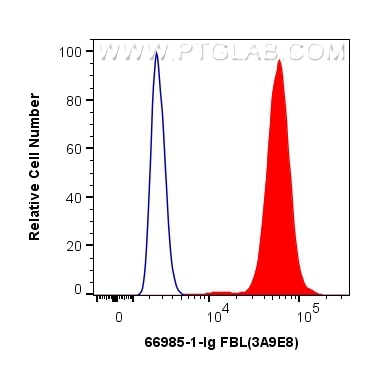
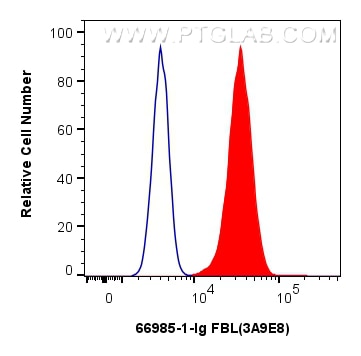
Tested Applications
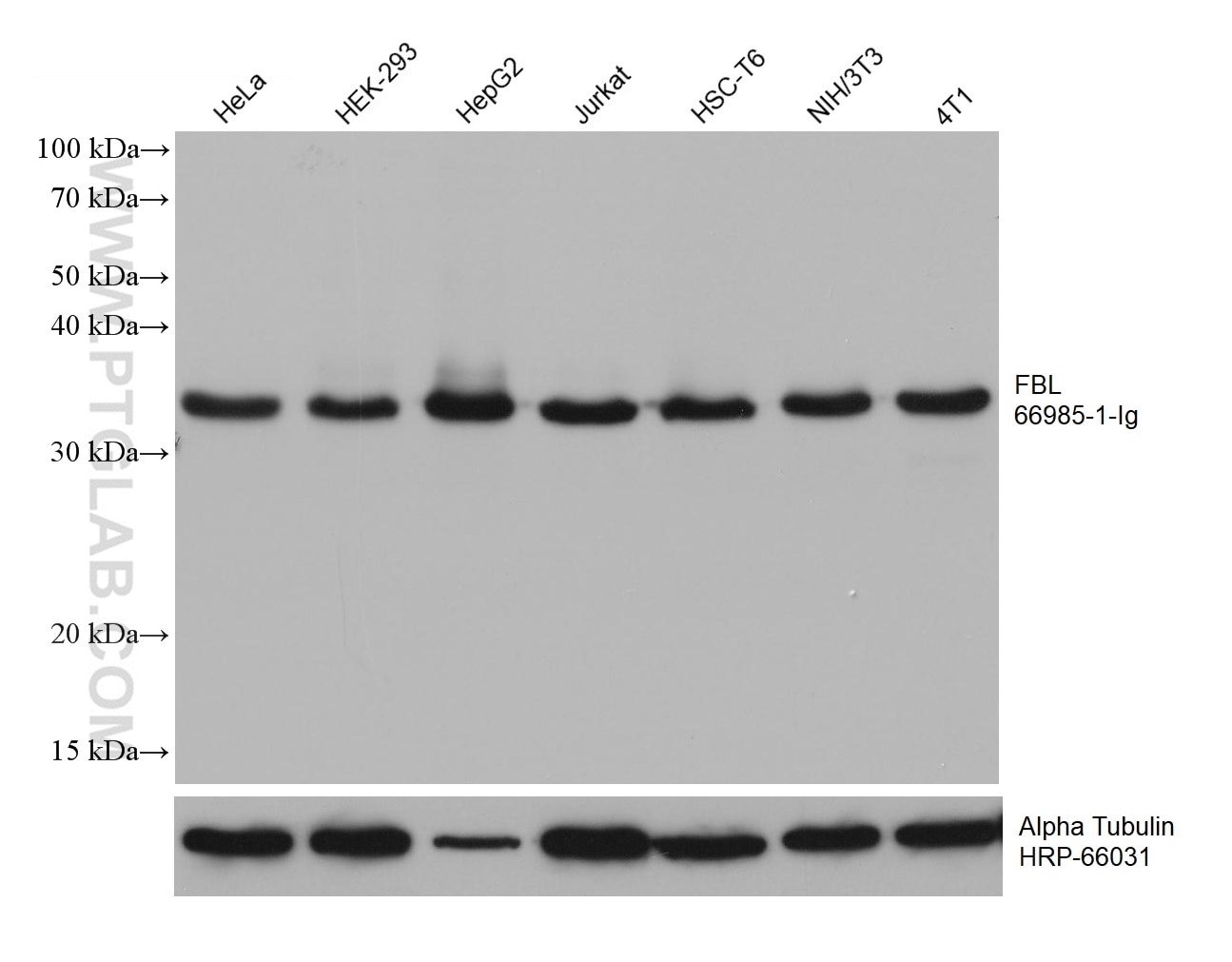
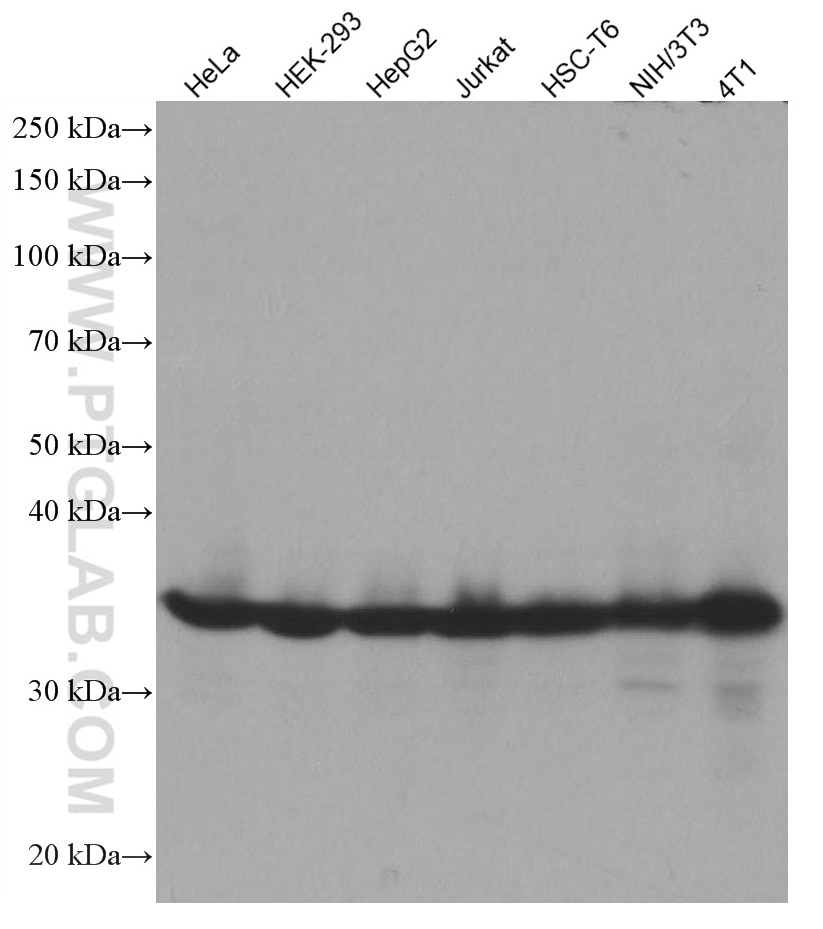
| Positive WB detected in | HeLa cells, HEK-293 cells, HepG2 cells, Jurkat cells, HSC-T6 cells, NIH/3T3 cells, 4T1 cells |
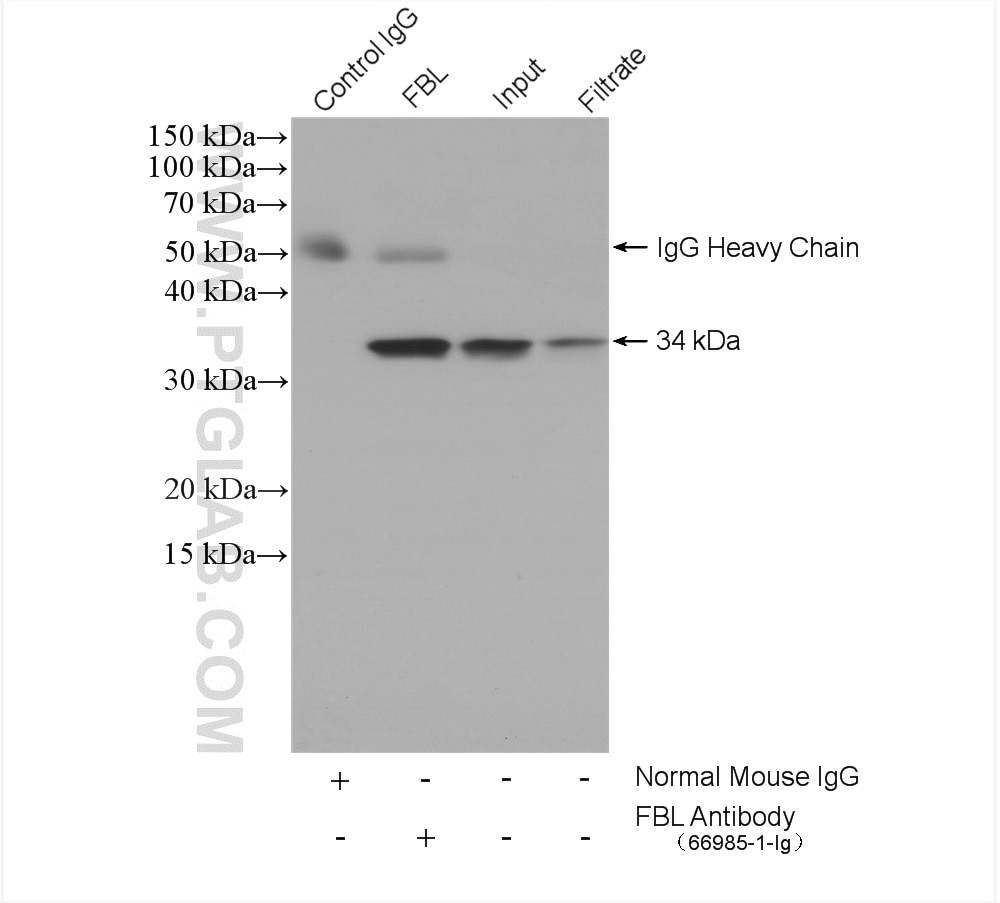
| Positive IP detected in | HeLa cells |
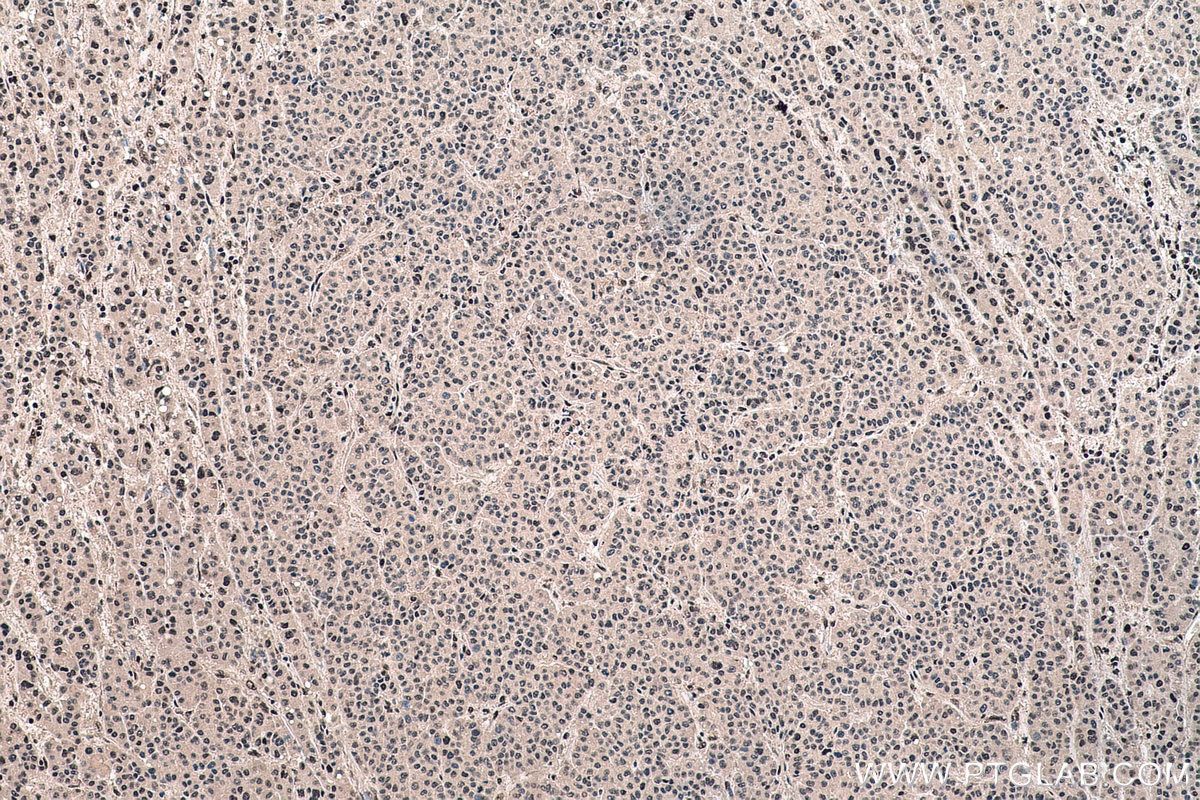
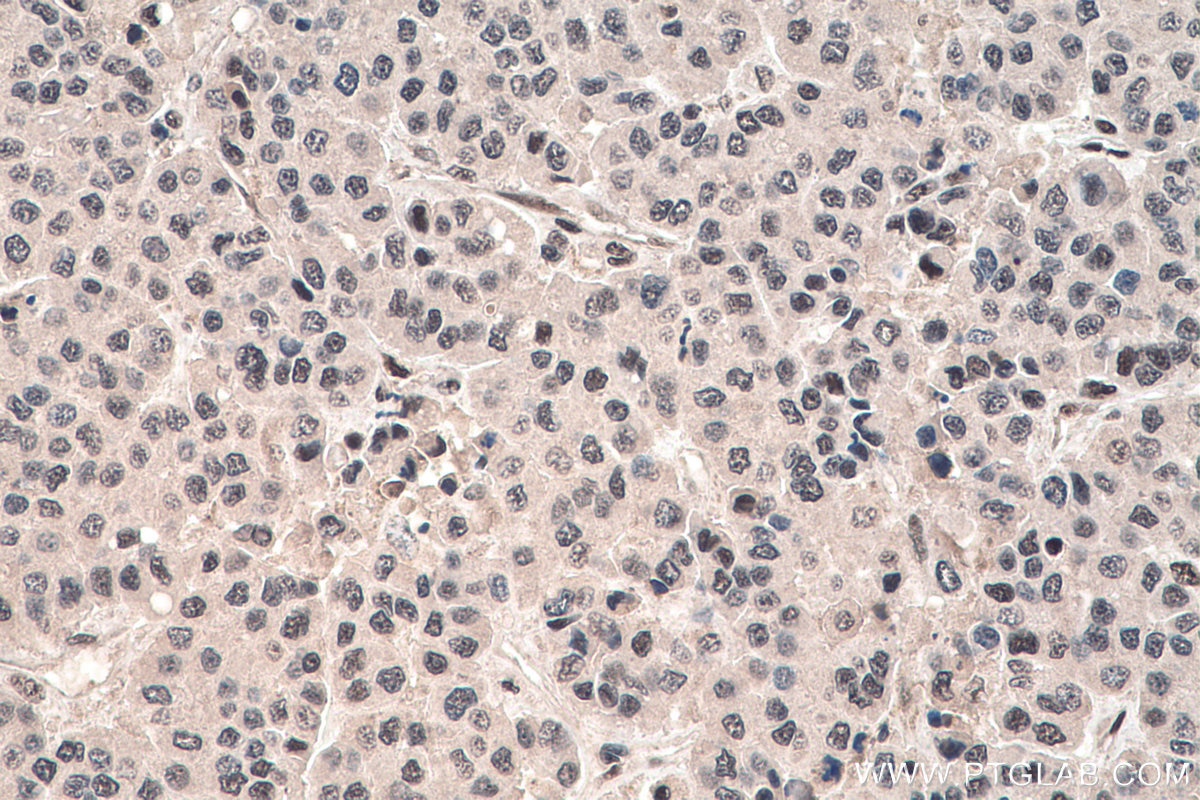
| Positive IHC detected in | human liver cancer tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
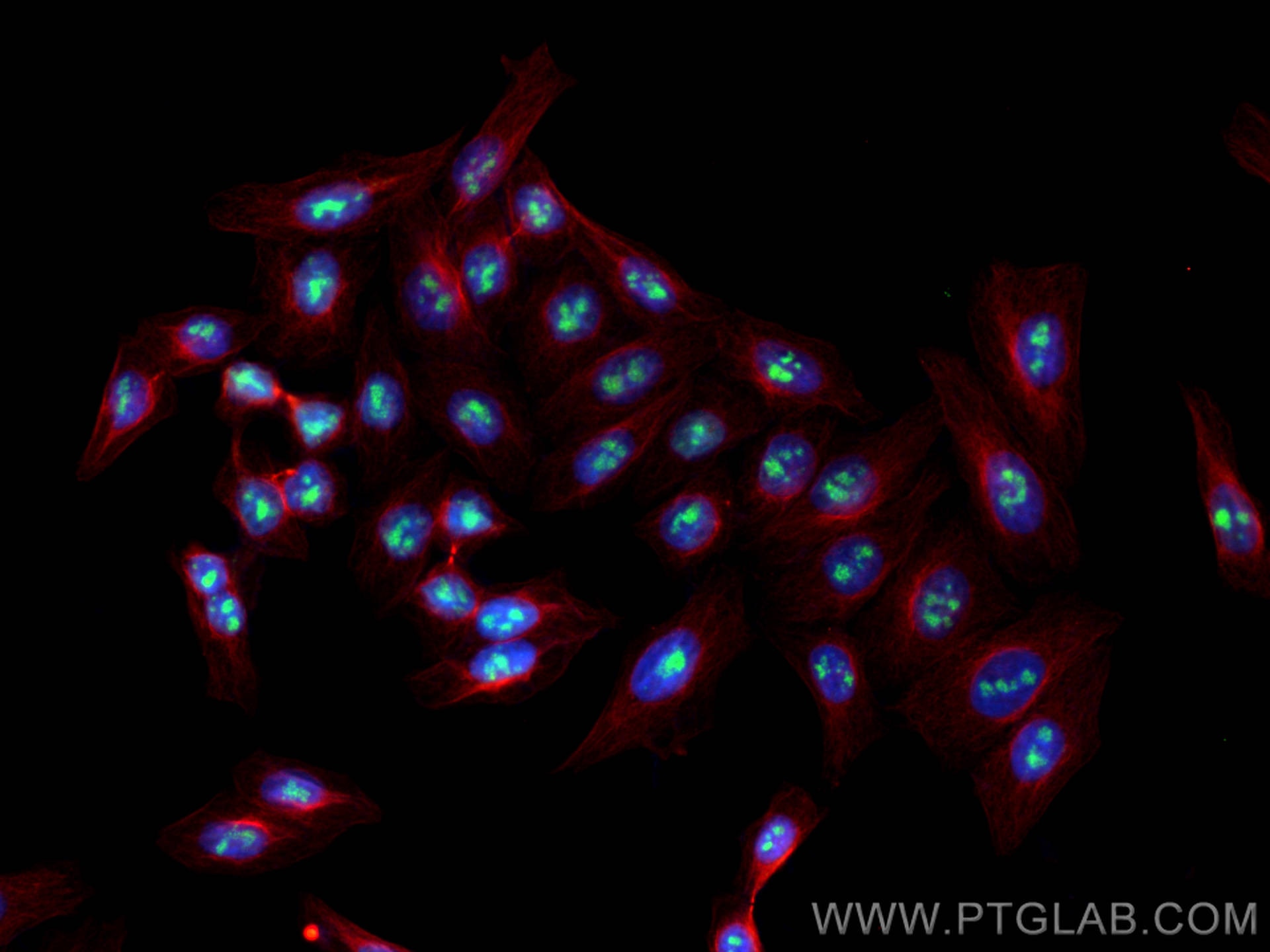
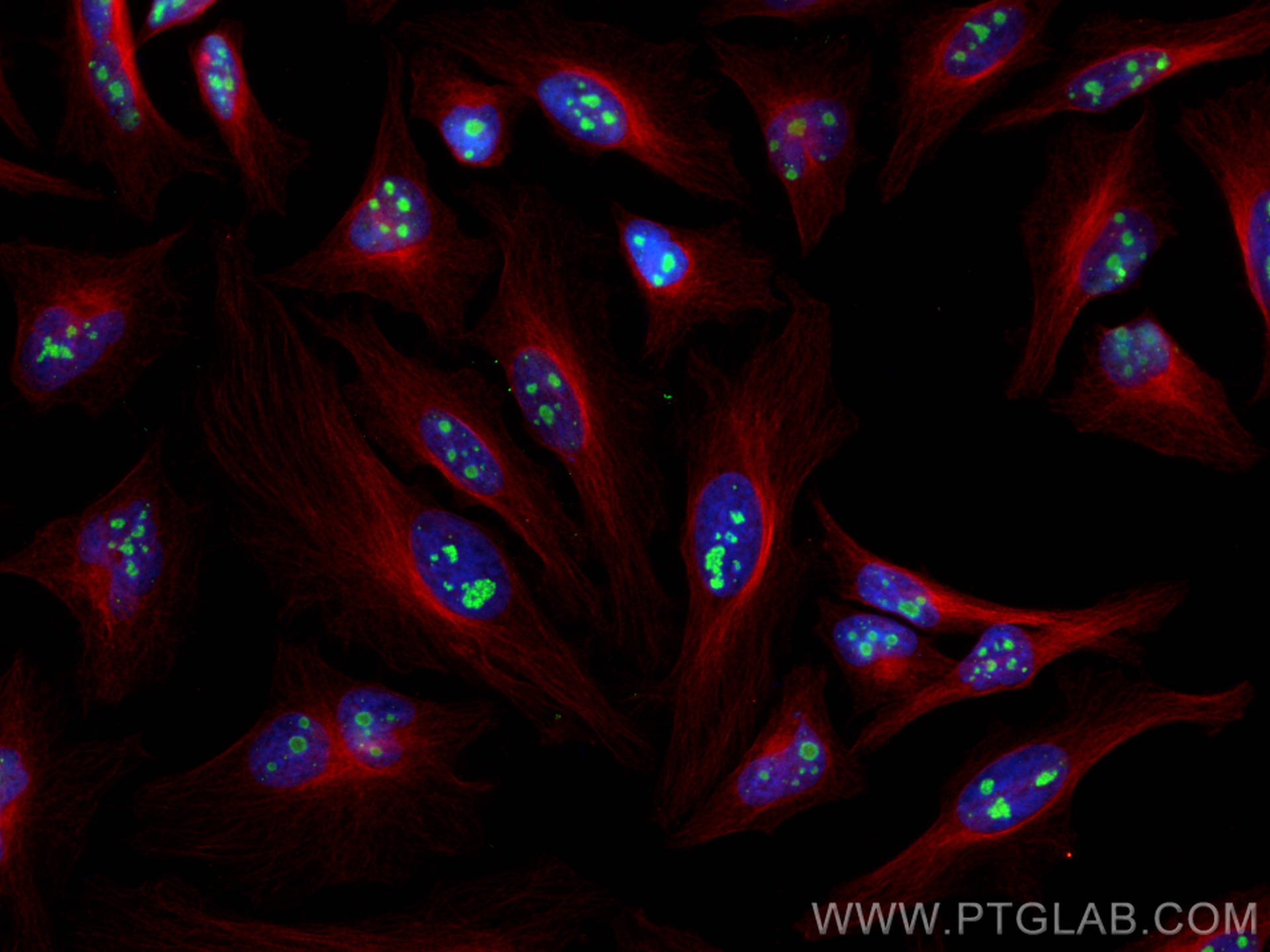
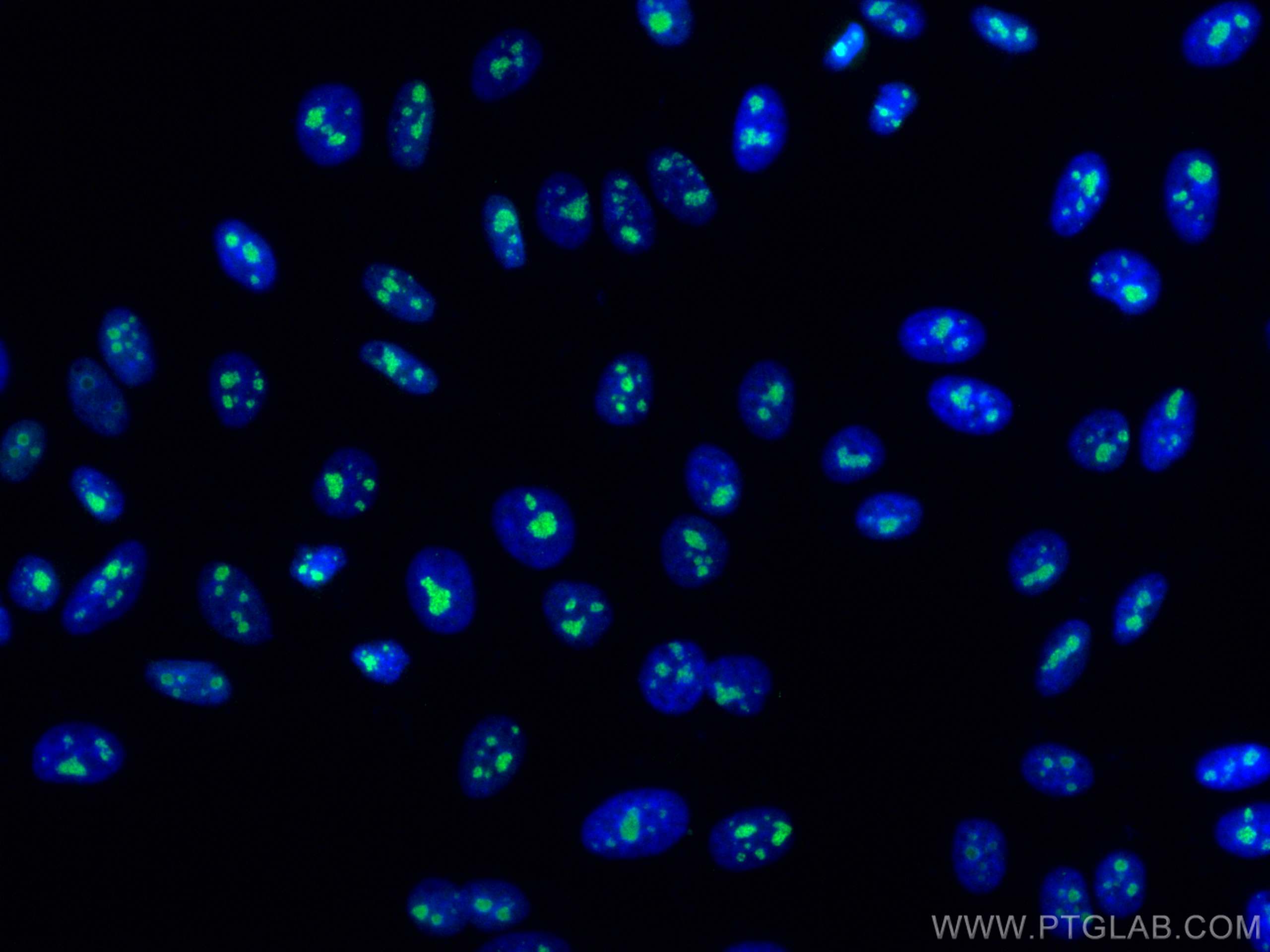
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HeLa cells, HepG2 cells |
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | HepG2 cells, HeLa cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.40 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 6 publications below |
| IF | See 5 publications below |
| RIP | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
66985-1-Ig targets Fibrillarin in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, RIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag8841 Product name: Recombinant human FBL protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 1-321 aa of BC019260 Sequence: MKPGFSPRGGGFGGRGGFGDRGGRGGRGGFGGGRGRGGGFRGRGRGGGGGGGGGGGGGRGGGGFHSGGNRGRGRGGKRGNQSGKNVMVEPHRHEGVFICRGKEDALVTKNLVPGESVYGEKRVSISEGDDKIEYRAWNPFRSKLAAAILGGVDQIHIKPGAKVLYLGAASGTTVSHVSDIVGPDGLVYAVEFSHRSGRDLINLAKKRTNIIPVIEDARHPHKYRMLIAMVDVIFADVAQPDQTRIVALNAHTFLRNGGHFVISIKANCIDSTASAEAVFASEVKKMQQENMKPQEQLTLEPYERDHAVVVGVYRPPPKVKN Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | fibrillarin |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 321 aa, 34 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 34 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC019260 |
| Gene Symbol | FBL |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2091 |
| RRID | AB_2882303 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P22087 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
Fibrillarin (Fbl) is an essential nucleolar protein that plays an essential role in ribosome biogenesis and more particularly in the methylation of ribosomal RNAs and rDNA histones. FBL is highly expressed in various cancers and correlates with poor survival outcomes in cancer patients,such as hepatocellular carcinoma(PMID: 33376525). Knockdown of FBL sensitizes tumor cells and xenografts to DNA crosslinking agents, and leads to homologous recombination-mediated DNA repair defects(PMID: 37489617).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for Fibrillarin antibody 66985-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for Fibrillarin antibody 66985-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for Fibrillarin antibody 66985-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for Fibrillarin antibody 66985-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for Fibrillarin antibody 66985-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Gastroenterology Nucleolar HEATR1 upregulated by mTORC1 signaling promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth by dominating ribosome biogenesis and proteome homeostasis | ||
Mol Cell lncRNAs maintain the functional phase state of nucleolar prion-like protein to facilitate rRNA processing | ||
BMC Biol A pair of long intergenic non-coding RNA LINC00887 variants act antagonistically to control Carbonic Anhydrase IX transcription upon hypoxia in tongue squamous carcinoma progression | ||
Thorac Cancer LncRNA FAM83A-AS1 promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression by enhancing the pre-mRNA stability of FAM83A. | ||
Cell Death Discov Protein expression of nucleolar protein 12 in the retina and its implication in protection of retina from UV irradiation damage | ||
Nat Commun NAP-seq reveals multiple classes of structured noncoding RNAs with regulatory functions |