Tested Applications
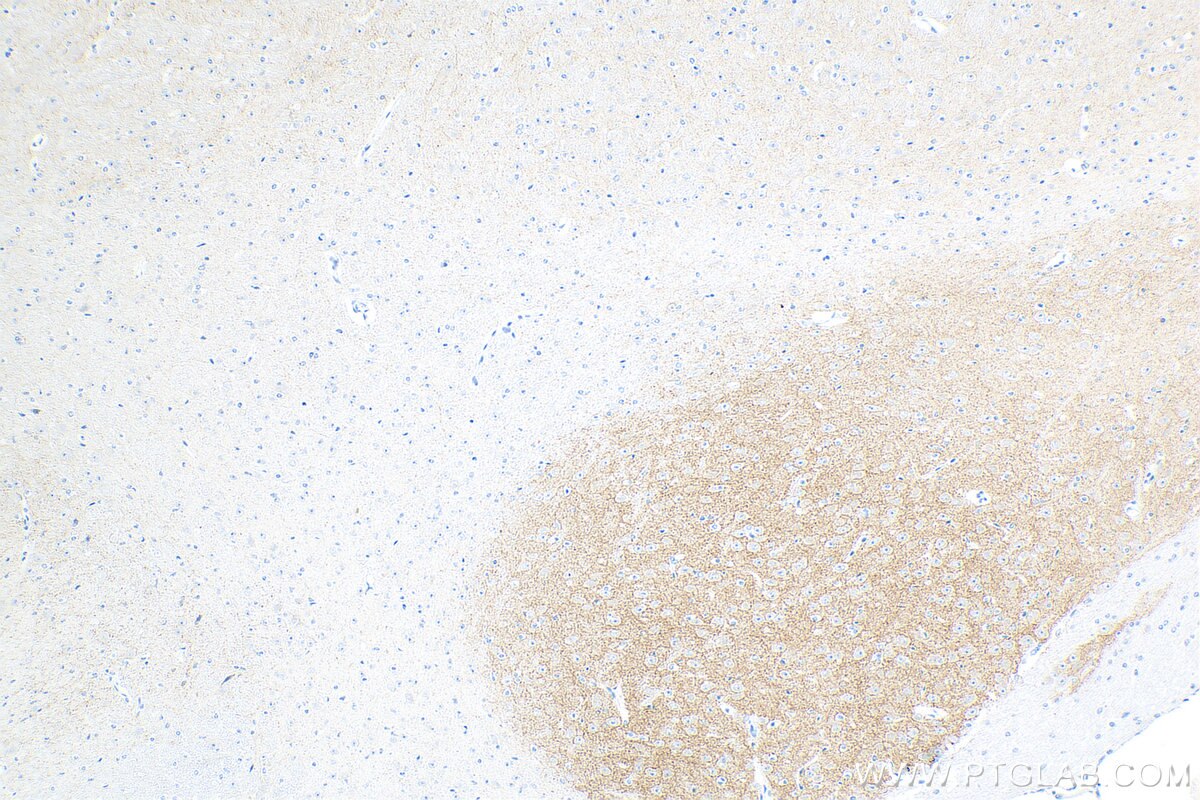
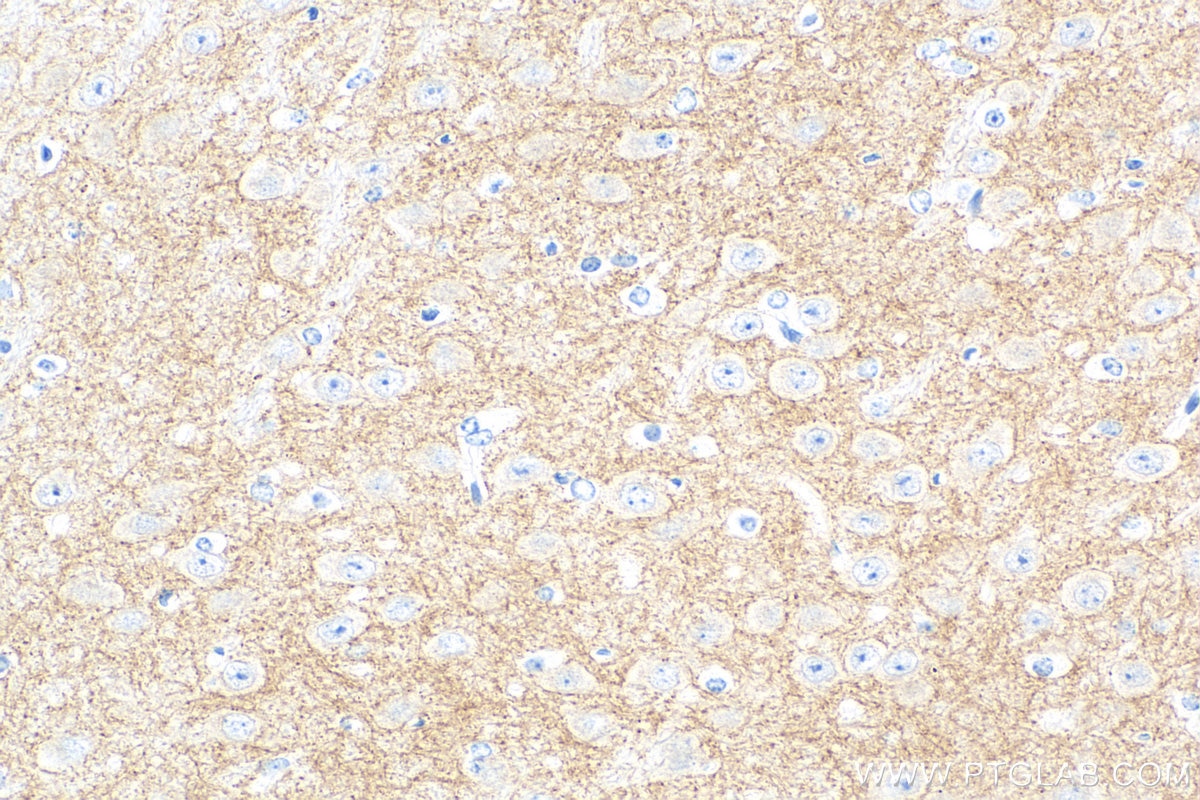
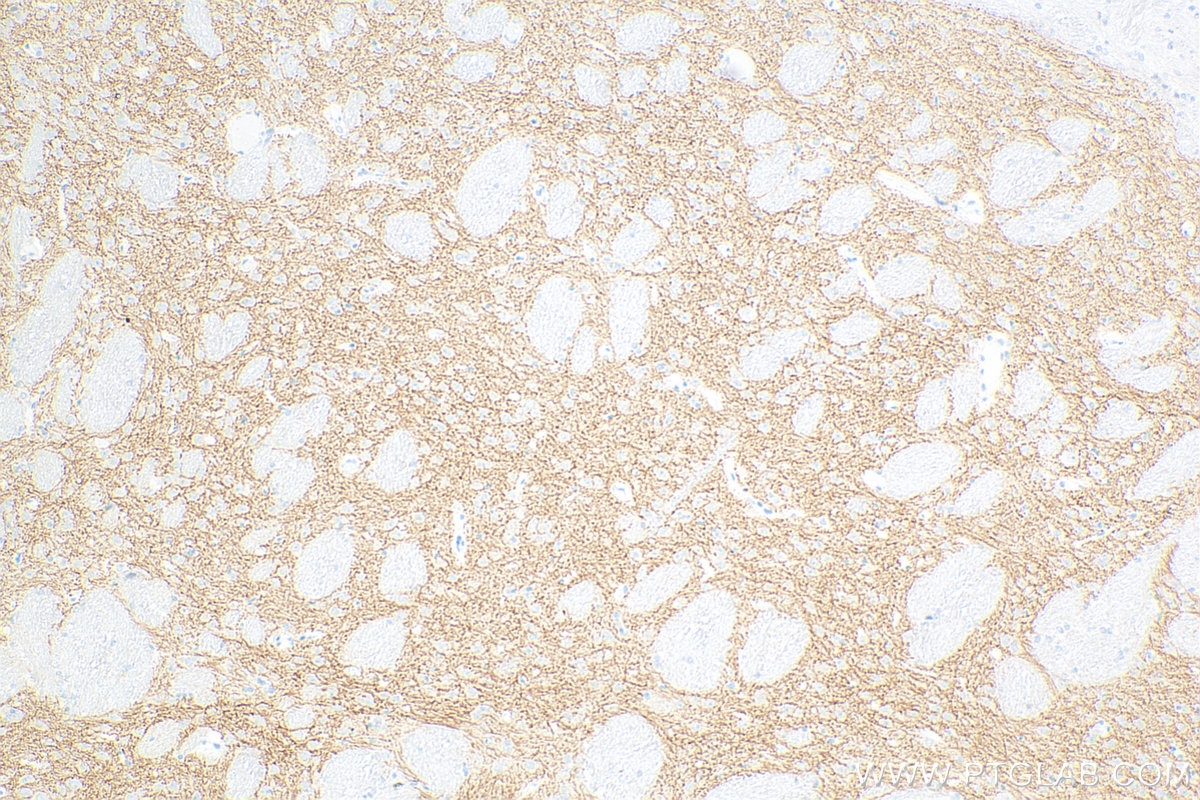
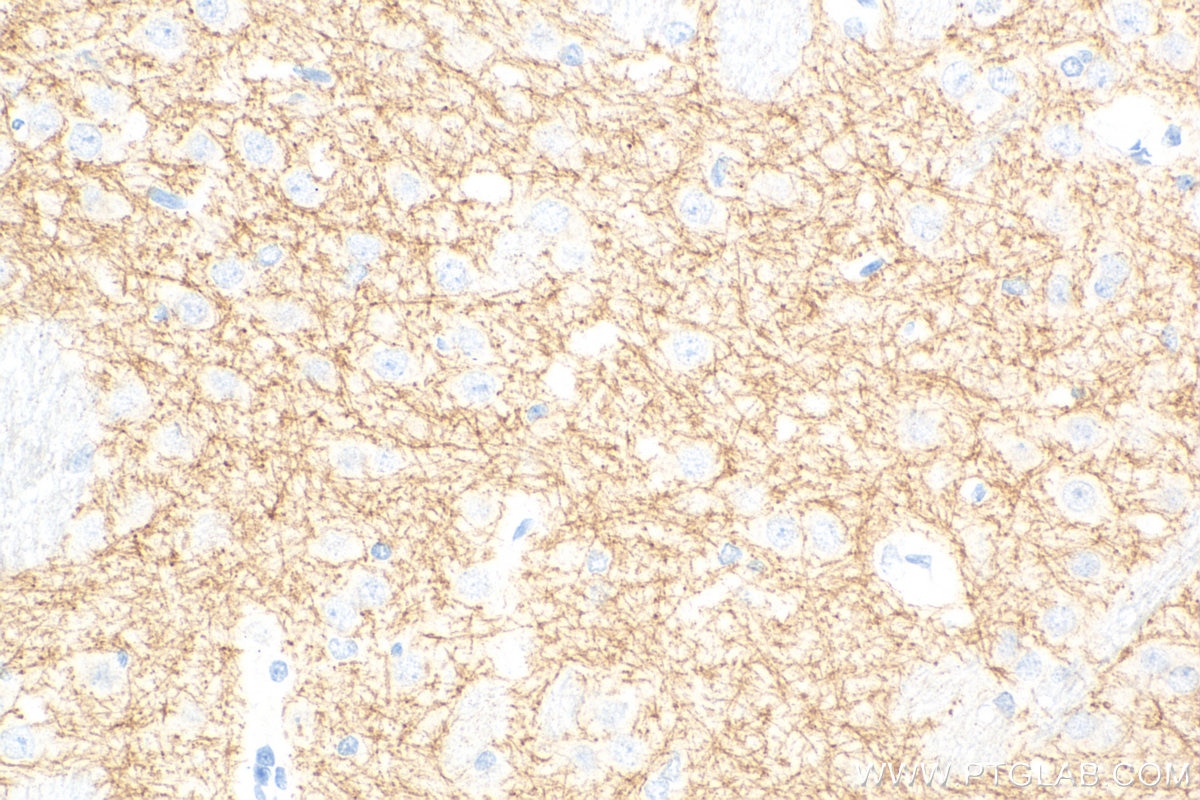
| Positive IHC detected in | rat brain tissue, mouse brain tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
83412-4-RR targets SLC6A7 in IHC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag34413 Product name: Recombinant human SLC6A7 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 138-214 aa of BC093785 Sequence: AYVLFYLFASLTSDLPWEHCGNWWNTELCLEHRVSKDGNGALPLNLTCTVSPSEEYWSRYVLHIQGSQGIGSPGEIR Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, L-proline), member 7 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 636 aa, 71 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC093785 |
| Gene Symbol | SLC6A7 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 6534 |
| RRID | AB_3671059 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purfication |
| UNIPROT ID | Q99884 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
SLC6A7 also known as PROT, belongs to the solute Carrier 6 gene family. SLC6A7 is a high-affinity mammalian brain L-proline transporter, which is different from other sodium-dependent plasma membrane carriers, and has unique pharmacological specificity, kinetic properties, and ionic requirements. SLC6A7 is a brain specific sodium (and chloride)-dependent proline transporter, that terminates the action of proline by its high affinity sodium-dependent reuptake into presynaptic terminals(PMID: 7651355).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for SLC6A7 antibody 83412-4-RR | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |