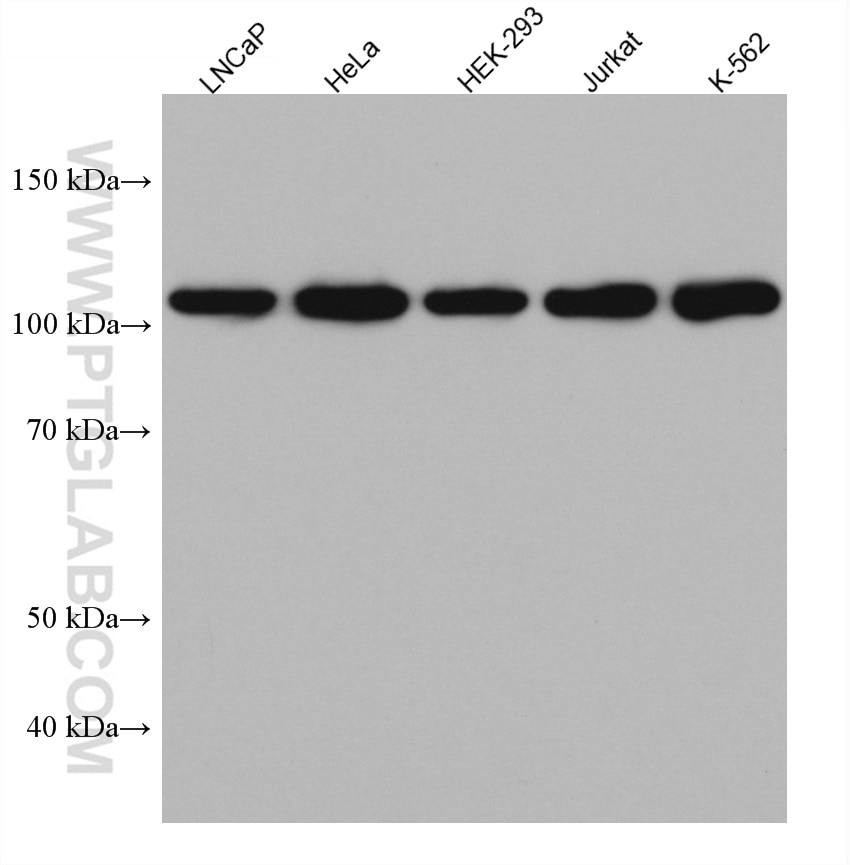
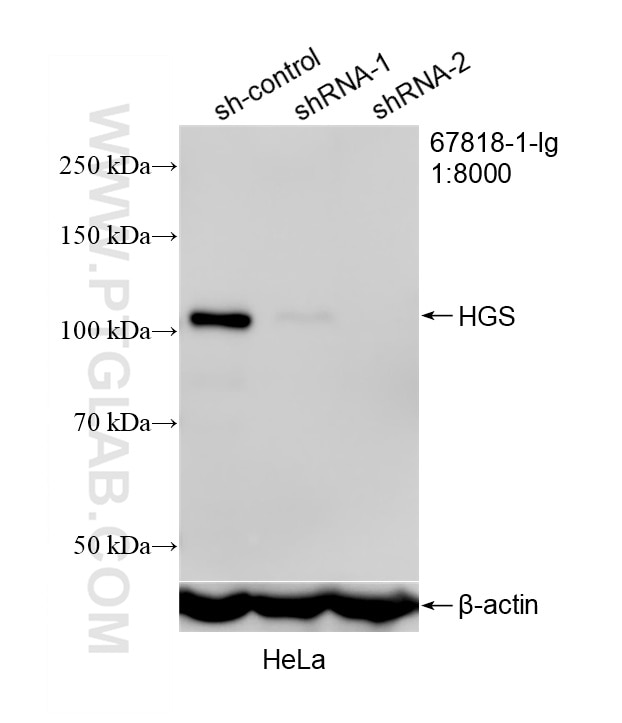
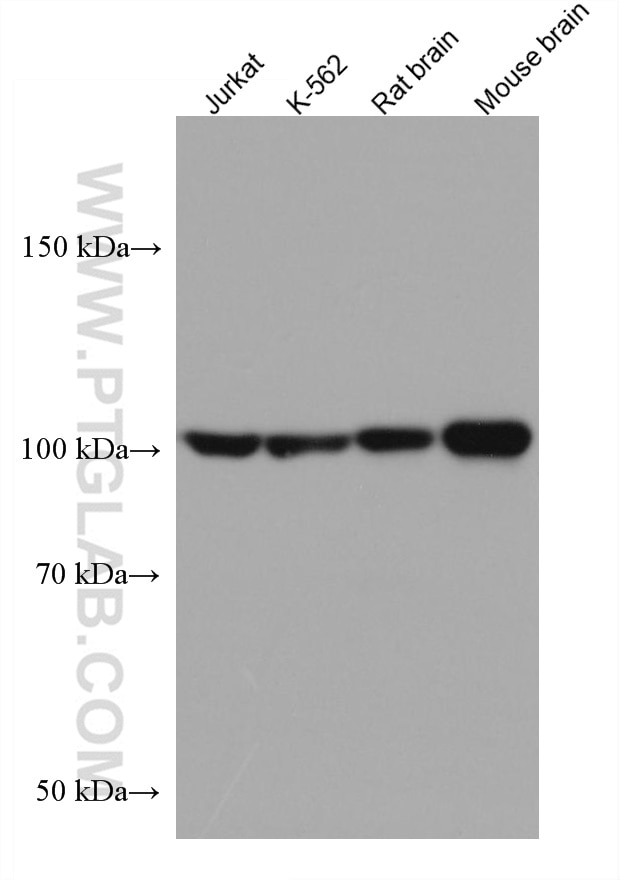
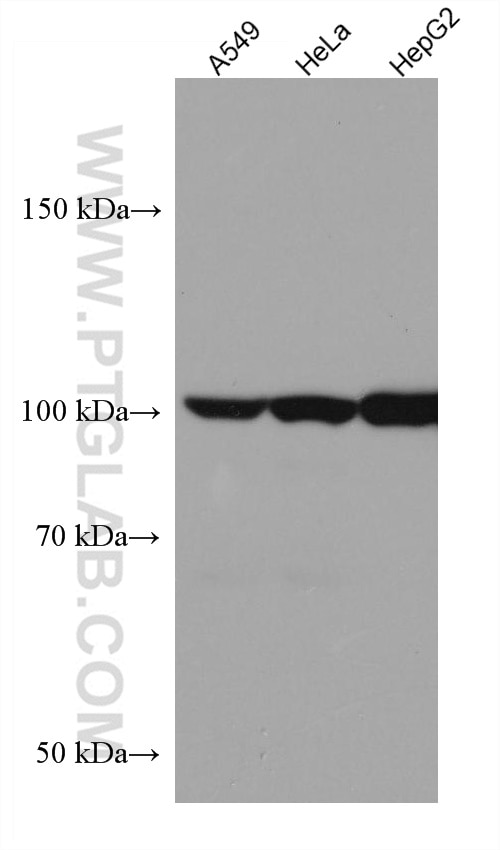
67818-1-PBS targets HGS in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag28610 Product name: Recombinant human HGS protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 186-387 aa of BC003565 Sequence: GQIFCGKCSSKYSTIPKFGIEKEVRVCEPCYEQLNRKAEGKATSTTELPPEYLTSPLSQQSQLPPKRDETALQEEEELQLALALSQSEAEEKERLRQKSTYTSYPKAEPMPSASSAPPASSLYSSPVNSSAPLAEDIDPELARYLNRNYWEKKQEEARKSPTPSAPVPLTEPAAQPGEGHAAPTNVVENPLPETDSQPIPPS Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 86 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 110 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC003565 |
| Gene Symbol | HGS |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 9146 |
| RRID | AB_2918581 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O14964 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate (HGS, synonyms: HRS, ZFYVE8) is a 110 to 115-kDa zinc finger phosphotyrosine protein inducible by stimulation with interleukin 2 (IL-2), granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) as well as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), and is associated with signal-transducing adaptor molecule (STAM). HGS suppresses DNA synthesis upon stimulation with IL-2 and GM-CSF, counteracting the function of STAM which is critical for cell growth signaling mediated by the cytokines. HGS also interacts with the neurofibromatosis 2 tumor suppressor protein schwannomin/merlin. The growth suppression activity of schwannomin/merlin requires HGS and the binding of schwannomin/merlin to HGS facilitates its ability to function as a tumor suppressor, probably by inhibiting STAT activation.