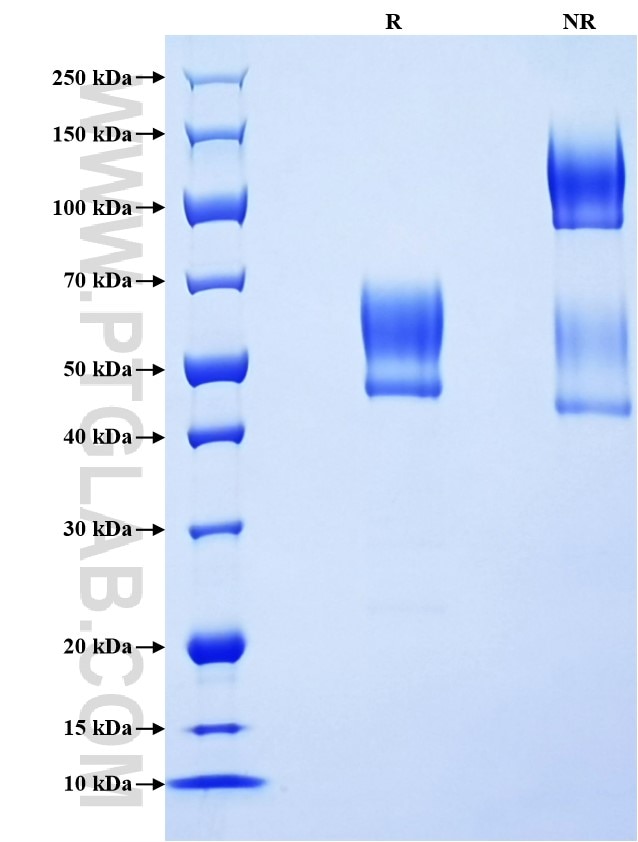
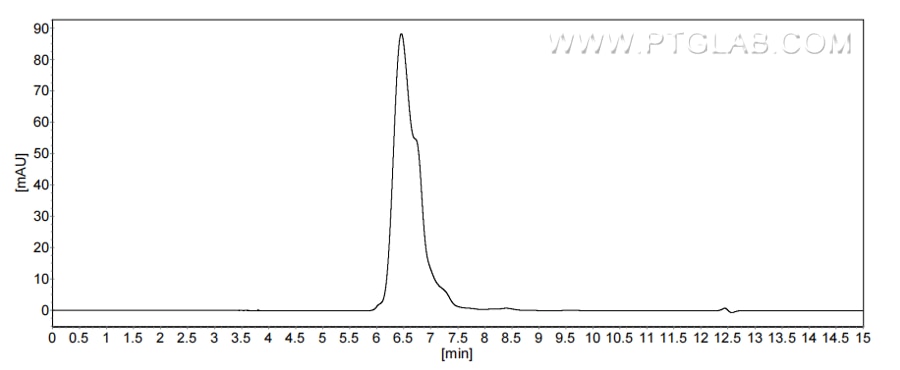
Recombinant Human Podoplanin protein (rFc Tag)(HPLC verified)
Species
Human
Purity
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
>90 %, SEC-HPLC
Tag
rFc Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg5024
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE >90 %, SEC-HPLC |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human Podoplanin protein Ala23-Leu131 (Accession# Q86YL7-1) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 10630 |
| Accession | Q86YL7-1 |
| PredictedSize | 37.4 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 48-68 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
Podoplanin (PDPN) is a transmembrane glycoprotein that plays a role in a variety of biological processes including regulation of blood-lymphatic vessel development, cerebral vascular pattern and integrity, cell motility, tumorigenesis and metastasis, and mediates tumor cell-induced platelet aggregation in different cancer types. It is a lymphatic marker because the expression of podoplanin has been detected in lymphatic but not blood vascular endothelium, and is useful as the marker of tumor-associated Lymphangiogenesis. When expressed in keratinocytes, PDPN induces changes in cell morphology with transfected cells showing an elongated shape, numerous membrane protrusions, major reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, increased motility and decreased cell adhesion.
References:
1. Ukaji T, et al . Cancer Sci. 2021; 112(6):2299-2313. 2. Krishnan H, et al. J Biol Chem. 2013 ;288(17):12215-21. 3. Wang X, et al. Cancer Gene Ther. 2023 ;30(2):345-357. 4.Astarita JL, et al. Front Immunol. 2012; 3:283.