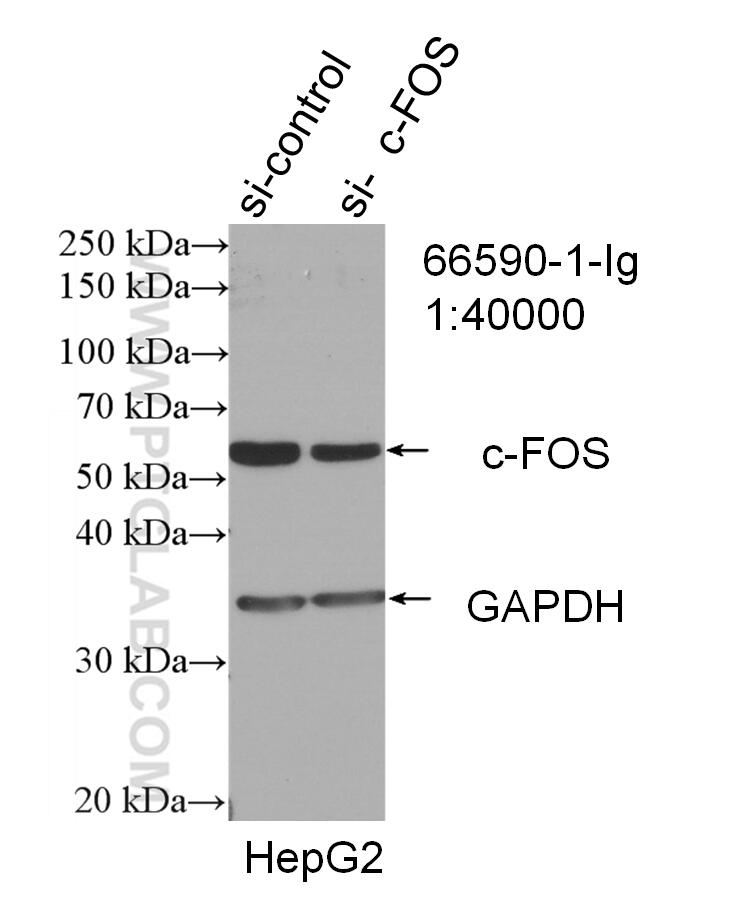
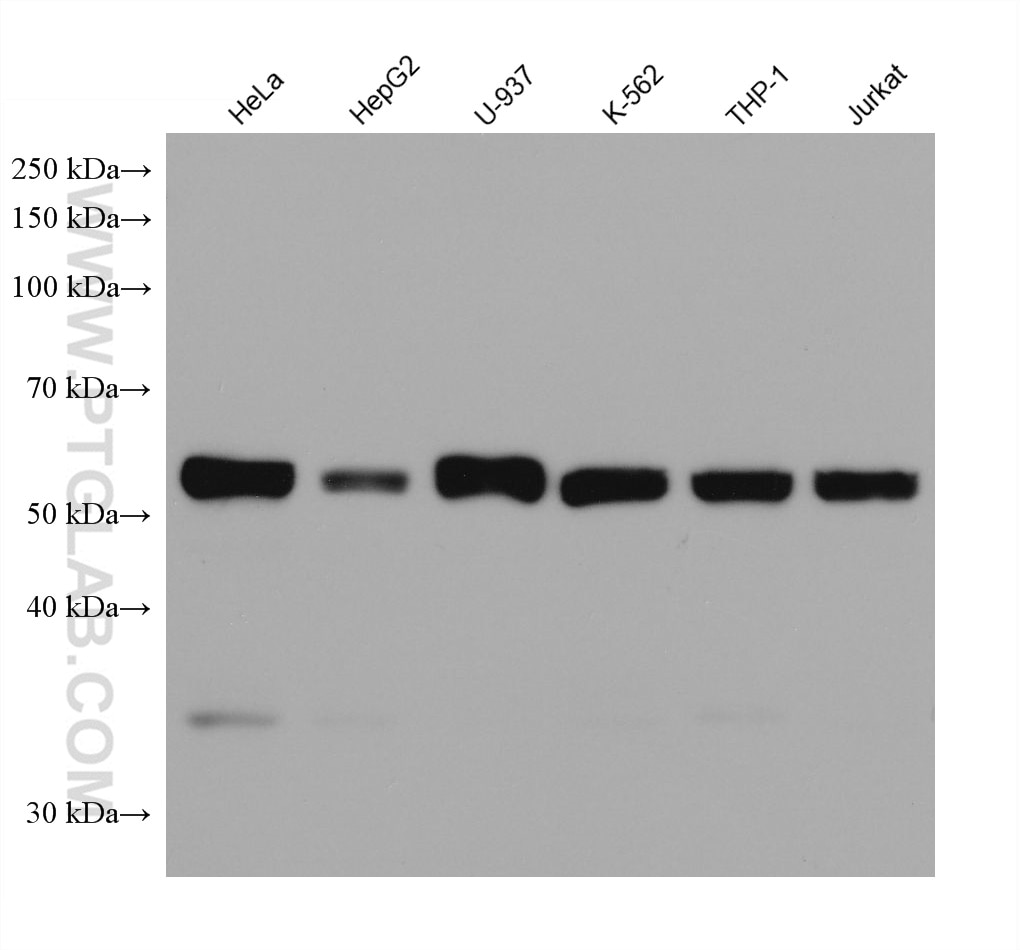
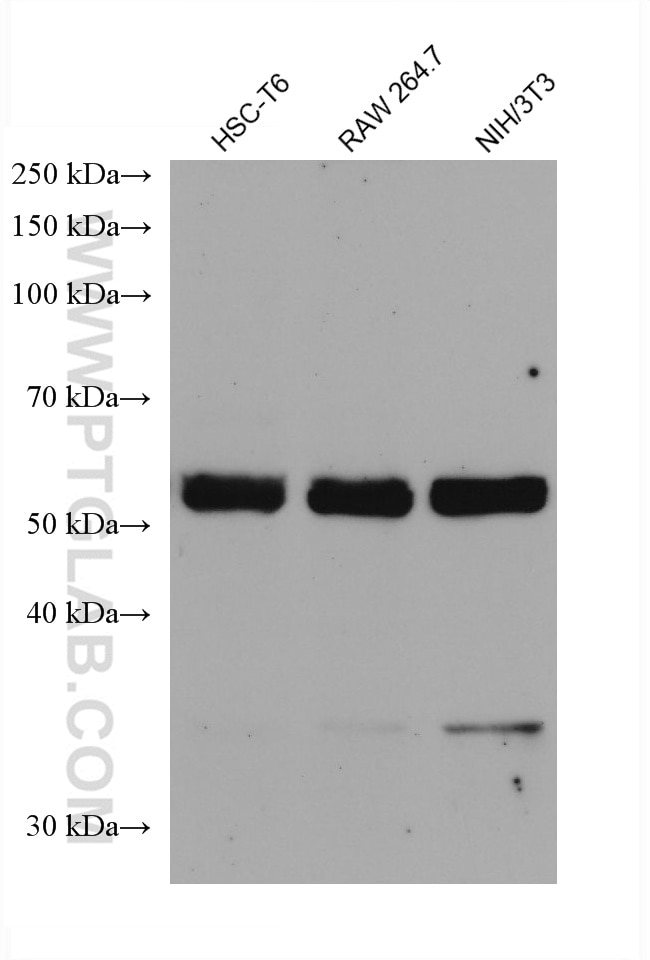
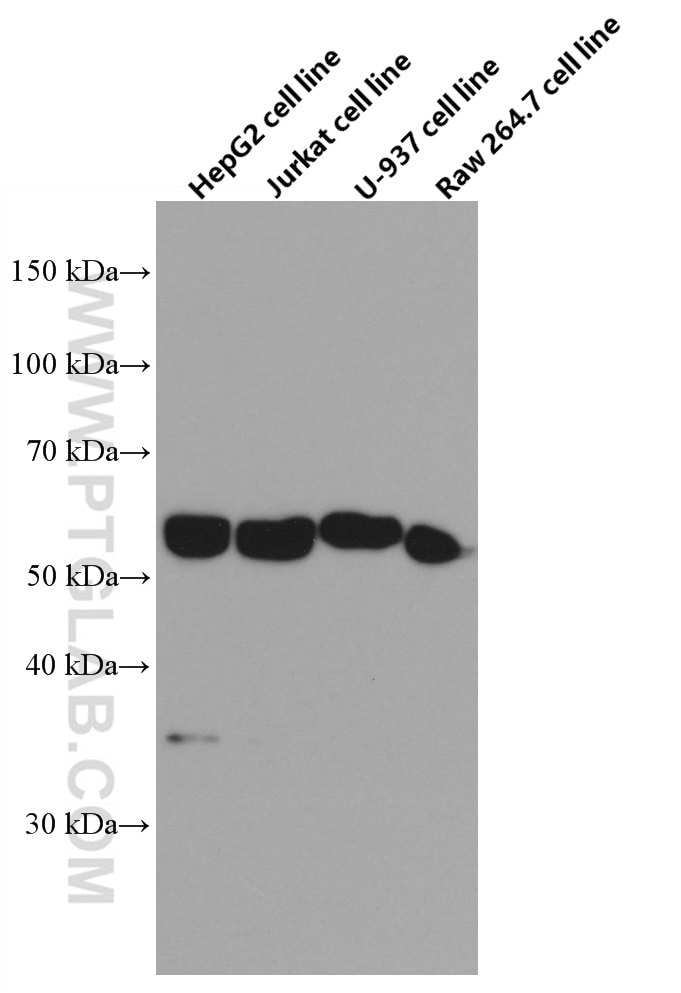
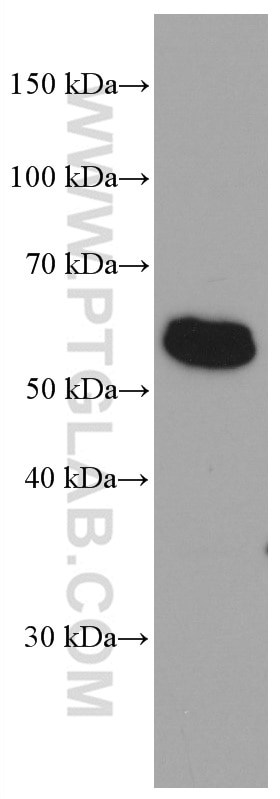
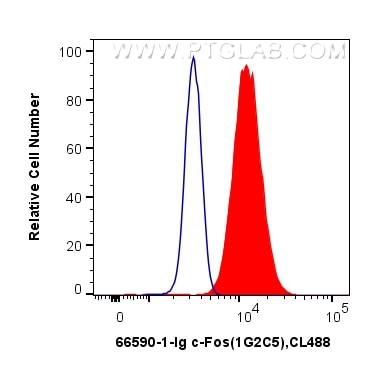
c-Fos is an extremely short-lived intracellular protein that needs to be detected in fresh samples to prevent its degradation.
Product Information
66590-1-PBS targets c-Fos in WB, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag24340 Product name: Recombinant human FOS protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 196-341 aa of BC004490 Sequence: ILAAHRPACKIPDDLGFPEEMSVASLDLTGGLPEVATPESEEAFTLPLLNDPEPKPSVEPVKSISSMELKTEPFDDFLFPASSRPSGSETARSVPDMDLSGSFYAADWEPLHSGSLGMGPMATELEPLCTPVVTCTPSCTAYTSSF Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | FOS |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 41 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 55-60 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC004490 |
| Gene Symbol | c-Fos |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2353 |
| RRID | AB_2881950 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P01100 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
c-Fos, also named as FOS and G0/G1 switch regulatory protein 7, is a 380 amino acid protein, which contains 1 bZIP (basic-leucine zipper) domain and belongs to the bZIP family. c-Fos is expressed at very low levels in quiescent cells. When cells are stimulated to reenter growth, c-Fos undergo 2 waves of expression, the first one peaks 7.5 minutes following FBS induction. At this stage, the c-Fos protein is localized endoplasmic reticulum. The second wave of expression occurs at about 20 minutes after induction and peaks at 1 hour. At this stage, the c-FOS protein becomes nuclear. c-Fos is a very short-lived intracellular protein, which is very easy to degrade. The calculated molecular weight of c-Fos is 40 kDa, but Phosphorylated c-Fos protein is about 60-65 kDa. It is involved in important cellular events, including cell proliferation, differentiation and survival; genes associated with hypoxia; and angiogenesis; which makes its dysregulation an important factor for cancer development. It can also induce a loss of cell polarity and epithelial-mesenchymal transition, leading to invasive and metastatic growth in mammary epithelial cells. Expression of c-Fos is an indirect marker of neuronal activity because c-Fos is often expressed when neurons fire action potentials. Upregulation of c-Fos mRNA in a neuron indicates recent activity.